No products in the cart.
Metoprolol, tablets 25 mg 60 pcs
€2.68 €2.44
Description
A cardioselective beta1-adrenoblocker without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. It has hypotensive, antianginal and antiarrhythmic effects. It reduces automatism of the sinus node, decreases heart rate, slows AV conduction, reduces myocardial contractility and excitability, decreases cardiac output, and decreases myocardial oxygen demand.
Suppresses the stimulating effect of catecholamines on the heart during physical and psycho-emotional stress.
Causes a hypotensive effect, which stabilizes by the end of the 2nd week of course use. In tension angina metoprolol reduces the frequency and severity of attacks. It normalizes the heart rhythm in supraventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation.
In myocardial infarction helps to limit the zone of ischemia of the heart muscle and reduces the risk of fatal arrhythmias, reduces the possibility of recurrent myocardial infarction. When used in medium therapeutic doses, it has less pronounced effect on the smooth muscle of the bronchi and peripheral arteries than non-selective beta-adrenoblockers.
Indications
Indications
– Arterial hypertension,
– prevention of angina attacks,
– heart rhythm disturbances (supraventricular tachycardia, extrasystole),
– secondary prevention after myocardial infarction,
– hyperkinetic cardiac syndrome (including with hyperthyroidism, NCD).
– prevention of migraine attacks.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Cardioselective beta1-blocker without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. It has hypotensive, antianginal and antiarrhythmic effects. Reduces the automaticity of the sinus node, reduces heart rate, slows AV conduction, reduces myocardial contractility and excitability, reduces cardiac output, and reduces myocardial oxygen demand.
Suppresses the stimulating effect of catecholamines on the heart during physical and psycho-emotional stress.
Causes a hypotensive effect, which stabilizes by the end of the 2nd week of course use. For angina pectoris, metoprolol reduces the frequency and severity of attacks. Normalizes heart rate during supraventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation.
In case of myocardial infarction, it helps to limit the ischemia zone of the heart muscle and reduces the risk of developing fatal arrhythmias, and reduces the possibility of relapses of myocardial infarction. When used in average therapeutic doses, it has a less pronounced effect on the smooth muscles of the bronchi and peripheral arteries than non-selective beta-blockers.
Special instructions
Special instructions
With caution: diabetes mellitus, metabolic acidosis, bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, enphysema, chronic obstructive bronchitis, impaired liver function, kidney function (creatinine clearance less than 40 ml/min), myasthenia gravis, pheochromocytoma (with simultaneous use of alpha-blockers), thyrotoxicosis, depression (including history), psoriasis, peripheral circulatory disorders (intermittent claudication, Raynaud’s syndrome), pregnancy, childhood (efficacy and safety have not been determined), elderly age, severe allergic history, AV block of the first degree.
Monitoring of patients taking beta-blockers includes monitoring heart rate and. Blood pressure (at the beginning of treatment – daily, then – once every 3-4 months), blood glucose concentration in patients with diabetes mellitus (once every 4-5 months). The patient should be taught how to calculate heart rate and instructed about the need for medical consultation if the heart rate is less than 50/min.
It is possible that the severity of allergic reactions may increase (against the background of a burdened allergic history) and there will be no effect from the administration of usual doses of epinephrine.
In elderly patients, it is recommended to monitor renal function (once every 4-5 months).
May increase symptoms of peripheral arterial circulation disorders.
For exertional angina, the selected dose of the drug should ensure the heart rate at rest within the range of 55-60 beats/min, and during exercise – no more than 110 beats/min.
Beta blockers are less effective in smokers.
Metoprolol Organic may mask some clinical manifestations of thyrotoxicosis (for example, tachycardia). Abrupt withdrawal in patients with thyrotoxicosis is contraindicated because it can increase symptoms.
In diabetes mellitus, it can mask tachycardia caused by hypoglycemia. Unlike non-selective beta-blockers, it practically does not enhance insulin-induced hypoglycemia and does not delay the restoration of blood glucose concentrations to normal values.
