No products in the cart.
Nifekard XL, 30 mg 30 pcs
€6.38 €5.67
Description
Nifecard XL is a hypotensive, antianginal.
Pharmacodynamics
Nifedipine is a selective slow calcium channel blocker, derivative of 1,4-dihydropyridine. It has antianginal and hypotensive effects. Reduces the flow of extracellular calcium inside cardiomyocytes and smooth muscle cells of coronary and peripheral arteries; in high doses it inhibits the release of calcium ions from intracellular depots. Reduces the number of functioning channels without affecting the time of their activation, inactivation and recovery.
Disassociates the processes of excitation and contraction in the myocardium mediated by tropomyosin and troponin and in vascular smooth muscle mediated by calmodulin. In therapeutic doses, it normalizes the transmembrane flow of calcium ions impaired in a number of pathological conditions, primarily in arterial hypertension. It does not affect the tone of the veins. Increases coronary blood flow, improves the blood supply to ischemic areas of the myocardium without the development of the phenomenon of circumcision, activates the functioning of collaterals.
It improves myocardial function, reduces the force of heart contractions and myocardial oxygen demand. By dilating peripheral arteries, it reduces BP and decreases total peripheral resistance and afterload on the heart. Almost has no effect on the sinoauricular and atrioventricular nodes. Increases renal blood flow, causes moderate natriuresis.
Inhibits platelet aggregation, has antiatherogenic properties (especially with long-term use). Lowers the pressure in the pulmonary artery, has a positive effect on the blood supply to the brain vessels.
Pharmacokinetics
Nifecard® HL due to delayed release of active substance provides gradual controlled increase of nifedipine plasma concentrations. The plasma concentration of nifedipine plateaus after approximately 6 h and is maintained with slight fluctuations for 24 h. Nifedipine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed after oral administration (92-98%). It is characterized by a high percentage of binding to plasma proteins (90%). T1/2 is approximately 2 h. Metabolized in the liver. No active metabolites were detected. It is excreted as inactive metabolites mainly by the kidneys (80%) and in the bile (20%).
Nifedipine penetrates through the BBB and the placental barrier and is excreted with breast milk.
There is no cumulative effect. Chronic renal failure, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis have no effect on pharmacokinetics. With prolonged use, development of nifedipine tolerance may be observed.
Indications
Indications
arterial hypertension; IHD: stable angina pectoris, vasospastic angina (Prinzmetal angina).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Nifecard CL – hypotensive, antianginal.
Pharmacodynamics
Nifedipine is a selective blocker of “slow” calcium channels, a 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative. Has antianginal and hypotensive effects. Reduces the flow of extracellular calcium into cardiomyocytes and smooth muscle cells of the coronary and peripheral arteries; in high doses inhibits the release of calcium ions from intracellular stores. Reduces the number of functioning channels without affecting the time of their activation, inactivation and recovery.
It uncouples the processes of excitation and contraction in the myocardium, mediated by tropomyosin and troponin, and in vascular smooth muscles, mediated by calmodulin. In therapeutic doses, it normalizes the transmembrane current of calcium ions, which is disturbed in a number of pathological conditions, primarily in arterial hypertension. Does not affect the tone of the veins. Strengthens coronary blood flow, improves blood supply to ischemic areas of the myocardium without developing the steal phenomenon, and activates the functioning of collaterals.
Improves myocardial function, reduces the force of heart contractions and myocardial oxygen demand. By dilating peripheral arteries, it lowers blood pressure and reduces total peripheral resistance and afterload on the heart. Almost no effect on the sinoauricular and atrioventricular nodes. Increases renal blood flow, causes moderate natriuresis.
Inhibits platelet aggregation and has antiatherogenic properties (especially with long-term use). Reduces pressure in the pulmonary artery and has a positive effect on the blood supply to the blood vessels of the brain.
Pharmacokinetics
Nifecard® CL, due to the delayed release of the active substance, provides a gradual, controlled increase in plasma concentrations of nifedipine. The plasma concentration of nifedipine reaches a plateau after approximately 6 hours and is maintained with minor fluctuations for 24 hours. Nifedipine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed after oral administration (92–98%). Characterized by a high percentage of binding to blood plasma proteins (90%). T1/2 is approximately 2 hours. Metabolized in the liver. No active metabolites were identified. It is excreted in the form of inactive metabolites mainly by the kidneys (80%) and bile (20%).
