No products in the cart.
Indomethacin, rectal 50 mg, 6 pcs.
€5.66 €5.03
Description
Pharmgroup:
NSAIDs.
Pharmic Action:
NSAID, indoleacetic acid derivative; has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects associated with indiscriminate inhibition of COX1 and COX2 that regulate Pg synthesis. It has antiaggregant effect.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption is fast. Bioavailability during oral administration of usual tablets, capsules is 90-98%, during administration of sustained-action tablets within 12 hours 90% of the administered dose is absorbed, for rectal suppositories – 80-90%. After oral administration the TCmax is 2 hours, Cmax is 0.69 mcg/ml.
Binding with plasma proteins is 90%. It is metabolized mainly in liver.
T1/2 – 4-9 h (this figure may vary depending on the severity of systemic metabolism, enterohepatic circulation and reabsorption). Excreted by the kidneys is 70%, with 30% unchanged, and by the gastrointestinal tract 30%. It penetrates into the breast milk, when the mother uses 200 mg of the drug per day, 0.5 to 2 mg is determined in the milk. The drug is not eliminated by dialysis.
Indications
Indications
Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system: rheumatoid, psoriatic, juvenile chronic arthritis, arthritis in Paget’s and Reiter’s disease, neuralgic amyotrophy (Personage-Turner disease), ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew’s disease), gouty arthritis (in case of an acute attack of gout, fast-acting dosage forms are preferred), rheumatism.
Pain syndrome: headache (including menstrual syndrome) and toothache, lumbago, sciatica, neuralgia, myalgia, after injuries and surgical interventions, accompanied by inflammation, bursitis and tendonitis (most effective when localized in the shoulder and forearm).
Algodismenorrhea; Bartter’s syndrome (secondary hyperaldosteronism); pericarditis (symptomatic treatment); childbirth (as an analgesic and tocolytic agent); inflammatory processes in the pelvis, incl. Adnexitis.
Non-closure of the ductus botallus.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs with severe pain syndrome (as part of complex therapy): pharyngitis, tonsillitis, otitis media.
Feverish syndrome (including with lymphogranulomatosis, other lymphomas and hepatic metastases of solid tumors) – in case of ineffectiveness of ASA and paracetamol. The drug is intended for symptomatic therapy, reducing pain and inflammation at the time of use, and does not affect the progression of the disease.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmaceutical group:
NSAIDs.
Pharmaceutical action:
NSAID, indoleacetic acid derivative; has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects associated with indiscriminate suppression of COX1 and COX2, which regulate the synthesis of Pg. Has an antiplatelet effect.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption is fast. Bioavailability when taken orally for regular tablets and capsules is 90-98%; when taking extended-release tablets, 90% of the administered dose is absorbed within 12 hours; for rectal suppositories – 80-90%. After oral administration, TCmax is 2 hours, Cmax is 0.69 mcg/ml.
Communication with plasma proteins – 90%. Metabolized mainly in the liver.
T1/2 – 4-9 hours (the indicator may vary depending on the severity of systemic metabolism, enterohepatic circulation and reabsorption). It is excreted by the kidneys by 70%, with 30% unchanged, and by the gastrointestinal tract – 30%. Penetrates into breast milk; when the mother uses 200 mg of the drug per day, the amount in milk is determined from 0.5 to 2 mg. The drug is not removed by dialysis.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Use with caution in elderly patients, as well as with a history of liver, kidney, gastrointestinal diseases, dyspeptic symptoms at the time of use, arterial hypertension, heart failure, immediately after major surgical interventions, parkinsonism, epilepsy.
If there is a history of allergic reactions to NSAIDs, they are used only in emergency cases.
During the treatment period, systematic monitoring of liver and kidney function and peripheral blood patterns is necessary.
Concomitant use with acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs is not recommended.
Indomethacin should not be used simultaneously with diflunisal.
When using indomethacin simultaneously with lithium preparations, one should keep in mind the possibility of symptoms of lithium toxicity.