If necessary, use in patients with concomitant bronchial asthma requires additional use of beta2-adrenergic agonists; for pheochromocytoma – alpha-blockers.
If surgical intervention is necessary, it is necessary to warn the anesthesiologist about taking Metoprolol Organic (the choice of a drug for general anesthesia with minimal negative inotropic effect); discontinuation of the drug is not recommended.
In case of increasing bradycardia (less than 50/min), arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg), AV blockade, bronchospasm, ventricular arrhythmias, severe liver and kidney dysfunction, it is necessary to reduce the dose or stop treatment.
It is recommended to discontinue therapy if skin rashes appear and depression develops caused by taking beta-blockers.
The drug is discontinued gradually, reducing the dose over 10 days. If treatment is abruptly stopped, withdrawal syndrome may occur (increased angina attacks, increased blood pressure). When discontinuing the drug, special attention should be paid to patients with angina pectoris.
Patients who use contact lenses should take into account that during treatment with beta-blockers, a decrease in the production of tear fluid may occur.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Metoprolol
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active substances:
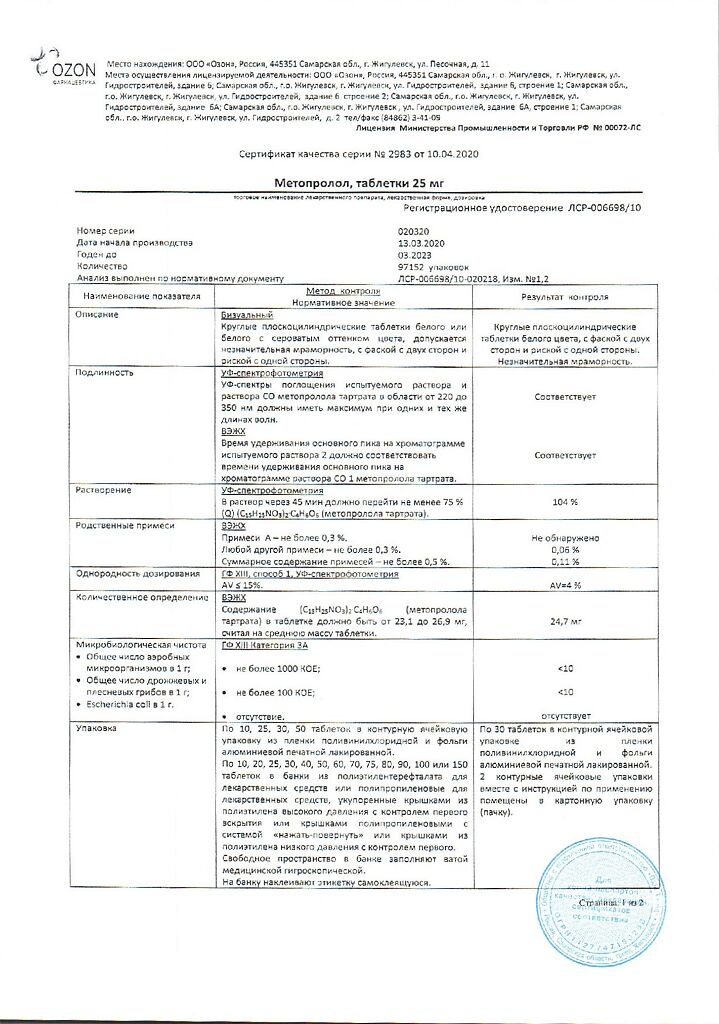
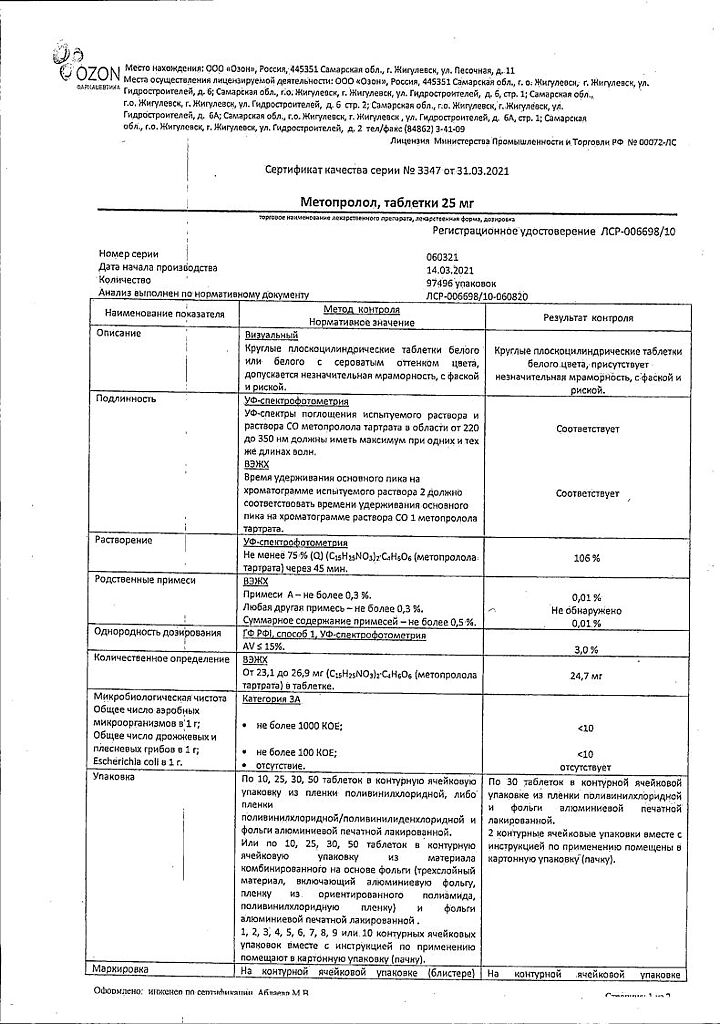
metoprolol tartrate 25 mg.
Excipients:
anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide,
microcrystalline cellulose,
sodium carboxymethyl starch (type A),
magnesium stearate.
Shell composition:
hypromellose,
polysorbate 80,
talc,
titanium dioxide (E171).
