No products in the cart.
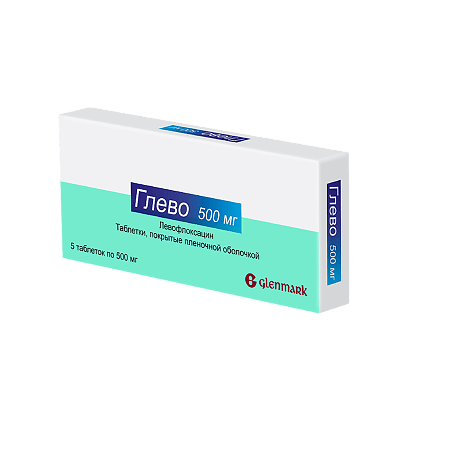
Glevo, 500 mg 5 pcs.
€1.56 €1.42
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antimicrobial agent – fluoroquinolone
b>Pharmacodynamics
A broad-spectrum antibacterial drug of the fluoroquinolone group. Levofloxacin blocks DNA-enzyme (topoisomerase II) and topoisomerase IV, breaks superspiralization and cross-linking of DNA breaks, inhibits DNA synthesis, causes deep morphological changes in cytoplasm, cell wall and membranes of microorganisms.
The drug is active against aerobic gram-positive microorganisms: Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Enterococcus spp. (including Enterococcus faecalis), Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus spp.Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-sensitive/methicillin-moderately sensitive strains), Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-sensitive strains), Staphylococcus epidermidis (methicillin-sensitive strains), Streptococcus spp. group C and G, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-sensitive/moderately sensitive/resistant strains), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus viridans (penicillin-moderately sensitive/resistant strains); aerobic gram-negative microorganisms: Acinetobacter spp. (including Acinetobacter baumannii), Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Citrobacter freundii, Eikenella corrodens, Enterobacter spp. Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter agglomerans, Enterobacter cloacae), Escherichia coli, Gardnerella vaginalis, Haemophilus ducreyi, Haemophilus influenzae (ampicillin-sensitive/resistant strains), Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Helicobacter pylori, Klebsiella spp. Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae), Moraxella catarrhalis (producing and non-producing ?-lactamases), Morganella morganii, Neisseria gonorrhoeae (producing and non-producing penicillinase), Neisseria meningitidis, Pasteurella spp. (including Pasteurella conis, Pasteurella dagmatis, Pasteurella multocida), Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia spp. (including Providencia rettgeri, Providencia stuartii), Pseudomonas spp. (including Pseudomonas aeruginosa), Salmonella spp, Serratia spp. (including Serratia marcescens); anaerobic microorganisms: Bacteroides fragilis, Bifidobacterium spp., Clostridium perfringens, Fusobacterium spp., Peptostreptococcus spp., Propionibacterium spp., Veilonella spp.; other microorganisms: Bartonella spp, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Chlamydia psittaci, Chlamydia trachomatis, Legionella pneumophila, Legionella spp., Mycobacterium spp. (including Mycobacterium leprae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis), Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Rickettsia spp., Ureaplasma urealyticum.
Pharmacokinetics
absorption
Ingestion is fast and almost completely absorbed. Food intake has little effect on the speed and completeness of absorption. Bioavailability is 99%. Tmax is 1-2 hours. When taking the drug in doses of 250 mg and 500 mg, Cmax is 2.8 mcg/ml and 5.2 mcg/ml, respectively.
Distribution
The binding to plasma proteins is 30-40%. It penetrates well into organs and tissues (lungs, bronchial mucosa, sputum, urogenital organs, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, alveolar macrophages).
Metabolism
In the liver, a small portion of the drug is oxidized and/or deacetylated.
Elimation
Renal clearance is 70% of total clearance. T1/2 is 6-8 h. It is excreted mainly by the kidneys by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Less than 5% of levofloxacin is excreted as metabolites. After oral administration about 70% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine within 24 hours, about 87% of the dose – within 48 hours; less than 4% – with the feces within 72 hours.
Indications
Indications
Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to the drug:
— infections of the ENT organs (including acute sinusitis);
— infections of the lower respiratory tract (including exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, community-acquired pneumonia);
– uncomplicated and complicated infections of the urinary tract and kidneys (including acute pyelonephritis, prostatitis);
– genital infections;
— infections of the skin and soft tissues (festering atheromas, abscess, furunculosis);
– infections of the abdominal cavity (in combination with drugs acting on anaerobic microflora).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group
antimicrobial agent – fluoroquinolone
Pharmacodynamics
Antibacterial drug of the fluoroquinolone group with a broad spectrum of action. Levofloxacin blocks DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) and topoisomerase IV, disrupts supercoiling and cross-linking of DNA breaks, suppresses DNA synthesis, and causes profound morphological changes in the cytoplasm, cell wall and membranes of microorganisms.
