No products in the cart.
Gunfort, eye drops 0.3 mg+5 mg/ml 3 ml
€32.28 €26.90
Description
Ganfort is a combination medication with bimatoprost and timolol decreasing intraocular pressure (IOP) through a synergistic interaction, resulting in a significantly more pronounced hypotensive effect compared to the effects of each component alone.
Bimatoprost is a synthetic prostamide with a chemical structure similar to prostaglandin F2a (PGF2a). Bimatoprost has no effect on any of the known types of prostaglandin receptors. The hypotensive effect of bimatoprost is achieved by enhancing the outflow of intraocular fluid through the trabecula and through the uveoscleral pathway of the eye.
Timolol is a non-selective beta-adrenoblocker and has no intrinsic sympathomimetic and membrane-stabilizing activity.
Timolol reduces IOP by reducing the formation of intraocular fluid. The exact mechanism of action is not known; it may be related to inhibition of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (c-AMP) synthesis and is caused by endogenous stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors.
Indications
Indications
Reduction of intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma and intraocular hypertension with insufficient effectiveness of local use of beta-blockers and prostaglandin analogues.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Ganfort is a combination drug, its constituents bimatoprost and timolol reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) due to combined interaction, leading to a significantly more pronounced hypotensive effect compared to the effect of each component separately.
Bimatoprost is a synthetic prostamid, similar in chemical structure to prostaglandin F2a (PGF2a). Bimatoprost does not affect any of the known types of prostaglandin receptors. The hypotensive effect of bimatoprost is due to increased outflow of intraocular fluid through the trabecula and along the uveoscleral pathway of the eye.
Timolol is a non-selective beta-blocker and does not have intrinsic sympathomimetic or membrane-stabilizing activity.
Timolol reduces IOP by reducing the formation of intraocular fluid. The exact mechanism of action has not been established; it may be associated with inhibition of the synthesis of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (c-AMP) and is caused by endogenous stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Just like other ophthalmic drugs, Ganfort can penetrate into the systemic circulation.
Symptoms of heart failure must be compensated before starting to use the drug Ganfort. Regular monitoring of the condition of patients with severe heart failure and determination of heart rate is necessary. With the use of timolol, there have been reports of side effects from the cardiovascular system and respiratory organs, including deaths due to bronchospasm in patients with bronchial asthma, and also less often from heart failure.
Bsta-blockers can mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia, hyperthyroidism and cause worsening of Prinzmetal’s angina, severe peripheral and central vascular disorders, as well as arterial hypotension.
In patients with a history of atopic manifestations and severe anaphylactic reactions to various allergens, doses of epinephrine (adrenaline), which are usually used to relieve anaphylactic reactions, may be ineffective against the use of beta-blockers. In patients with mild liver disease or initially elevated levels of the liver enzymes alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and/or total bilirubin, bimatoprost had no effect on liver function over a 4-hour study period of more than 24 months.
Before starting treatment, patients should be informed about the possible growth of eyelashes, increased pigmentation of the skin of the eyelids and pigmentation of the iris, since these side effects were established during studies of bimatoprost and the drug Ganfort. Some changes may be permanent, and may be accompanied by differences between eyes if the drug is installed in only one eye. After discontinuation of the drug Ganfort, pigmentation of the iris may remain permanent. After 12 months of treatment with Ganfort, the incidence of iris pigmentation was noted in 0.2% of patients. And after 12 months of treatment with only bimatoprost in the form of eye drops 1.5%, a further increase in the frequency of this effect was not observed during therapy lasting 3 years. Increased pigmentation of the iris is due to increased production of melanocytes, and not simply an increase in their number.
The excipient benzalkonium chloride, which is part of the drug Ganfort, can cause irritation of the mucous membrane of the eyes and discoloration of soft contact lenses. Contact lenses must be removed before administering the drug; they can be put on 15 minutes after instillation. Benzalkonium chloride may cause acute keratitis and/or toxic corneal ulcer. In this regard, it is necessary to monitor the patient’s condition during frequent or prolonged treatment with Ganfort in persons with dry eye syndrome and changes in the cornea.
