No products in the cart.
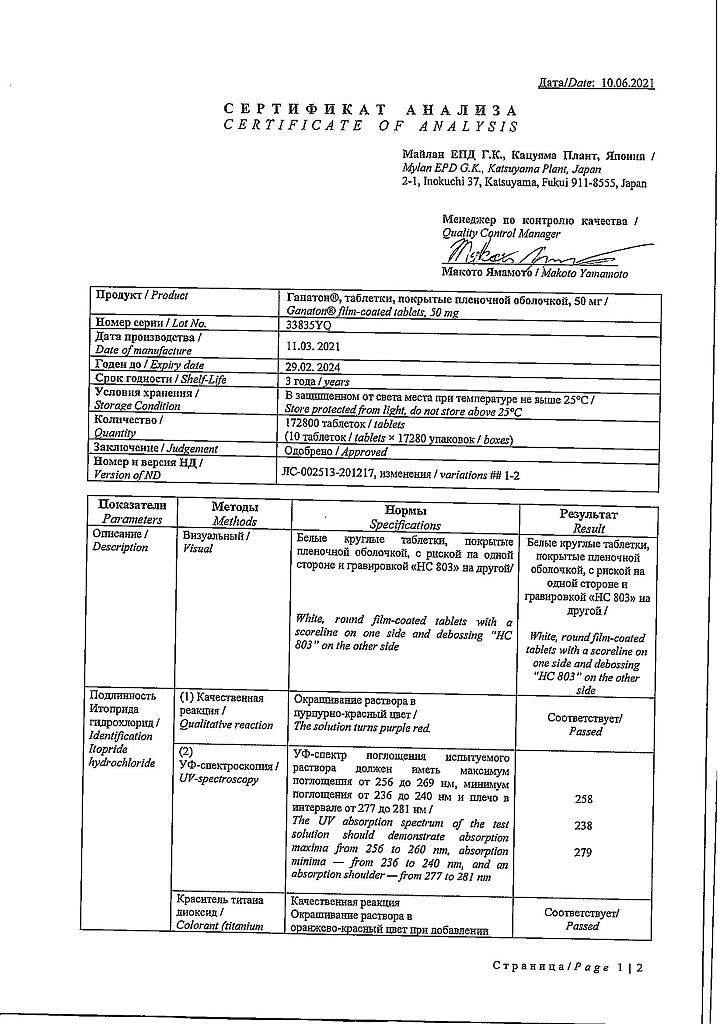
Ganaton, 50 mg 10 pcs
€12.60 €11.02
Description
Ganaton is a stimulant of gastrointestinal tone and motility.
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action. