No products in the cart.
Ketoprofen MB, 150 mg 20 pcs.
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacodynamics.
A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects associated with inhibition of cyclooxygenases 1 and 2 regulating the synthesis of prostaglandins and bradykinin; stabilizes lysosomal membranes.
It does not adversely affect articular cartilage.
Pharmacokinetics.
Absorption – fast, bioavailability – more than 90%. Binding with plasma proteins – 99 %. Minimum effective concentration is determined after 45-60 minutes. During oral use of ketoprofen tablets with modified action the maximum concentration of the drug in plasma is reached after 4-6 hours.
Therapeutic concentration in synovial fluid is maintained for 6-8 hours. It does not penetrate through the blood-brain barrier in a significant amount.
It is almost completely metabolized in the liver by glucuronidation, has an effect through the liver.
Extracted by the kidneys (mainly as ketoprofen glucuronide) and the intestine (1%). The elimination half-life is 1.6-1.9 hours. It does not cumulate.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
the active ingredient:
ketoprofen – 150 mg,
excipients:
Hypromellose (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 15000),
Calcium hydrophosphate dihydrate,
Silicon dioxide colloid (aerosil),
Magnesium stearate.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Orally, during or after meals, 1 tablet (150 mg) once a day.
The tablets should be swallowed whole, without chewing, with plenty (at least 100 ml) of water or milk.
The lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible course.
Interaction
Interaction
Ketoprofen may weaken the effect of diuretics and hypotensive agents and increase the effect of oral hypoglycemic and some anticonvulsants (phenytoin).
Co-administration with other NSAIDs, glucocorticosteroids, salicylates, ethanol, corticotropin increases the risk of adverse effects of the gastrointestinal tract.
Concomitant administration with anticoagulants, thrombolytics, antiaggregants, as well as with cefaperazone, cefamandol, cefotetan and moxalactam increases the risk of bleeding.
The simultaneous use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with diuretics and ACE inhibitors increases the risk of impaired renal function.
Enhances plasma concentrations of cardiac glycosides, slow calcium channel blockers, lithium drugs, cyclosporine, methotrexate.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may decrease the effectiveness of mifepristone. NSAIDs should not be started before 8-12 days after mifepristone withdrawal.
The inducers of microsomal oxidation in the liver (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants) increase production of hydroxylated active metabolites.
Co-administration with sodium valproate causes impairment of platelet aggregation.
It increases hypoglycemic action of insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs (recalculation of the dose is necessary).
Myelotoxic drugs increase manifestations of hematotoxicity of the drug.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Ketoprofen may be washed with milk or taken with antacids to reduce the incidence of gastrointestinal disturbances; antacids and milk do not affect absorption of the drug.
Peripheral blood count and monitoring of liver and kidney function is necessary during treatment, especially in elderly patients.
Dose reduction and close monitoring are necessary if renal and hepatic function is impaired.
If it is necessary to determine 17-ketosteroids, the drug should be discontinued 48 hours before the study.
The administration of the drug may mask signs of infectious disease.
The drug should not be used concomitantly with other NSAIDs.
When using the drug, caution must be exercised while driving motor vehicle and engaging in other potentially dangerous activities requiring increased concentration and quick psychomotor reactions.
Contraindications
Contraindications
WARNING
. Anemia, bronchial asthma, coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular and peripheral artery disease, chronic heart failure, peptic ulcer in history, dyslipidemia/hyperlipidemia, liver failure, hyperbilirubinemia, alcoholic cirrhosis, renal failure (CK less than 60 ml/min), arterial hypertension, edema, blood diseases (incl.Ñ. leukopenia), stomatitis, dehydration, sepsis, diabetes mellitus, history of gastrointestinal ulcers, Helicobacter pylori infection, tobacco smoking, alcoholism, concomitant therapy with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiaggregants (e.g., acetylsalicylic acid), oral glucocorticosteroids (e.g., prednisolone), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (e.g., citalopram, fluoxetine, sertraline), long-term use of NSAIDs, severe medical conditions, advanced age, pregnancy (I, II trimester), lactation.
Side effects
Side effects
Digestive system disorders: Frequently – dyspepsia (nausea, diarrhea or constipation,
flatulence, vomiting, heartburn, decreased appetite,) NSAID-gastropathy, abdominal pain, stomatitis,
liver function disorders; rarely – gastrointestinal tract perforation, exacerbation of Crohn’s disease, melena, gum, gastrointestinal, hemorrhoidal bleeding.
The central nervous system: often – headache, dizziness, insomnia, drowsiness, fatigue, agitation, nervousness, depression, asthenia; rarely – confusion or loss of consciousness, forgetfulness, migraine, peripheral neuropathy; very rarely – hallucinations, disorientation and speech disorders.
