No products in the cart.
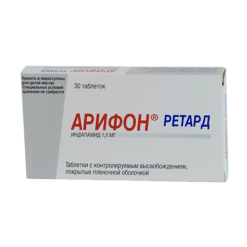
Indapamide, 2.5mg 30 pcs
€3.56 €3.24
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Indapamide is a thiazide-like diuretic, an antihypertensive agent.
Indapamide causes reduction of arterial smooth muscle tone, decreases PPS, also has moderate saluretic activity due to impaired reabsorption of sodium, chlorine and water ions in the cortical segment of the loop of Genle and proximal convoluted tubule of nephron.
The decrease of RPS is caused by several mechanisms: a decrease in the sensitivity of the vascular wall to noradrenaline and angiotensin II; increased synthesis of prostaglandins, which have vasodilatory activity; inhibition of the influx of calcium ions into the smooth muscle elements of the vascular wall.
In therapeutic doses has almost no effect on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
Hypotensive effect appears only at initially elevated BP, develops by the end of the first week and reaches a maximum after 3 months of systematic use.
After oral administration, it is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, Cmax in plasma is reached after 1-2 hours. Binding to plasma proteins is 79%. Widely distributed in the body. It does not cumulate.
T1/2 is 18 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys mainly as metabolites, 5% – unchanged.
Indications
Indications
Arterial hypertension; sodium and water retention in chronic heart failure.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Indapamide is a thiazide-like diuretic and antihypertensive agent.
Causes a decrease in the tone of the smooth muscles of the arteries, a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance, and also has moderate saluretic activity due to impaired reabsorption of sodium, chlorine and water ions in the cortical segment of the loop of Henle and the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron.
The decrease in peripheral vascular resistance is due to several mechanisms: a decrease in the sensitivity of the vascular wall to norepinephrine and angiotensin II; increased synthesis of prostaglandins with vasodilating activity; inhibition of the influx of calcium ions into the smooth muscle elements of the vascular wall.
In therapeutic doses, it has virtually no effect on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
The hypotensive effect appears only when blood pressure is initially elevated, develops by the end of the first week and reaches a maximum after 3 months of systematic use.
After oral administration, it is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, Cmax in plasma is reached within 1-2 hours. Plasma protein binding is 79%. Widely distributed in the body. Does not cumulate.
T1/2 is 18 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys mainly in the form of metabolites, 5% – unchanged.
Special instructions
Special instructions
In patients taking cardiac glycosides, laxatives, against the background of hyperaldosteronism, as well as in the elderly, regular monitoring of the content of K + ions and creatinine is indicated.
While taking indapamide, the concentration of K +, Na +, Mg 2+ ions in the blood plasma (electrolyte disturbances may develop), pH, concentration of glucose, uric acid and residual nitrogen should be systematically monitored.
The most careful monitoring is indicated in patients with liver cirrhosis (especially with edema or ascites – the risk of developing metabolic alkalosis, which increases the manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy), coronary heart disease, heart failure, as well as in the elderly.
The high-risk group also includes patients with an increased QT interval on the electrocardiogram (congenital or developed against the background of some pathological process).
The first measurement of K+ concentration in the blood should be carried out during the first week of treatment.
Hypercalcemia while taking indapamide may be a consequence of previously undiagnosed hyperparathyroidism.
In patients with diabetes mellitus, it is extremely important to control blood glucose levels, especially in the presence of hypokalemia.
Significant dehydration can lead to the development of acute renal failure (decreased glomerular filtration rate). Patients need to compensate for water loss and carefully monitor renal function at the beginning of treatment.
Result of doping control.
Patients with arterial hypertension and hyponatremia (due to taking diuretics) should stop taking diuretics 3 days before starting angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
(if necessary, diuretics can be resumed a little later), or they are prescribed an initial low dose of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
Sulfonamide derivatives can aggravate the course of systemic lupus erythematosus (must be kept in mind when prescribing indapamide).