After opening the bottle, the possibility of microbial contamination of its contents cannot be ruled out, which can lead to inflammatory eye lesions. The shelf life of the drug after first opening the bottle is 28 days. After the specified time has expired, the bottle should be discarded, even if the solution is not completely used.
It is recommended to write down the date the bottle was opened on the cardboard package of the medicinal product.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
There may be a transient deterioration in vision after administration of the drug, so the patient should wait until vision is completely restored before driving a car or operating machinery.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Bimatoprost, Timolol
Composition
Composition
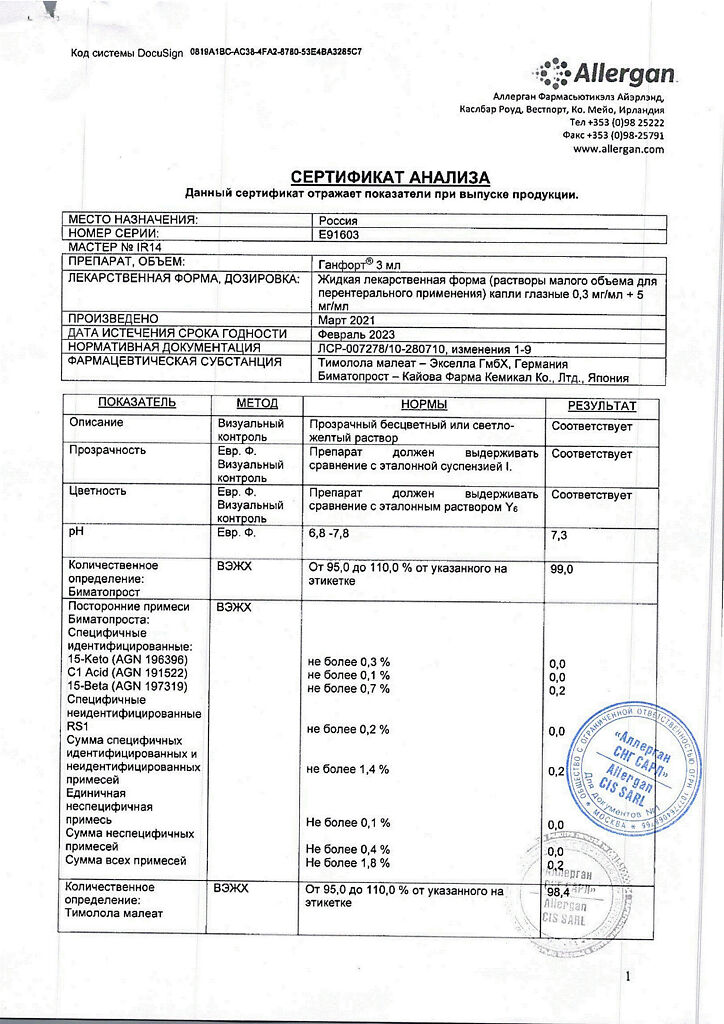
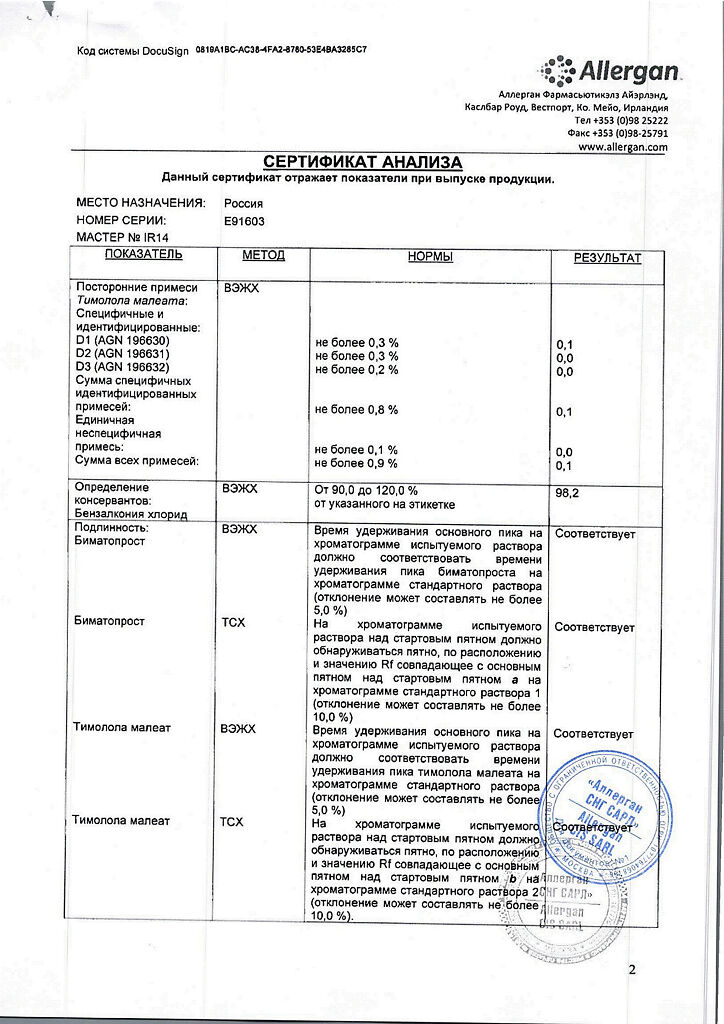
1 ml of eye drop solution contains:
Active ingredient
Bimatoprost 0.3 mg.