Nifedipine penetrates the blood-brain barrier and the placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk.
There is no cumulative effect. Chronic renal failure, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis do not affect pharmacokinetics. With long-term use, the development of tolerance to nifedipine may occur.
Special instructions
Special instructions
It is recommended to discontinue treatment with Nifecard® XL gradually. It should be borne in mind that angina pectoris may occur at the beginning of treatment, especially after recent abrupt withdrawal of beta-blockers (the latter should be withdrawn gradually).
The simultaneous administration of beta-blockers must be carried out under conditions of careful medical supervision, as this may cause an excessive decrease in blood pressure, and in some cases, aggravation of symptoms of heart failure.
In case of severe heart failure, the drug is dosed with great caution.
Diagnostic criteria for prescribing the drug for vasospastic angina are: the classic clinical picture, accompanied by an increase in the ST segment, the occurrence of ergonovine-induced angina or coronary artery spasm, the detection of coronary spasm during angiography or the identification of an angiospastic component without confirmation (for example, with a different voltage threshold or with unstable angina, when ECG data indicate a transient vasospasm).
For patients with severe obstructive cardiomyopathy, there is a risk of increased frequency, severity and duration of angina attacks after taking nifedipine; in this case, discontinuation of the drug is necessary.
In patients on hemodialysis with high blood pressure and irreversible kidney failure, with a reduced total blood volume, the drug should be used with caution; a sharp drop in blood pressure may occur.
Patients with impaired liver function are closely monitored and, if necessary, reduce the dose of the drug and/or use other dosage forms of nifedipine.
If during therapy the patient requires surgery under general anesthesia, it is necessary to inform the anesthesiologist about the nature of the therapy being performed.
During treatment, positive results are possible with direct Coombs test and laboratory tests for antinuclear antibodies.
Impact on psycho-emotional abilities
During the treatment period, you must be careful when engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions, and refrain from drinking ethanol.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Nifedipine
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
nifedipine;
Excipients:
povidone – 75/100 mg;
sodium lauryl sulfate – 2.4/4.8 mg;
hypromellose – 185.8 mg (30 mg tablets);
hypromellose-2906 – 203.84 mg and hypromellose-2208 – 123.36 mg (60 mg tablets);
Ludipress® (lactose monohydrate – 93%, povidone – 3.5%, crospovidone – 3.5%) – 70/50 mg;
magnesium hydrosilicate (talc) – 6 mg; magnesium stearate – 0.8/2 mg
Shell:
hypromellose phthalate (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate) – 18.2/40 mg; triethyl citrate – 1.8/4 mg; hypromellose-2910 (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose – 3/4.5 mg; hyprolose (hydroxypropylcellulose) – 3/4.5 mg; macrogol (polyethylene glycol) – 1/1.5 mg; magnesium hydrosilicate (talc) – 0.5/0.75 mg; titanium dioxide – 1.93/2.9 mg; iron dye yellow oxide – 0.57/0.85 mg;
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of nifedipine in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy is indicated only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
Nifedipine passes into breast milk, so if prescribed during lactation, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to nifedipine or components of the drug and other 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives;
severe arterial hypotension (sBP below 90 mm Hg);
severe stenosis of the aortic valve;
chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation, cardiogenic shock (risk of developing myocardial infarction), acute period of myocardial infarction (during the first 4 weeks);
I trimester of pregnancy, lactation period.
With caution: severe stenosis of the aortic orifice or mitral valve, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, severe tachycardia, sick sinus syndrome, malignant arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction with left ventricular failure, unstable angina, simultaneous administration of beta-blockers or cardiac glycosides, simultaneous use rifampicin, severe cerebrovascular accidents, impaired liver and/or kidney function, hemodialysis (risk of arterial hypotension), age under 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the cardiovascular system: manifestations of excessive vasodilation (asymptomatic decrease in blood pressure, flushing of the facial skin, flushing of the facial skin, feeling of heat), tachycardia, palpitations, arrhythmia, peripheral edema, chest pain; rarely – excessive decrease in blood pressure, fainting, syncope; in some patients, especially at the beginning of treatment, angina attacks may occur, which requires discontinuation of the drug. Isolated cases of myocardial infarction have been described.