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, cardiogenic shock, AV block II and III degrees, sinoatrial block, chronic (in the stage of decompensation) heart failure, sick sinus syndrome, severe sinus bradycardia (heart rate less than 60 beats/min), Prinzmetal’s angina, acute myocardial infarction (heart rate less than 45 beats, PQ interval more than 0.24 sec, systolic blood pressure less than 100 mm Hg).
Pregnancy, lactation period. Simultaneous intravenous administration of “slow” calcium channel blockers such as verapamil. Age up to 18 years. Pheochromocytoma. patients receiving long-term or intermittent therapy with inotropic agents acting on beta-adrenergic receptors.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the cardiovascular system: bradycardia, arterial hypotension, AV conduction disturbances, and symptoms of heart failure are possible.
From the digestive system: at the beginning of therapy, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation are possible; in some cases – liver dysfunction.
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: at the beginning of therapy, weakness, fatigue, dizziness, headache, muscle cramps, feeling of cold and paresthesia in the extremities are possible; possible decrease in the secretion of tear fluid, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, depression, sleep disturbances, nightmares.
From the hematopoietic system: in some cases – thrombocytopenia.
From the endocrine system: hypoglycemic conditions in patients with diabetes mellitus.
From the respiratory system: in predisposed patients, symptoms of bronchial obstruction may appear.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching.