Use in pediatrics: efficacy and safety in children have not been established.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Indapamide
Active components
Active components
Indapamide
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
Indapamide 2.5 mg;
Excipients:
Pregelatinized starch;
MCC;
Colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil);
Magnesium stearate;
Hypromellose;
Macrogol;
Lactose monohydrate;
Titanium dioxide
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Indapamide is not recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to indapamide, other sulfonamide derivatives or other components of the drug; anuria, refractory hypokalemia, hepatic encephalopathy or severe hepatic
failure, severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), pregnancy, breastfeeding, age under 18 years (insufficient data on effectiveness and safety);
lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption (the drug contains lactose).
Side Effects
Side Effects
The frequency of possible side effects is indicated in accordance with the classification of the World Health Organization: very often – more than 10%; often – more than 1% and less than 10%; infrequently – more than 0.1% and less than 1%;
rarely – more than 0.01% and less than 0.1%; very rarely – less than 0.01% (including isolated cases); frequency unknown—cannot be determined from available data.
From the blood and lymphatic system: very rarely – thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia.
From the nervous system, rarely – vertigo, fatigue, headache, paresthesia; frequency unknown – fainting.
From the cardiovascular system – very rarely – arrhythmia, arterial hypotension; frequency unknown – increase in the QT interval on the ECG, arrhythmia of the “torsade de pointes” type (possibly fatal).
From the digestive system: infrequently – vomiting; rarely – nausea, constipation, dry mouth; very rarely – pancreatitis.
From the kidneys and urinary tract: very rarely – renal failure.
From the liver and biliary tract: very rarely – impaired liver function; frequency is unknown – with liver failure, hepatic encephalopathy and hepatitis may occur.
From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions, mainly dermatological, in patients with a predisposition to allergic and asthmatic reactions: often – maculopapular rash;
uncommon – hemorrhagic vasculitis; very rarely – angioedema, urticaria, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome; frequency unknown – in patients with acute form of systemic lupus erythematosus, the course of the disease may worsen.
Cases of photosensitivity reactions have been described.
Laboratory indicators: very rarely – hypercalcemia; frequency unknown – increased concentrations of uric acid and glucose in the blood (thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics should be used with caution in patients with gout and diabetes mellitus);
increased activity of “liver” transaminases; a decrease in potassium levels and the development of hypokalemia, especially significant for patients at risk (see section “Special Instructions”); hyponatremia, accompanied by hypovolemia, dehydration and orostatic hypotension.
Simultaneous hypochloremia can lead to compensatory metabolic alkalosis (the likelihood and severity of this effect is low).
Interaction
Interaction
With the simultaneous use of GCS and tetracosactide for systemic use, the hypotensive effect is reduced due to the retention of water and sodium ions under the influence of GCS.
When used simultaneously with ACE inhibitors, the risk of developing hyponatremia increases.
When used simultaneously with NSAIDs (for systemic use), the hypotensive effect of indapamide may be reduced. With significant fluid loss, acute renal failure may develop (due to a sharp decrease in glomerular filtration).
When used simultaneously with calcium supplements, hypercalcemia may develop due to decreased excretion of calcium ions in the urine.
When used simultaneously with cardiac glycosides and corticosteroids, the risk of developing hypokalemia increases.
With the simultaneous use of drugs that can cause hypokalemia (amphotericin B, gluco- and mineralocorticoids, tetracosactide, laxatives that stimulate intestinal motility), the risk of developing hypokalemia increases.
When used simultaneously with tricyclic antidepressants (including imipramine), the hypotensive effect is enhanced and the risk of developing orthostatic hypotension increases (additive effect).
When used simultaneously with astemizole, bepridil, erythromycin (iv), pentamidine, sultopride, terfenadine, vincamine, quinidine, disopyramide, amiodarone, bretylium tosylate, sotalol, there is a risk of developing pirouette-type arrhythmia.
When used simultaneously with baclofen, the hypotensive effect is enhanced.
When used simultaneously with halofantrine, the likelihood of cardiac arrhythmia (including ventricular arrhythmia of the “pirouette” type) increases.
When used simultaneously with lithium carbonate, the risk of developing the toxic effect of lithium increases due to a decrease in its renal clearance.
When used simultaneously with metformin, lactic acidosis may occur, which is apparently associated with the development of functional renal failure caused by the action of diuretics (mainly loop diuretics).