When applied topically, it should not be applied to the wounded surface of the skin, and also avoid contact with the eyes or mucous membranes.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the treatment period, you should refrain from potentially hazardous activities associated with the need for concentration and increased speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Indomethacin
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
indomethacin 50 mg
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Indomethacin is contraindicated in the third trimester of pregnancy. In the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, as well as during lactation (breastfeeding), use is not recommended.
Indomethacin is excreted in small quantities into breast milk.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Individual hypersensitivity to indomethacin, aspirin or other NSAIDs (history of bronchospasm, urticaria or rhinitis caused by taking acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs);
peptic ulcer of the stomach and/or intestines in the acute phase;
pregnancy and breastfeeding;
children’s age (up to 14 years).
hematopoietic disorders;
severe dysfunction of the liver and/or kidneys;
severe forms of chronic heart failure, arterial hypertension, pancreatitis;
for rectal use: proctitis, recent bleeding from the rectum.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: nausea, anorexia, vomiting, pain and discomfort in the abdomen, constipation or diarrhea, erosive and ulcerative lesions, bleeding and perforation of the gastrointestinal tract; rarely – intestinal strictures, stomatitis, gastritis, flatulence, bleeding from the sigmoid colon or from a diverticulum, jaundice, hepatitis.
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: dizziness, headache, depression, feeling of fatigue; rarely – anxiety, fainting, drowsiness, convulsions, peripheral neuropathy, muscle weakness, involuntary muscle movements, sleep disorders, mental disorders (depersonalization, psychotic episodes), paresthesia, dysarthria, parkinsonism.
From the cardiovascular system: edema, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, chest pain, arrhythmia, palpitation, arterial hypotension, congestive heart failure, hematuria.
Allergic reactions: rarely – itching, urticaria, angiitis, erythema nodosum, skin rash, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, hair loss, acute respiratory distress, sharp drop in blood pressure, anaphylactic reactions, angioedema, dyspnea, bronchial asthma, edema lungs.
From the hematopoietic system: rarely – leukopenia, petechiae or ecchymosis, purpura, aplastic and hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
From the senses: rarely – impaired clarity of visual perception, diplopia, orbital and periorbital pain, tinnitus, hearing impairment, deafness.
From the urinary system: rarely – proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, interstitial nephritis, renal dysfunction, renal failure.
Metabolism: rarely – hyperglycemia, glucosuria, hyperkalemia.
Other: rarely – vaginal bleeding, hot flashes, increased sweating, nosebleeds, enlarged and tense breasts, gynecomastia.
Local reactions: at the site of intramuscular injection in some cases – formation of infiltrate, abscess; When used rectally, irritation of the rectal mucosa, tenesmus, and exacerbation of chronic colitis are possible.
For external use: itching, redness, rash at the site of application.
Interaction
Interaction
With simultaneous use, indomethacin can reduce the effects of saluretics and beta-blockers; enhance the effects of indirect anticoagulants.
With the simultaneous use of indomethacin and diflunisal, there is a risk of severe bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
When used simultaneously with probenecid, an increase in the concentration of indomethacin in the blood plasma is possible.
Indomethacin may reduce the tubular secretion of methotrexate, resulting in increased toxicity.
When used simultaneously with NSAIDs, the toxicity of cyclosporine increases.
Indomethacin at a dose of 50 mg 3 times a day increases the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma and reduces the clearance of lithium from the body in patients with mental illness.
With simultaneous use of indomethacin with digoxin, it is possible to increase the concentration of digoxin in the blood plasma and increase the half-life of digoxin.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, severe headache, dizziness, memory impairment, disorientation. In severe cases, paresthesia, numbness of the limbs, convulsions.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature below 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Sopharma JSC, Bulgaria
Additional information
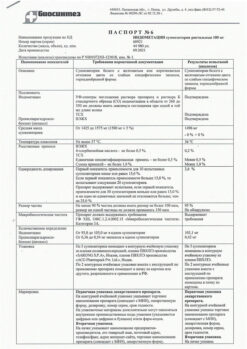
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place, at a temperature below 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Sofarma JSC, Bulgaria |
| Medication form | rectal suppositories |
| Brand | Sofarma JSC |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Indomethacin, rectal 50 mg, 6 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.