The drug is active against aerobic gram-positive microorganisms: Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Enterococcus spp. (including Enterococcus faecalis), Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus spp. (coagulase-negative, including methicillin-sensitive/methicillin-moderately sensitive strains), Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-sensitive strains), Staphylococcus epidermidis (methicillin-sensitive strains), Streptococcus spp. groups C and G, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-sensitive/moderately sensitive/resistant strains), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus viridans (penicillin-moderately sensitive/resistant strains); aerobic gram-negative microorganisms: Acinetobacter spp. (including Acinetobacter baumannii), Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Citrobacter freundii, Eikenella corrodens, Enterobacter spp. (including Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter agglomerans, Enterobacter cloacae), Escherichia coli, Gardnerella vaginalis, Haemophilus ducreyi, Haemophilus influenzae (ampicillin-sensitive/resistant strains), Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Helicobacter pylori, Klebsiella spp. (including Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae), Moraxella catarrhalis (producing and non-producing β-lactamases), Morganella morganii, Neisseria gonorrhoeae (producing and non-producing penicillinase), Neisseria meningitidis, Pasteurella spp. (including Pasteurella conis, Pasteurella dagmatis, Pasteurella multocida), Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia spp. (including Providencia rettgeri, Providencia stuartii), Pseudomonas spp. (including Pseudomonas aeruginosa), Salmonella spp., Serratia spp. (including Serratia marcescens); anaerobic microorganisms: Bacteroides fragilis, Bifidobacterium spp., Clostridium perfringens, Fusobacterium spp., Peptostreptococcus spp., Propionibacterium spp., Veilonella spp.; other microorganisms: Bartonella spp., Chlamydia pneumoniae, Chlamydia psittaci, Chlamydia trachomatis, Legionella pneumophila, Legionella spp., Mycobacterium spp. (including Mycobacterium leprae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis), Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Rickettsia spp., Ureaplasma urealyticum.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
When taken orally, it is quickly and almost completely absorbed. Food intake has little effect on the speed and completeness of absorption. Bioavailability – 99%. Tmax – 1-2 hours. When taking the drug in doses of 250 mg and 500 mg, Cmax is 2.8 mcg/ml and 5.2 mcg/ml, respectively.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding – 30-40%. Penetrates well into organs and tissues (lungs, bronchial mucosa, sputum, genitourinary organs, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, alveolar macrophages).
Metabolism
In the liver, a small part of the drug is oxidized and/or deacetylated.
Removal
Renal clearance accounts for 70% of the total clearance. T1/2 – 6-8 hours. Excreted from the body mainly by the kidneys through glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Less than 5% of levofloxacin is excreted as metabolites. After oral administration, about 70% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine within 24 hours, about 87% of the dose within 48 hours; less than 4% – in feces within 72 hours.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Although levofloxacin is more soluble than other quinolones, patients should be kept adequately hydrated.
During treatment, it is necessary to avoid solar and artificial UV irradiation to avoid damage to the skin (photosensitization).
If signs of tendonitis or pseudomembranous colitis appear, levofloxacin is immediately discontinued and appropriate therapy is prescribed.
It should be borne in mind that in patients with a history of brain damage (stroke, severe trauma), seizures may develop; with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, the risk of hemolysis increases.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Levofloxacin
Composition
Composition
Levofloxacin (as hemihydrate)500 mg
Excipients: microcrystalline cellulose, povidone (K-30), crospovidone, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose (Avicel pH101).
Film shell composition: hypromellose, macrogol (polyethylene glycol 6000), dibutyl phthalate, talc, titanium dioxide, red iron oxide dye, yellow iron oxide dye.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Glevo is contraindicated in children under 18 years of age, as well as during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Contraindications
Contraindications
— epilepsy;
– tendon damage due to previous treatment with quinolones;
— pregnancy;
– period of lactation (breastfeeding);
– childhood and adolescence (up to 18 years);
– hypersensitivity to levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones.
The drug should be prescribed with caution to elderly patients (due to the high likelihood of a concomitant decrease in renal function), with deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea (including blood), indigestion, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, pseudomembranous enterocolitis, increased activity of liver transaminases, hyperbilirubinemia, hepatitis, dysbacteriosis.
From the cardiovascular system: decreased blood pressure, vascular collapse, tachycardia, prolongation of the QT interval; extremely rarely – atrial fibrillation.
From the endocrine system: hypoglycemia (increased appetite, increased sweating, trembling, nervousness).
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: headache, dizziness, weakness, drowsiness, insomnia, tremor, anxiety, paresthesia, fear, hallucinations, confusion, depression, movement disorders, epileptic seizures (in predisposed patients).
From the senses: disturbances of vision, hearing, smell, taste and tactile sensitivity.
From the musculoskeletal system: arthralgia, muscle weakness, myalgia, tendon rupture, tendonitis, rhabdomyolysis.
From the urinary system: hypercreatininemia, interstitial nephritis, acute renal failure.
From the hematopoietic system: eosinophilia, hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, hemorrhages.
Allergic reactions: itching and redness of the skin, swelling of the skin and mucous membranes, urticaria, malignant exudative erythema (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal.
Interaction
Interaction
With simultaneous use, levofloxacin increases T1/2 of cyclosporine.
The effect of the drug is reduced by drugs that inhibit intestinal motility, sucralfate, aluminum/magnesium-containing antacid drugs and iron salts (a break of at least 2 hours is required between doses).
With simultaneous use of Glevo with NSAIDs and theophylline, convulsive readiness increases.
When using Glevo simultaneously with GCS, the risk of tendon rupture increases.
Cimetidine and drugs that block tubular secretion slow down the elimination of levofloxacin.
With the simultaneous use of hypoglycemic drugs with levofloxacin, hypo- and hyperglycemia may develop. Therefore, strict control of blood glucose levels is necessary.
Overdose
Overdose
Nausea, erosive lesions of the gastrointestinal mucosa, prolongation of the QT interval, confusion, dizziness, convulsions.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Storage temperature 2℃ to 25℃
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd, India
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Storage temperature from 2℃ to 25℃ |
| Manufacturer | Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd, India |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Glevo, 500 mg 5 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.