No products in the cart.
Groprinosin, tablets 500 mg 50 pcs
€48.30 €40.25
Description
The drug with immunostimulatory and antiviral action.
It is a complex containing inosine and 4-acetamidobenzoic acid salt with N,N-dimethylamino-2-propanol in the molar ratio of 1:3.
The effectiveness of the complex is determined by the presence of inosine; the second component increases its availability to lymphocytes. Groprinosin blocks the multiplication of viral particles by damaging the genetic apparatus, and stimulates macrophage activity, lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine formation.
Limits clinical manifestations of viral diseases, accelerates recuperation, increases the body’s resistance.
When Groprinosin is administered as an adjunctive medicine for infectious lesions of the mucous membranes and skin caused by Herpes simplex virus, the affected surface heals more quickly than with traditional treatment. New blisters, edema, erosions, and recurrences of the disease are less common.
The timely use of the drug reduces the frequency of viral infections and the duration and severity of the disease.
Indications
Indications
Immunodeficiency conditions caused by viral infections in patients with normal and weakened immune systems, incl. diseases caused by Herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2 (including genital herpes and herpes of other localizations); subacute sclerosing panencephalitis.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
A drug with immunostimulating and antiviral effects.
It is a complex containing inosine and a salt of 4-acetamidobenzoic acid with N,N-dimethylamino-2-propanol in a molar ratio of 1:3.
The effectiveness of the complex is determined by the presence of inosine; the second component increases its availability to lymphocytes. Groprinosin blocks the reproduction of viral particles by damaging the genetic apparatus, stimulates the activity of macrophages, the proliferation of lymphocytes and the formation of cytokines.
Reduces the clinical manifestations of viral diseases, accelerates convalescence, and increases the body’s resistance.
When Groprinosin is prescribed as an auxiliary drug for infectious lesions of the mucous membranes and skin caused by the Herpes simplex virus, faster healing of the affected surface occurs than with traditional treatment. New blisters, swelling, erosions and relapses of the disease occur less frequently.
With timely use of the drug, the incidence of viral infections is reduced, the duration and severity of the disease is reduced.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Groprinosin, like other antiviral drugs, is most effective for acute viral infections if treatment is started at an early stage of the disease (preferably from the first day).
Since inosine is excreted from the body in the form of uric acid, with long-term use it is recommended to periodically monitor the concentration of uric acid in the blood serum and urine. Patients with significantly increased concentrations of uric acid in the body can simultaneously take medications that lower their concentrations.
It is necessary to monitor the concentration of uric acid in the blood serum when prescribing Groprinosin simultaneously with drugs that increase the concentration of uric acid or drugs that impair renal function.
Groprinosin should be used with caution in patients with acute liver failure, since the drug is metabolized in the liver.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
The effect of the drug Groprinosin on the psychomotor functions of the body and the ability to drive vehicles and moving mechanisms has not been studied. When using the drug, the possibility of dizziness and drowsiness should be taken into account.
Use for liver dysfunction
Patients with acute liver failure require a reduction in the dose of the drug, because The process of metabolism of inosine pranobex occurs in the liver.