Timolol maleate 6.8 mg.
In terms of timolol 5.0 mg.
Excipients
Benzalkonium chloride,
citric acid monohydrate,
sodium hydrogen phosphate heptahydrate,
sodium chloride,
hydrochloric acid,
sodium hydroxide,
water.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Ganfort is contraindicated for children under 18 years of age, pregnant women and lactation.
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
syndrome of increased reactivity of the respiratory tract, including bronchial asthma in the acute stage and past episodes in history, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
sinus bradycardia, atrioventricular block II and III degrees, clinically significant heart failure, cardiogenic shock.
With caution: impaired liver and kidney function (the drug has not been sufficiently studied in this category of patients). In patients with risk factors for macular edema (for example, aphakia, pseudophakia, lens rupture).
In patients with diabetes mellitus (unstable course) and impaired glucose tolerance, since the beta-blocker timolol included in the drug Ganfort can mask the signs of hypoglycemia. In patients with inflammatory changes in the eyes, neovascular, inflammatory, closed-angle glaucoma, congenital glaucoma or narrow-angle glaucoma (no data on efficacy and safety studies).
Side Effects
Side Effects
The frequency of side effects identified during studies was assessed as follows: very often (>1/10), often (>1/100.1/1000,
Clinical studies of the drug Ganfort revealed the following side effects:
From the central nervous system: infrequently – headache;
From the organ of vision: very often – conjunctival hyperemia, eyelash growth; often – superficial keratitis, corneal erosion, burning sensation, itching, burning pain in the eyes, foreign body sensation, dry mucous membrane of the eyes, redness of the eyelids, pain in the eyes, photophobia, discharge from the eyes, blurred vision, itching of the skin of the eyelids; uncommon – iridocyclitis, irritation of the mucous membrane of the eyes, conjunctival edema, blepharitis, epiphora, swelling of the eyelids, soreness of the eyelids, decreased visual acuity, asthenopia, trichiasis; frequency unknown: cystoid macular edema.
From the respiratory system: infrequently – rhinitis;
From the skin and subcutaneous fat: often – pigmentation of the skin of the eyelids; infrequently – hirsutism.
Other side effects that were observed when using one of the components of the drug and are potentially possible during treatment with Ganfort:
Bimatoprost
From the cardiovascular system: increased blood pressure.
General disorders and changes at the injection site: asthenia, peripheral edema.
From the organ of vision: allergic conjunctivitis, cataracts, darkening of eyelashes, increased pigmentation of the iris, blepharospasm, eyelid retraction, retinal hemorrhage, uveitis.
Laboratory indicators: changes in the activity of liver enzymes.
Timolol
Mental disorders: insomnia, nightmares, decreased libido.
From the central nervous system: myasthenia gravis, paresthesia, cerebral ischemia.
On the part of the organ of vision: decreased sensitivity of the cornea, diplopia, ptosis, retinal detachment (after surgical treatment), changes in refraction (due to discontinuation of miotic therapy in some cases), keratitis.
From the organ of hearing and vestibular apparatus: tinnitus.
