No products in the cart.
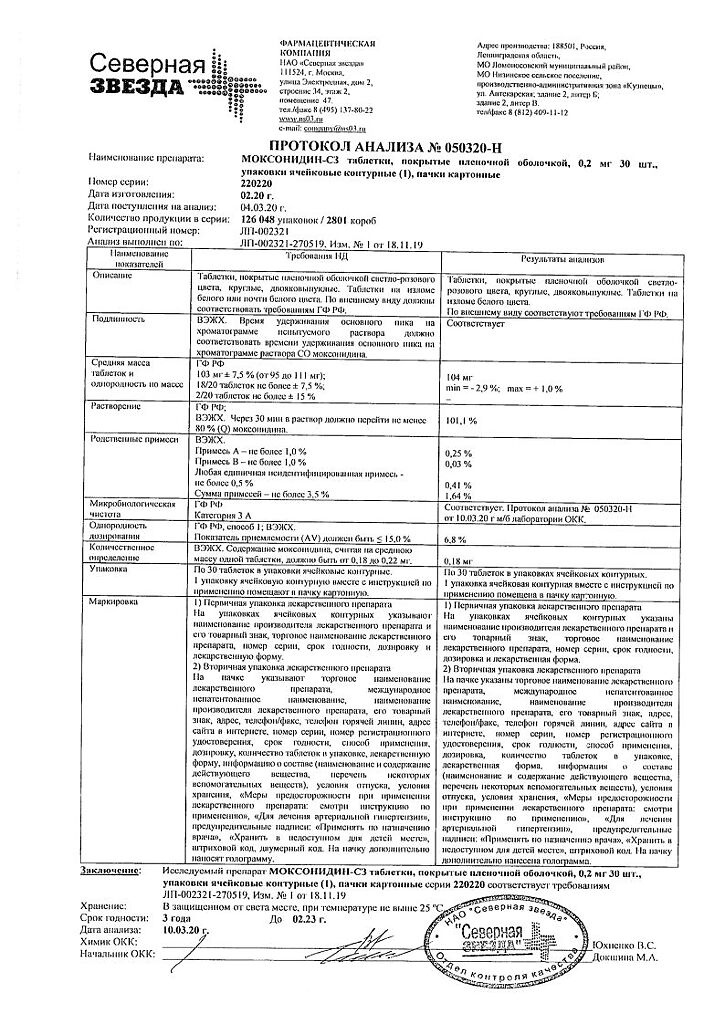
Moxonidine-SZ, 0.2 mg 30 pcs.
€5.47 €4.86
Description
Moxonidine is a hypotensive agent with a central mechanism of action. In brain stem structures (rostral layer of lateral ventricles) moxonidine selectively stimulates imidazoline-sensitive receptors involved in tonic and reflex regulation of sympathetic nervous system.
Indications
Indications
Arterial hypertension.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Moxonidine is an antihypertensive drug with a central mechanism of action. In the brain stem structures (rostral layer of the lateral ventricles), moxonidine selectively stimulates imidazoline-sensitive receptors that take part in the tonic and reflex regulation of the sympathetic nervous system.
Special instructions
Special instructions
If it is necessary to cancel simultaneously taken beta-blockers and the drug Moxonidine-SZ, first cancel the beta-blockers and only after a few days Moxonidine-SZ.
There is currently no evidence that discontinuation of Moxonidine-SZ leads to an increase in blood pressure. However, it is not recommended to stop taking Moxonidine-SZ suddenly; instead, you should gradually reduce the dose of the drug over two weeks.
Avoid drinking alcohol during treatment.