When used simultaneously with cyclosporine, an increase in the creatinine content in the blood plasma is possible, which is observed even with normal levels of water and sodium ions.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, weakness, dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, disturbances in water and electrolyte balance, in some cases – excessive decrease in blood pressure, respiratory depression. Patients with liver cirrhosis may develop hepatic coma.
Treatment: gastric lavage, correction of water and electrolyte balance; If necessary, carry out symptomatic therapy. There is no specific antidote.
Specifications
Specifications
Round, biconvex, white film-coated tablets.
On a cross section, the core is white or almost white.
Complete set of goods
Complete set of goods
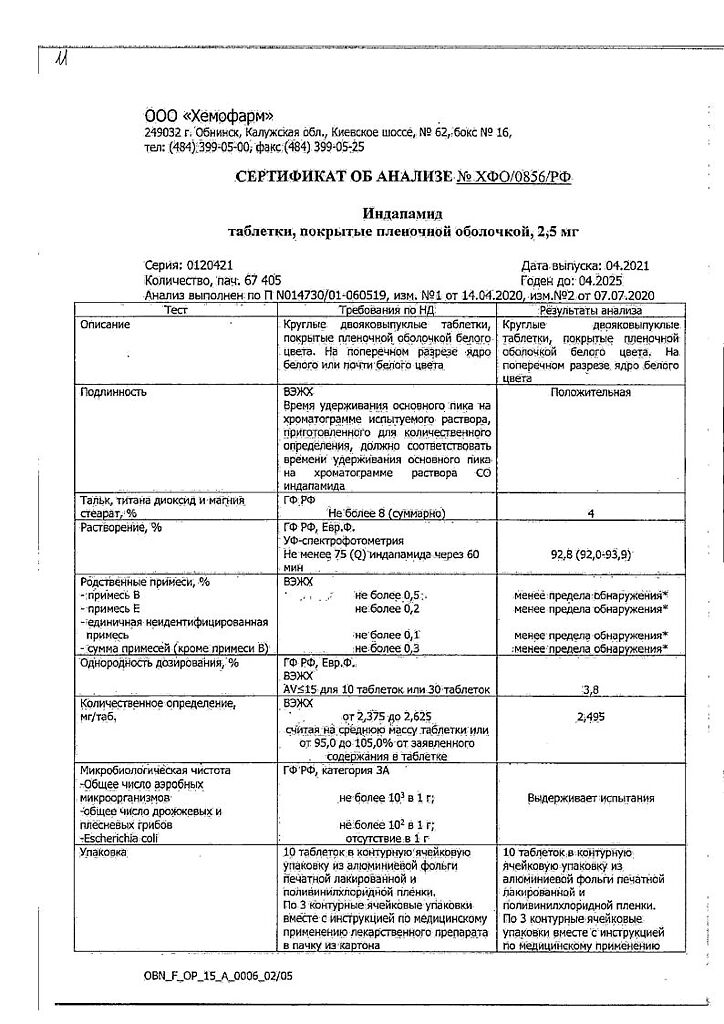
Film-coated tablets, 2.5 mg.
10 tablets in a blister (blister pack) made of printed varnished aluminum foil and polyvinyl chloride film.
3 blisters (blister packs) along with instructions for use of the medicinal product in a cardboard pack.
Functional features
Functional features
After oral administration, it is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract; bioavailability is high (93%). Eating slightly slows down the rate of absorption, but does not affect the amount of substance absorbed.
The maximum concentration in blood plasma is achieved 1-2 hours after oral administration. With repeated doses, fluctuations in the concentration of the drug in the blood plasma in the interval between two doses decrease.
Equilibrium concentration is established after 7 days of regular use. The half-life of the drug is 14-24 hours (on average 18 hours), the connection with blood plasma proteins is −79%.
It also binds to elastin of smooth muscles of the vascular wall. It has a high volume of distribution, passes through histohematic barriers (including placental), and penetrates into breast milk.
Metabolized in the liver. 60-80% is excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites (about 5% is excreted unchanged), and 20% is excreted through the intestines. In patients with renal failure, pharmacokinetics do not change. Does not cumulate.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light and moisture, at a temperature of 15–25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
4 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Hemofarm LLC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 4 years. Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a place protected from light and moisture, at 15-25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Chemopharm LLC, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Chemopharm LLC |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Indapamide, 2.5mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.