No products in the cart.
Meloxicam, tablets 15 mg 20 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmgroup:
NSAIDs.
Pharmacological action:
PNPS, has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, analgesic effects. Belongs to the class of oxycams; a derivative of enolic acid.
Mechanism of action – inhibition of Pg synthesis as the result of selective suppression of COX2 enzymatic activity. When administered in high doses, prolonged use and individual characteristics of COX2 selectivity decreases. Suppresses Pg synthesis in the area of inflammation to a greater extent than in the gastric mucosa or kidneys, which is associated with a relatively selective inhibition of COX2.
Rarely causes gastrointestinal erosive and ulcerative diseases.
Pharmacokinetics:
Gastrointestinal absorption after oral or rectal administration is 89%; tablets and suppositories are bioequivalent. Food intake does not affect absorption. Plasma concentration is dose-dependent. TCmax – 5 – 6 h. Css is formed after 3-5 days.
The binding to plasma proteins is 99%. Passes through histohematic barriers, penetrates into synovial fluid. Concentration in synovial fluid is 50% of that in plasma. Metabolism in the liver – to inactive metabolites.
Extracted through the intestine and the kidneys (about equal proportion), 5% of the daily dose (through the intestine) is unchanged. T1/2 is 20 hours. Plasma clearance – on average 8 ml/min (decreases in old age).
Indications
Indications
Rheumatoid arthritis; osteoarthritis; ankylosing spondylitis (Behterev’s disease) and other inflammatory and degenerative joint diseases accompanied by pain syndrome.
It is intended for symptomatic therapy, reduction of pain and inflammation at the time of use, does not affect the progression of the disease.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
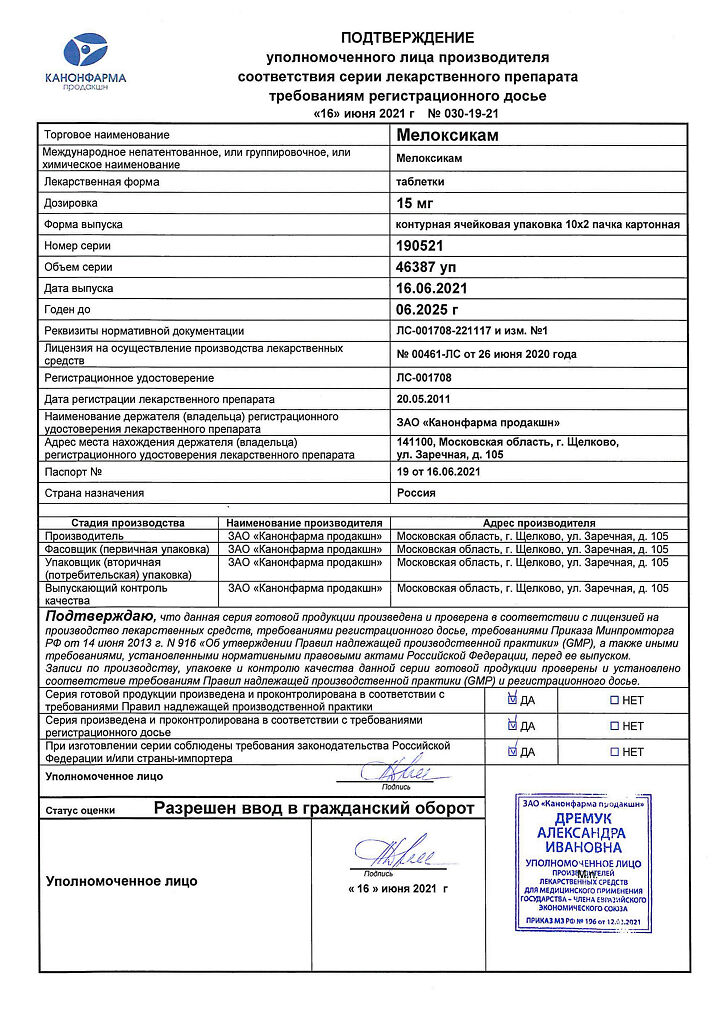
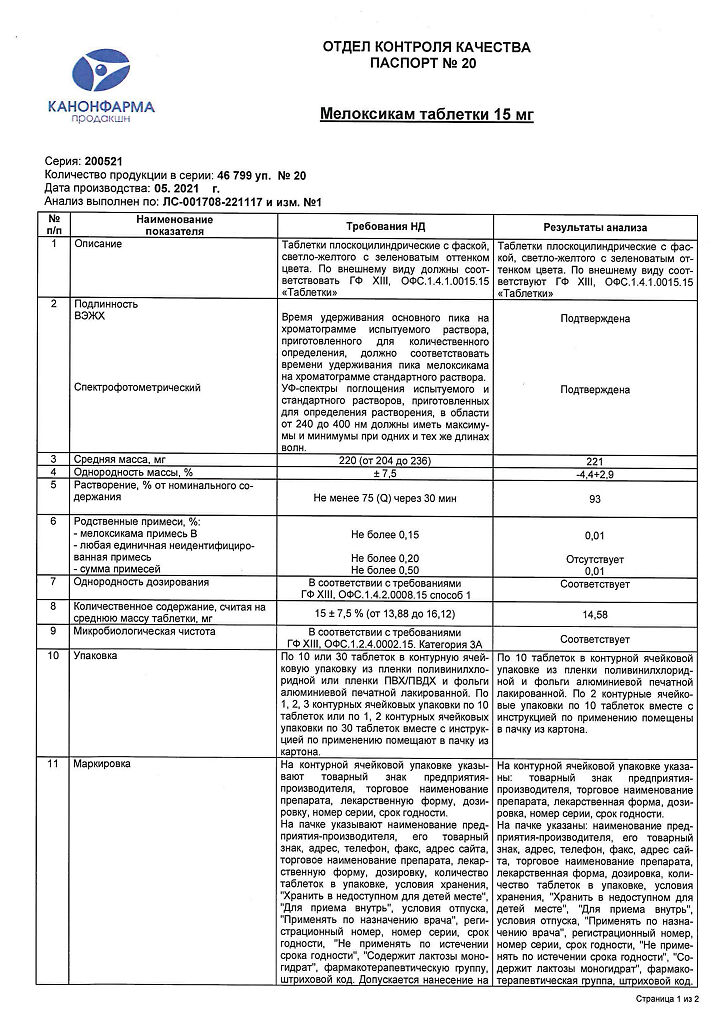
Meloxicam 15 mg.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Overly, with meals, in a daily dose of 7.5-15 mg.