During treatment, regular monitoring of heart rate and electrocardiography is necessary.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and fur.:
The effect of Moxonidine-SZ on the ability to drive vehicles or operate machinery has not been studied. However, taking into account the possibility of dizziness and drowsiness, patients should be careful when engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased attention, such as driving a vehicle or operating equipment that requires increased concentration.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Moxonidine
Composition
Composition
1 tab. contains:
active substance:
moxonidine – 0.2 mg;
excipients (core):
croscarmellose sodium (primellose) – 3.0 mg;
lactose monohydrate (lactopress) (milk sugar) – 95.3 mg;
colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil) – 0.5 mg;
sodium stearyl fumarate – 1.0 mg;
excipients (shell):
opadry II (polyvinyl alcohol, partially hydrolyzed – 1.32 mg; titanium dioxide E171 – 0.6027 mg; talc – 0.6 mg; macrogol (polyethylene glycol 3350) – 0.3705 mg; soy lecithin E322 – 0.105 mg; iron dye oxide (II) yellow – 0.0003 mg; red iron oxide dye – 0.0015 mg).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy There are no clinical data on the use of Moxonidine-SZ in pregnant women. In animal studies, the embryotoxic effect of the drug was established.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to the active substance and other components of the drug;
– sick sinus syndrome;
– severe bradycardia (resting heart rate less than 50 beats/min);
– atrioventricular block II and III degrees;
– severe heart rhythm disturbances;
– acute and chronic heart failure (III-IV functional class according to the NYHA classification);
– simultaneous use with tricyclic antidepressants (see section “Interaction with other drugs”);
– severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min);
– hemodialysis;
– lactation period;
– hereditary lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption;
– age over 75 years;
– age under 18 years (due to the lack of data on safety and effectiveness).
With caution:
Particular care must be taken when using moxonidine in patients with first degree atrioventricular block (risk of developing bradycardia); severe coronary artery disease, severe coronary heart disease or unstable angina (insufficient experience), chronic heart failure, severe liver failure, with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance more than 30 ml/min).
Side Effects
Side Effects
The frequency of side effects listed below was determined according to the following: very often (>1/10); often (>1/100, 1/1000, <1/100); including individual messages.
From the central nervous system:
Common: headache*, dizziness (vertigo), drowsiness.
Uncommon: fainting*.
From the cardiovascular system:
Uncommon: marked decrease in blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension*, bradycardia.
From the gastrointestinal tract:
Very common: dry mouth.
Common: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia.
For the skin and subcutaneous tissues:
Common: skin rash, itching.
Uncommon: angioedema.
Mental disorders:
Common: insomnia.
Uncommon: nervousness.
Hearing and labyrinth disorders:
Uncommon: ringing in the ears.
From the musculoskeletal and connective tissue side:
Common: back pain.
Uncommon: neck pain.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site:
Often: asthenia.
Uncommon: peripheral edema.
(* – frequency comparable to placebo).
Interaction
Interaction
The combined use of moxonidine with other antihypertensive drugs leads to an additive effect.
Tricyclic antidepressants may reduce the effectiveness of centrally acting antihypertensive drugs, and therefore their use together with moxonidine is not recommended.
Moxonidine may enhance the effect of tricyclic antidepressants, tranquilizers, ethanol, sedatives and hypnotics.
Moxonidine may moderately improve impaired cognitive function in patients receiving lorazepam.
Moxonidine may enhance the sedative effect of benzodiazepine derivatives when administered simultaneously.
Moxonidine is released by tubular secretion. Therefore, its interaction with other drugs released by tubular secretion is not excluded.
Beta-blockers increase bradycardia and the severity of negative ino- and dromotropic effects.
Overdose
Overdose
There have been reports of several cases of non-fatal overdose when doses up to 19.6 mg were used simultaneously.
Symptoms: headache, sedation, marked decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, asthenia, bradycardia, dry oral mucosa, vomiting, fatigue, pain in the epigastric region, respiratory depression and impaired consciousness. In addition, short-term increases in blood pressure, tachycardia and hyperglycemia are also possible, as shown in several high-dose animal studies.
Treatment
There is no specific antidote. In the case of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, it may be necessary to restore the volume of circulating blood by introducing fluid and dopamine (injection).
Bradycardia can be stopped with atropine (injection).
In severe cases of overdose, it is recommended to carefully monitor disturbances of consciousness and avoid respiratory depression.
Alpha-adrenergic antagonists may reduce or eliminate the paradoxical hypertensive effects of moxonidine overdose.
Moxonidine is excreted to a small extent during hemodialysis.
Recommendations for use
Recommendations for use
Inside, regardless of food intake.
In most cases, the initial dose of Moxonidine-SZ is 0.2 mg per day. The maximum single dose is 0.4 mg. The maximum daily dose, which should be divided into 2 doses, is 0.6 mg.
Individual adjustment of the daily dose is necessary depending on the patient’s tolerance to the therapy.
No dose adjustment is required for patients with hepatic impairment. The starting dose for patients with moderate or severe renal impairment is 0.2 mg/day.
If necessary and if well tolerated, the daily dose can be increased to a maximum of 0.4 mg.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
North Star NAO, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | North Star NAO, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | North Star NAO |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Moxonidine-SZ, 0.2 mg 30 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.