No products in the cart.
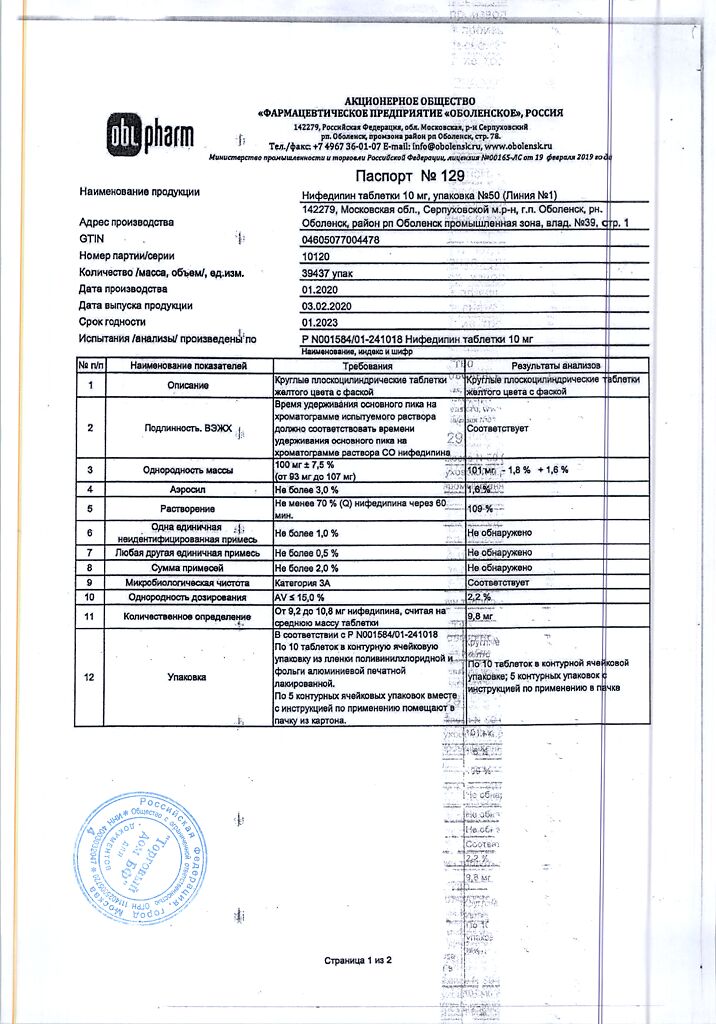
Nifedipine, tablets 10 mg 50 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Nifedipine is a selective “slow calcium channel blocker” derivative of 1,4-dihydropyridine. It has antianginal and antihypertensive effects. It reduces the flow of extracellular calcium ions inside cardiomyocytes and smooth muscle cells of coronary and peripheral arteries.
Limits spasm and dilates coronary and peripheral (mainly arterial) vessels, reduces blood pressure, total peripheral vascular resistance, reduces postload and myocardial oxygen demand.
Enhances coronary blood flow. Negative chrono-, dromo- and inotropic effects are overridden by reflex activation of the sympathoadrenal system in response to peripheral vasodilatation. It enhances renal blood flow, causes moderate natriuresis. Time of onset of clinical effect is 20 min, duration of clinical effect is 4-6 h.
Pharmacokinetics
Nifedipine is rapidly and almost completely (more than 90%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After oral administration its bioavailability is 40-60%. Food intake increases the bioavailability. It has a “first pass” effect through the liver.
The maximum concentration in plasma is observed after 1-3 hours and is 65 ng/ml. It penetrates through the blood-brain barrier and the placental barrier, is excreted with breast milk. Binding with blood plasma proteins is 90%. It is completely metabolized in liver. It is excreted by kidneys as inactive metabolites (70-80% of the dose taken).
The elimination half-life is 2-4 hours. There is no cumulative effect. Chronic renal failure, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis do not affect pharmacokinetics. Tolerance to the action of the drug develops with prolonged use (for 2-3 months).
Indications
Indications
Coronary heart disease – exertional and resting angina (including variant); arterial hypertension (as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Nifedipine is a selective blocker of “slow calcium ropes”, a 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative. Has antianginal and antihypertensive effects. Reduces the flow of extracellular calcium ions into cardiomyocytes and smooth muscle cells of the coronary and peripheral arteries.
Reduces spasm and dilates coronary and peripheral (mainly arterial) vessels, reduces blood pressure, total peripheral vascular resistance, reduces afterload and myocardial oxygen demand.
Increases coronary blood flow. The negative chrono-, dromo- and inotropic effects are overlapped by reflex activation of the sympathoadrenal system in response to peripheral vasodilation. Increases renal blood flow, causes moderate natriuresis. The onset time of the clinical effect is 20 minutes, the duration of the clinical effect is 4-6 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Nifedipine is quickly and almost completely (more than 90%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After oral administration, its bioavailability is 40-60%. Eating increases bioavailability. Has a “first pass” effect through the liver.
The maximum concentration in blood plasma is observed after 1-3 hours and is 65 ng/ml. Penetrates the blood-brain and placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk. Communication with blood plasma proteins – 90%. Completely metabolized in the liver. Excreted by the kidneys in the form of inactive metabolites (70-80% of the dose taken).
The half-life is 2-4 hours. There is no cumulative effect. Chronic renal failure, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis do not affect pharmacokinetics. With long-term use (for 2-3 months), tolerance to the action of the drug develops.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Nifedipine should be used only in a clinical setting under the strict supervision of a physician for acute myocardial infarction, severe cerebrovascular accidents, diabetes mellitus, liver and kidney dysfunction, malignant arterial hypertension and hypovolemia, as well as in patients on hemodialysis. In patients with impaired liver and/or kidney function, the use of nifedipine in high doses should be avoided. Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased cerebral blood flow due to acute peripheral vasodilation.