From the side of the central nervous system: headache, dizziness, increased fatigue, weakness, drowsiness. With long-term oral administration in high doses – paresthesia of the limbs, depression, anxiety, extrapyramidal (parkinsonian) disorders (ataxia, mask-like face, shuffling gait, stiffness in the movements of the arms and legs, tremor of the hands and fingers, difficulty swallowing).
From the digestive system: dry mouth, loss of appetite, dyspepsia (nausea, diarrhea or constipation); rarely – gum hyperplasia (bleeding, pain, swelling), with long-term use – liver dysfunction (intrahepatic cholestasis, increased activity of liver transaminases).
From the hematopoietic organs: anemia, asymptomatic agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, leukopenia.
Allergic reactions: rarely – skin itching, exanthema, exfoliative dermatitis, photodermatitis; very rarely – autoimmune hepatitis.
From the musculoskeletal system: arthritis; rarely – arthralgia, swelling of the joints, myalgia, convulsions of the upper and lower extremities.
From the urinary system: increased daily diuresis, deterioration of renal function (in patients with renal failure).
Other: rarely – difficulty breathing, cough; very rarely – visual impairment (including transient blindness at the maximum concentration of nifedipine in the blood plasma), gynecomastia (in elderly patients, completely disappearing after discontinuation of the drug), hyperglycemia, galactorrhea, pulmonary edema, bronchospasm, weight gain.
Interaction
Interaction
The severity of the decrease in blood pressure increases with the simultaneous use of other antihypertensive drugs, beta-blockers, nitrates, cimetidine (to a lesser extent ranitidine), inhalational anesthetics, diuretics and tricyclic antidepressants.
Nifedipine causes a decrease in the concentration of quinidine in the blood plasma; after discontinuation of nifedipine, a sharp increase in the concentration of quinidine may occur.
Increases the plasma concentration of digoxin and theophylline, and therefore the clinical effect and the content of digoxin and theophylline in the blood plasma should be monitored.
Inducers of microsomal liver enzymes (rifampicin, etc.) reduce the concentration of nifedipine.
In combination with nitrates, tachycardia increases. The hypotensive effect is reduced by sympathomimetics, NSAIDs, estrogens, and calcium supplements.
Nifedipine can displace drugs characterized by a high degree of binding from protein binding (including indirect anticoagulants – coumarin and indanedione derivatives, anticonvulsants, NSAIDs, quinine, salicylates, sulfinpyrazone), as a result of which their concentration in the blood plasma may increase.
Nifedipine inhibits the elimination of vincristine from the body and may cause increased side effects of vincristine; if necessary, the dose of vincristine is reduced.
Nifedipine may enhance the toxic effects of lithium preparations (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, ataxia, tremor, tinnitus).
With the simultaneous administration of cephalosporins (for example, cefixime) and nifedipine, the bioavailability of cephalosporin increases by 70%.
Grapefruit juice suppresses the metabolism of nifedipine in the body, and therefore their simultaneous use is contraindicated.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: peripheral vasodilation with severe and possibly prolonged systemic arterial hypotension (headache, flushing of the facial skin, prolonged pronounced decrease in blood pressure, depression of the sinus node, bradycardia and/or tachycardia, bradyarrhythmia).
In case of severe poisoning – loss of consciousness, coma.
Treatment: consists of standard procedures for removing the drug from the body (prescription of activated carbon, gastric lavage), restoration of stable hemodynamic parameters, careful monitoring of the activity of the heart, lungs and excretory system. Due to the high degree of binding to plasma proteins, hemodialysis is ineffective. The antidote is calcium preparations.