Use for renal impairment
The drug is contraindicated for urolithiasis.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Inosine Pranobex
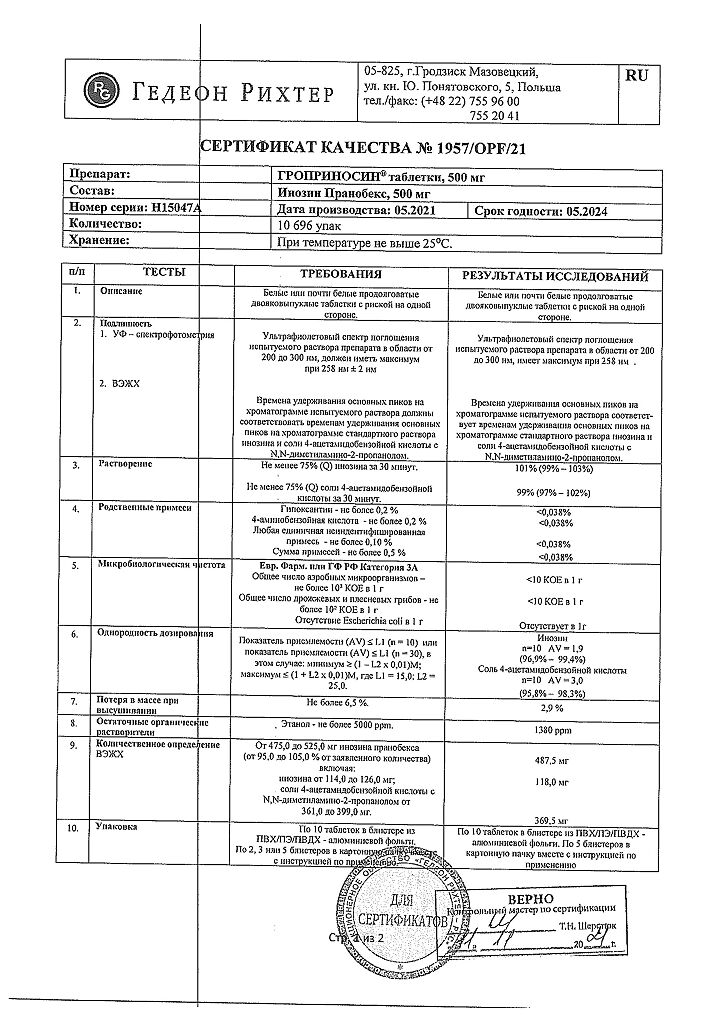
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
inosine pranobex 500 mg;
Excipients:
potato starch – 85 mg,
polyvinylpyrrolidone K25 – 45 mg,
magnesium stearate – 10 mg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
gout;
urolithiasis;
arrhythmia;
chronic renal failure;
children under 3 years of age (body weight up to 15-20 kg);
pregnancy;
lactation period (breastfeeding);
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
The drug should be prescribed with caution with xanthine oxidase inhibitors, diuretics, zidovudine, in acute renal failure.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Side effects are defined as frequent (>1/100 and 1/1000 and
From the nervous system: often – headache, dizziness, fatigue, poor health; infrequently – nervousness, drowsiness, insomnia.
From the gastrointestinal tract: often – loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain; infrequently – diarrhea, constipation.
From the hepatobiliary system: often – increased activity of liver enzymes, alkaline phosphatase.
From the skin and subcutaneous fat: often – itching, rash.
From the kidneys and urinary tract: infrequently – polyuria.
Allergic reactions: uncommon – maculopapular rash, urticaria, angioedema.
From the musculoskeletal system: often – joint pain, exacerbation of gout.
Other: often – increased blood urea nitrogen concentration.
Interaction
Interaction
Immunosuppressants weaken the immunostimulating effect of the drug Groprinosin.
Groprinosin should be used with caution in patients taking concomitant xanthine oxidase inhibitors (allopurinol) or loop diuretics (furosemide, torsemide, ethacrynic acid), because this may lead to increased serum uric acid concentrations.
The combined use of the drug Groprinosin with zidovudine leads to an increase in the concentration of zidovudine in the blood plasma and lengthens its half-life. Thus, when using the drug Groprinosin together with zidovudine, a dose adjustment of zidovudine may be required.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of overdose, gastric lavage and symptomatic therapy are indicated.
Functional features
Functional features
Suction
After oral administration, the drug is quickly and almost completely (> 90%) absorbed and has good bioavailability. When taken orally at a dose of 1500 mg, the Cmax of inosine pranobex is reached after 1 hour and is 600 mcg/ml. Not detectable in the blood 2 hours after administration.