When taken orally, nifedipine can be chewed to accelerate the effect.
If chest pain occurs during treatment, nifedipine should be discontinued. Nifedipine should be discontinued gradually, since withdrawal syndrome may develop if it is suddenly stopped (especially after long-term treatment).
When administered intracoronarily in the presence of stenosis of two vessels, nifedipine cannot be administered into the third open vessel due to the danger of a pronounced negative inotropic effect.
During the course of treatment, avoid drinking alcohol due to the risk of excessive reduction in blood pressure.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
At the beginning of treatment, you should avoid driving vehicles and other potentially dangerous activities that require rapid psychomotor reactions. In the process of further treatment, the degree of restrictions is determined depending on the individual tolerance of nifedipine.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Nifedipine
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to nifedipine and other dihydropyridine derivatives;
acute stage of myocardial infarction (first 4 weeks);
cardiogenic shock, collapse;
arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure below 90 mmHg);
sick sinus syndrome;
heart failure (in the stage of decompensation);
severe aortic stenosis;
severe mitral stenosis;
tachycardia;
idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis;
pregnancy, lactation period;
age under 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
Use with caution in patients:
with chronic heart failure, severe liver and/or kidney dysfunction; severe cerebrovascular accidents, diabetes mellitus, malignant arterial hypertension, patients on hemodialysis (due to the risk of arterial hypotension).
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the cardiovascular system: hyperemia of the skin, sensation of warmth, tachycardia, arterial hypotension, peripheral edema; rarely – bradycardia, ventricular tachycardia, asystole, increased angina attacks.
From the digestive system: nausea, heartburn, diarrhea; rarely – deterioration of liver function; in isolated cases – gum hyperplasia. With long-term use in high doses, dyspeptic symptoms, increased activity of liver transaminases, and intrahepatic cholestasis are possible.
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: headache. With long-term use in high doses, paresthesia, muscle pain, tremors, mild visual disturbances, and sleep disturbances are possible.
From the hematopoietic system: in isolated cases – leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
From the urinary system: increased daily diuresis. With long-term use in high doses, renal dysfunction is possible.
From the endocrine system: in isolated cases – gynecomastia.
Allergic reactions: skin rash.
Local reactions: with intravenous administration, a burning sensation at the injection site is possible.
Within 1 minute after intracoronary administration, the negative inotropic effect of nifedipine, an increase in heart rate, and arterial hypotension may occur; these symptoms gradually disappear after 5-15 minutes.
Interaction
Interaction
When used simultaneously with antihypertensive drugs, diuretics, phenothiazine derivatives, the antihypertensive effect of nifedipine is enhanced.
When used simultaneously with anticholinergic drugs, memory and attention problems may occur in elderly patients.
When used simultaneously with beta-blockers, severe arterial hypotension may develop; in some cases – the development of heart failure.
When used simultaneously with nitrates, the antianginal effect of nifedipine is enhanced.
When used simultaneously with calcium preparations, the effectiveness of nifedipine decreases due to an antagonistic interaction caused by an increase in the concentration of calcium ions in the extracellular fluid.
Cases of the development of muscle weakness have been described when used simultaneously with magnesium salts.
When used simultaneously with digoxin, it is possible to slow down the excretion of digoxin from the body and, consequently, increase its concentration in the blood plasma.
When used simultaneously with diltiazem, the antihypertensive effect is enhanced.
When used simultaneously with theophylline, changes in the concentration of theophylline in the blood plasma are possible.
Rifampin induces the activity of liver enzymes, accelerating the metabolism of nifedipine, which leads to a decrease in its effectiveness.
When used simultaneously with phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine, the concentration of nifedipine in the blood plasma decreases.
There are reports of an increase in the concentration of nifedipine in the blood plasma and an increase in its AUC when used simultaneously with fluconazole and itraconazole.
When used simultaneously with fluoxetine, the side effects of nifedipine may increase.
In some cases, when used simultaneously with quinidine, a decrease in the concentration of quinidine in the blood plasma is possible, and when nifedipine is discontinued, a significant increase in the concentration of quinidine is possible, which is accompanied by a prolongation of the QT interval on the ECG.
Cimetidine and, to a lesser extent, ranitidine, increase the concentration of nifedipine in the blood plasma and, thus, enhance its antihypertensive effect.
Ethanol may enhance the effect of nifedipine (excessive hypotension), which causes dizziness and other undesirable reactions.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: headache, flushing of the facial skin, decreased blood pressure, depression of the sinus node, bradycardia, arrhythmia.
Treatment: gastric lavage with the administration of activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy aimed at stabilizing the activity of the cardiovascular system. The antidote is calcium; slow intravenous administration of 10% calcium chloride or calcium gluconate is indicated, followed by switching to a long-term infusion.
With a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, intravenous administration of dopamine or dobutamine. In case of conduction disturbances, the administration of atropine, isoprenaline or the installation of an artificial pacemaker is indicated.
For the development of heart failure, intravenous administration of strophanthin. Catecholamines should be used only in case of life-threatening circulatory failure (due to their reduced effectiveness, a high dosage is required, which increases the risk of increasing the tendency to arrhythmia due to intoxication). It is recommended to control blood glucose and electrolytes (potassium and calcium ions), as insulin release is impaired.
Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
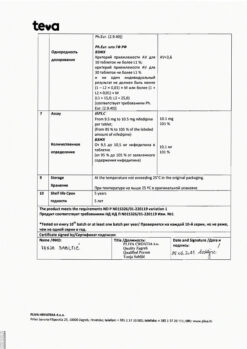
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 20 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Alium JSC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 20 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Alium JSC, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Alium JSC |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Nifedipine, tablets 10 mg 50 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.