The clearance of nifedipine is increased in patients with impaired liver function.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
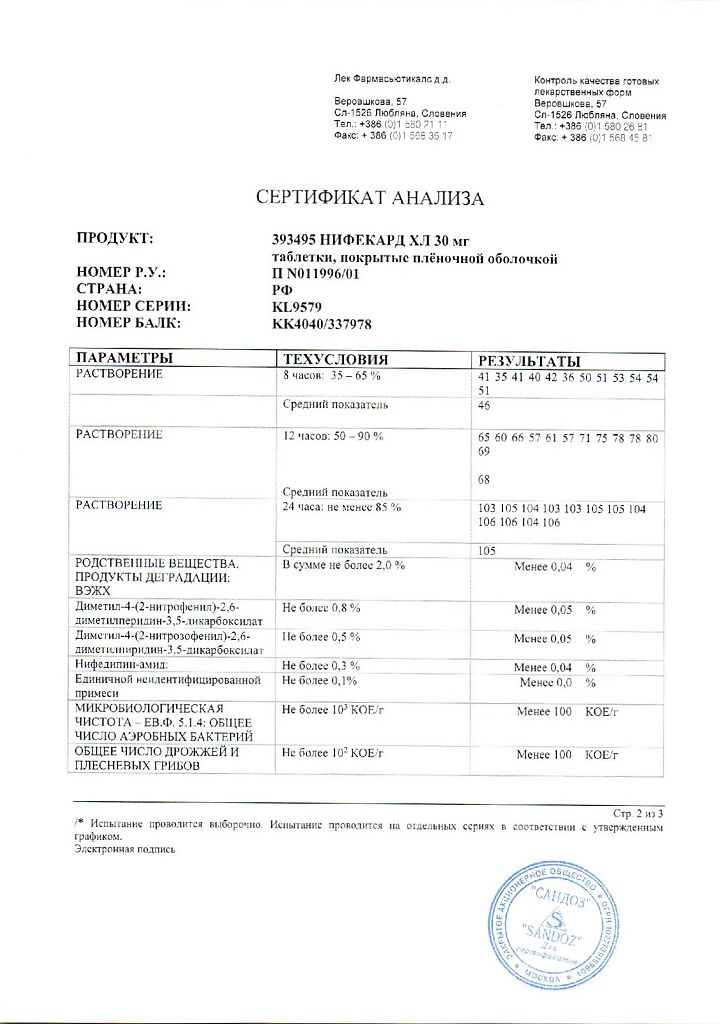
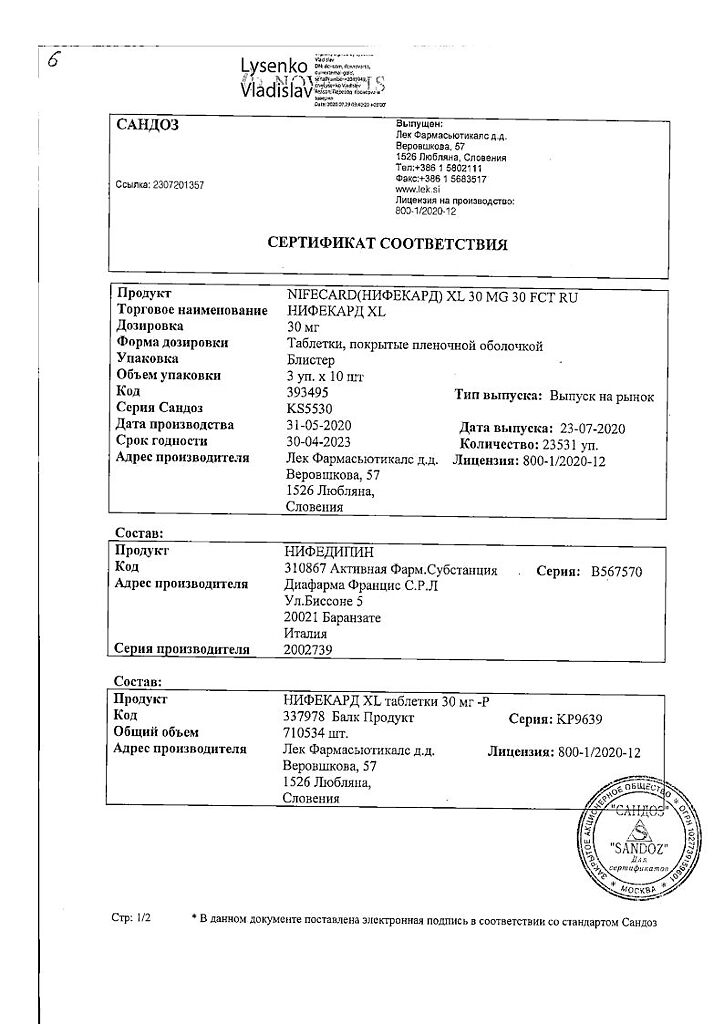
Lek d.d., Slovenia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Lek d.d., Slovenia |
| Medication form | sustained release tablets |
| Brand | Lek d.d. |
Related products
Buy Nifekard XL, 30 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.