Distribution and metabolism
Inosine pranobex consists of inosine and the salt of p-acetamidobenzoic acid with N,N-dimethylamino-2-propanol. Each of the components of inosine pranobex is rapidly metabolized. Almost 100% of metabolites are detected in urine within 8 to 24 hours from the moment of administration. Inosine undergoes metabolism in a cycle typical of purine nucleotides, producing uric acid, the concentration of which in the blood serum may increase.
As a result, uric acid crystals may form in the urinary tract. The increase in uric acid concentration is nonlinear and can vary by ± 10% within 1-3 hours after taking the drug orally. As a result of the metabolism of p-acetamidobenzoic acid, o-acyl glucuronide is formed; N,N-dimethylamino-2-propanol is metabolized to N-oxide. AUC of p-acetamidobenzoic acid >88%, AUC of N, N – dimethylamino-2-propanol >77%. No accumulation of the drug in the body was detected.
Removal
Inosine and its metabolites are excreted in the urine. When steady state concentration is reached when taking a daily dose of 4 g, the daily urinary excretion of p-acetamidobenzoic acid and its metabolite is approximately 85% of the dose taken; T1/2 – 50 min. T1/2 N,N-dimethylamino-2-propanol – 3-5 hours.
Complete elimination of inosine pranobex and its metabolites from the body occurs within 48 hours.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter, Hungary
Additional information
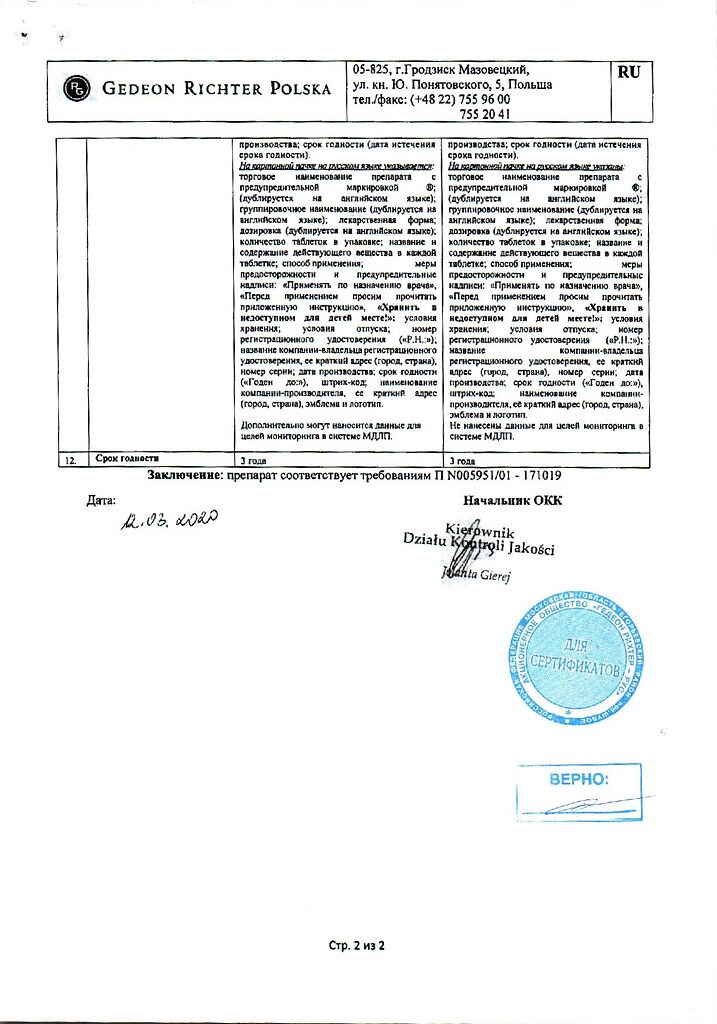
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Gedeon Richter, Hungary |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Gedeon Richter |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Groprinosin, tablets 500 mg 50 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.