From the cardiovascular system: heart block, cardiac arrest, cardiac arrhythmias, loss of consciousness, bradycardia, heart failure, congestive heart failure; decreased blood pressure, chest pain, cerebrovascular accident, intermittent claudication, Raynaud’s syndrome, cold extremities, palpitations.
From the respiratory system: bronchospasm (mainly in persons with a history of episodes of bronchospasm), shortness of breath, cough.
From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia, dry oral mucosa.
From the skin and subcutaneous fat: alopecia, psoriasis-like rashes, exacerbation of psoriasis.
From the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue: systemic lupus erythematosus.
From the urinary system: Peyronie’s disease.
Other: swelling, chest pain, fatigue.
Overdose
Overdose
No cases of overdose of the drug Ganfort have been reported; When administered as eye drops, overdose is unlikely.
Bimatoprost
In case of unintentional ingestion of the drug Ganfort, the following information may be useful: no symptoms of toxic effects of bimatoprost were noted in doses up to 100 mg/kg/day. during a 2-week oral administration in an experiment on rats and mice. The dose used in the study, expressed in mg/m2, is 70 times higher than the possible dose of bimatoprost if the contents of a bottle of Ganfort were accidentally ingested by a child weighing 10 kg.
Timolol
In case of an overdose of timolol, the following symptoms may be observed: bradycardia, decreased blood pressure, bronchospasm, headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, cardiac arrest. Studies have shown that timolol is not completely eliminated by hemodialysis. If an overdose occurs, symptomatic therapy is necessary.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
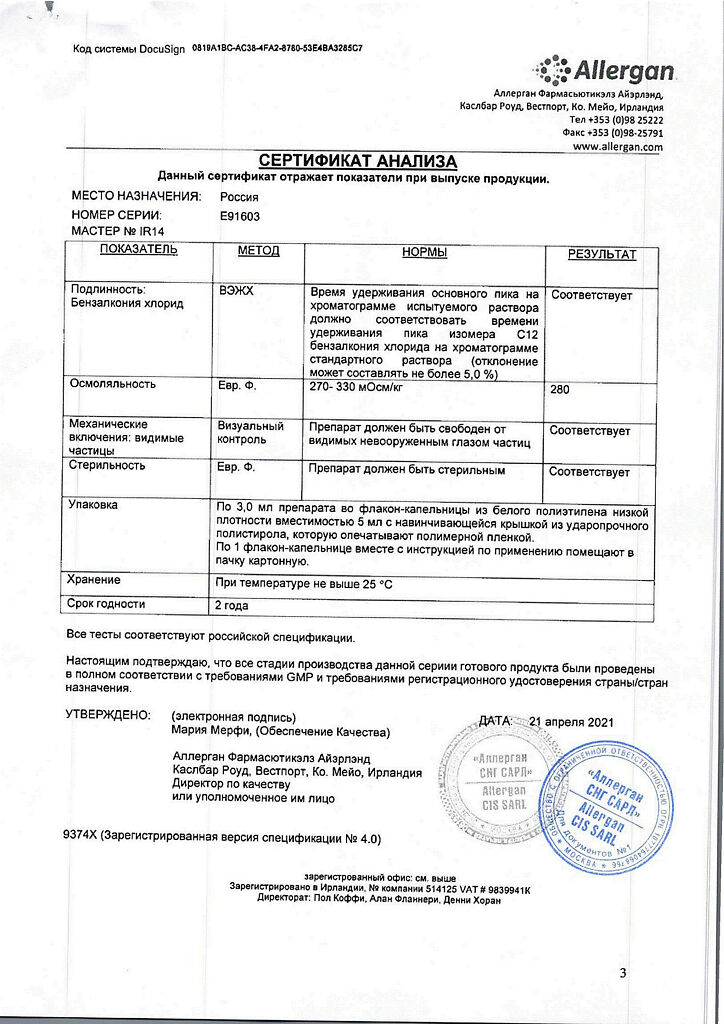
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Allergan Pharmaceuticals Ireland, Ireland
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Allergan Pharmaceuticals Ireland |
| Medication form | eye drops |
| Brand | #Н/Д |
Related products
Buy Gunfort, eye drops 0.3 mg+5 mg/ml 3 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.