Interaction
Interaction
When used simultaneously:
antiarrhythmic drugs (quinine-like drugs and amiodarone) may enhance inotropic and dromotropic effects;
calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem, nifedipine) or other antiarrhythmics cause a decrease in cardiac output and stroke volume, heart rate, and with intravenous administration of verapamil there is a risk of cardiac arrest;
barbiturates accelerate the metabolism of Metoprolol Organic, which leads to a decrease in its effectiveness;
inducers or inhibitors of microsomal enzymes, it is possible to change the concentration of Metoprolol Organics in plasma – decrease when taking rifampicin, – increase when taking cimetidine, ethanol, hydralazine, serotonin reuptake inhibitors (paroxetine, fluoxetine, sertraline), oral contraceptives;
indomethacin and other NSAIDs, COX inhibitors may reduce the antihypertensive effect;
calcium channel blockers, cardiac glycosides, reserpine, nitrates increase the risk of developing arterial hypotension, bradycardia, AV block, negative inotropic effect;
insulin and oral antidiabetic agents increase the risk of hypoglycemia;
narcotic drugs, inhalational anesthetics and some other drugs that affect the central nervous system, in particular hypnotics (bromazepam, lorazepam), tranquilizers (chlordiazepoxide, trimethocin, tofisopam), tri- and tetracyclic antidepressants; mutual potentiation of the cardiodepressive effect;
allergens used for immunotherapy or allergen extracts for skin testing increases the risk of severe systemic reactions and anaphylaxis;
iodine-containing radiopaque drugs for intravenous administration increase the risk of anaphylactic reactions;
norepinephrine, epinephrine and other sympathomimetics increase the risk of developing arterial hypertension;
phenylpropanolamine in high doses – a paradoxical increase in blood pressure (up to a hypertensive crisis);
clonidine – there is a risk of a pronounced increase in blood pressure if clonidine is abruptly discontinued while taking Metoprolol Organic simultaneously, therefore, if clonidine is discontinued, gradual cessation of Metoprolol Organic should be started several days before its discontinuation;
sympathomimetic agents, ganglion blockers, other β-adrenergic receptor blockers (for example, eye drops), MAO type B inhibitors require careful monitoring of the patient’s condition;
diazepam, there may be a decrease in clearance and an increase in the AUC of diazepam, which can lead to an increase in its effects and a decrease in the speed of psychomotor reactions;
lidocaine may impair the elimination of lidocaine;
fluoxetine leads to inhibition of the metabolism of Metoprolol Organic and its accumulation, which can enhance the cardiodepressive effect and cause bradycardia; the likelihood of drug interaction persists even several days after discontinuation;
fluoxetine. A case of lethargy has been described;
ciprofloxacin – decreased clearance of Metoprolol Organic from the body;
ergotamine may increase peripheral circulatory disorders;
estrogen reduces the antihypertensive effect of Metoprolol Organica;
mibefradil in patients with low activity of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme may increase the concentration of Metoprolol Organic in the blood plasma and increase the risk of developing toxic effects.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: severe sinus bradycardia, dizziness, AV block (up to the development of complete transverse block and cardiac arrest), marked decrease in blood pressure, fainting, arrhythmia/ventricular extrasystole, acute heart failure; cardiogenic shock, cardiac arrest, bronchospasm, loss of consciousness, coma, nausea, vomiting, cyanosis, hypoglycemia, convulsions. The first signs of overdose appear 20 minutes -2 hours after taking the drug.
Treatment: gastric lavage and administration of adsorbent drugs, symptomatic therapy: with a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, the patient should be in the Trendelenburg position; in case of excessive decrease in blood pressure, bradycardia and heart failure – intravenous administration of beta-adrenergic stimulants at intervals of 2-5 minutes until the desired effect is achieved or intravenous administration of 0.5-2 mg of atropine sulfate. If there is no positive effect, dopamine, dobutamine or norepinephrine. As a follow-up measure, it is possible to install a transvenous intracardial pacemaker. For bronchospasm, beta-agonists should be administered intravenously. For convulsions – slow intravenous administration of diazepam. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
See packaging.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ozon, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | See on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. |
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Metoprolol, tablets 25 mg 60 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.