The maximum daily dose is 15 mg, in patients with severe renal impairment who are on hemodialysis – 7.5 mg. No dose adjustment is required in mild to moderate renal function impairment (CKD greater than 25 ml/min) and in liver cirrhosis in stable clinical condition. The initial dose in patients with increased risk of side effects is 7.5 mg/day.
Rectally, 15 mg (one suppository) once daily.
Interaction
Interaction
In concomitant use with other NSAIDs increases the risk of gastrointestinal ulcers. NSAIDs increases the risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and gastrointestinal bleeding;
increases the concentration of Li+ in the plasma when used simultaneously with Li+ preparations;
reduces the effectiveness of IUDs, hypotensive drugs;
indirect anticoagulants, ticlopidine, heparin, thrombolytics increase the risk of bleeding;
methotrexate increases the myelodepressant effect;
/p>
Diuretics increase the risk of renal dysfunction;
Cyclosporine increases nephrotoxic effects; colestyramine accelerates excretion.
Myelotoxic drugs increase manifestations of hematotoxicity of the drug.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
In case of peptic ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding, development of skin and mucous membrane side effects, the drug should be discontinued.
In patients with decreased RBC and glomerular filtration (dehydration, CHF, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, clinically manifested renal disease, use of diuretics, dehydration after major surgery) there may be clinically manifested CPN which is completely reversible after discontinuation of the drug (daily urine output and renal function should be monitored in such patients at the beginning of treatment). In case of steady and significant increase of transaminases and changes of other liver function parameters the drug should be discontinued and control tests should be performed.
In patients with increased risk of side effects, treatment should be started with 7.5 mg. In terminally ill CKD patients on dialysis, the dose should not exceed 7.5 mg/day. During the treatment it is necessary to be careful when driving motor transport and other potentially dangerous activities that require high concentration and quick psychomotor reactions (if dizziness and somnolence occur). To decrease the risk of gastrointestinal side effects it is necessary to use the minimal effective dose with the shortest possible course.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to other groups of NSAIDs).
Hypersensitivity (including other groups of NSAIDs), combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent nasal and paranasal sinus polyposis and intolerance of ASA and pyrazolone-type drugs;
Gastric and 12 duodenal ulcer (acute phase), severe hepatic insufficiency, CKD in patients not undergoing dialysis (CK
Side effects
Side effects
Frequency: frequently – more than 1%; infrequently – 0.1-1%; rarely – 0.01-0.1%; very rarely – less than 0.01%.
Digestive system: often – dyspepsia, including. nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, flatulence, diarrhea; infrequent – transient increase in “liver” transaminases activity, hyperbilirubinemia, belching, esophagitis, gastroduodenal ulcer, GI bleeding (including latent), stomatitis; rarely – GI perforation, colitis, hepatitis, gastritis.
Hematopoietic organs: frequently – anemia; infrequently – changes in the blood count, including leukopenia and thromocytopenia.
The skin: often – itching, skin rash, infrequent – urticaria, rarely – photosensitization, bullous rash, erythema multiforme, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Respiratory system disorders: rarely – bronchospasm.
Nervous system disorders: frequently – dizziness, headache; infrequently – vertigo, tinnitus, somnolence; rarely – confusion, disorientation, emotional lability.
Particularly: peripheral edema frequently; infrequently – increase of blood pressure, palpitations, “rushes” of blood to the skin.
Urinary system: infrequent – hypercreatininemia and/or increased serum urea concentrations; rarely – acute renal failure; relationship with meloxicam administration is not determined – interstitial nephritis, albuminuria, hematuria.
Sensory organs: rarely – conjunctivitis, visual impairment, including blurred vision.
Allergic reactions: rare – angioedema, anaphylactoid/anaphylactic reactions.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: impaired consciousness, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, GI bleeding, acute renal failure, acute liver failure, respiratory arrest, asystole.
Treatment: gastric lavage, administration of activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy. Forced diuresis, urine alkalinization, hemodialysis are ineffective due to the high degree of binding of meloxicam to plasma proteins. There is no specific antidote.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Kanonfarma Production ZAO, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Kanonfarma Production ZAO |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Meloxicam, tablets 15 mg 20 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.