Sensory organs: rare – noise or ringing in the ears, blurred vision, changes in taste, conjunctivitis, decreased hearing, dry mucous membrane of the eye, pain in the eye, conjunctival hyperemia, vertigo.
Systemic system disorders: rarely – tachycardia, arterial hypertension, peripheral edema.
Hematopoietic organs: ketoprofen decreases platelet aggregation, transient increase of liver enzymes, rarely – agranulocytosis, anemia, thrombocytopenia, purpura, hemolytic anemia, leukopenia.
Urinary system disorders: rarely – renal dysfunction, cystitis, urethritis, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, hematuria (more often developed in patients who take NSAIDs and diuretics for a long time).
Allergic reactions: common – skin reactions (itching, urticaria); rarely – rhinitis, shortness of breath, bronchospasm, angioedema, anaphylactoid reactions, exfoliative dermatitis.
Others: increased sweating, rarely – hemoptysis, nasal bleeding, menometrorrhagia, muscle twitching, thirst, photosensitization.
Overdose
Overdose
In overdose with ketoprofen, as well as other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, nausea, vomiting, vomiting with blood, abdominal pain, melena, impaired consciousness, respiratory depression, seizures, renal dysfunction and renal failure may occur.
There is no specific antidote.
The treatment is symptomatic. The effects of ketoprofen on the gastrointestinal tract can be weakened with the help of H2-receptor antagonists, proton pump inhibitors and prostaglandins. Gastric lavage and use of activated charcoal are indicated.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
The use of ketoprofen is contraindicated in the third trimester of pregnancy.
In the first and second trimesters of pregnancy the drug may be administered only if the estimated benefit to the mother exceeds the potential risk to the fetus.
In lactation, when taking the drug, it is necessary to consider stopping breastfeeding.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
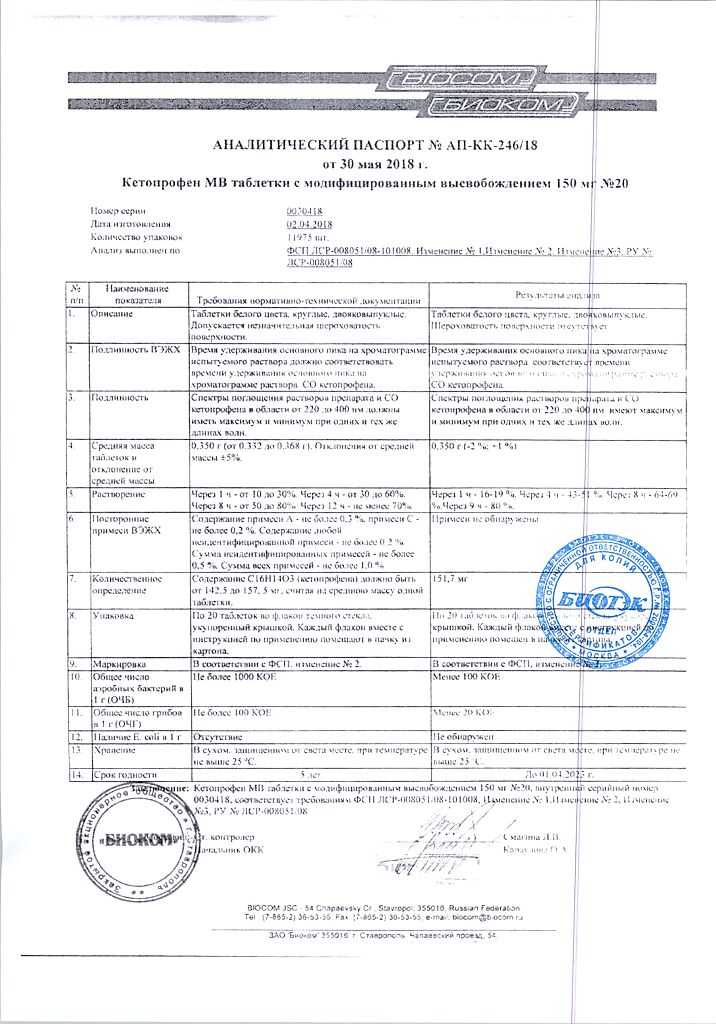
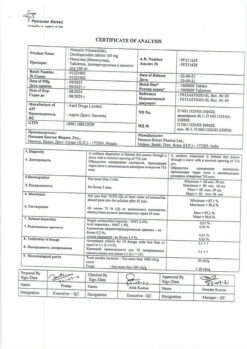
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Biocom AO, Russia |
| Medication form | controlled release tablets |
| Brand | Biocom AO |
Related products
Buy Ketoprofen MB, 150 mg 20 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.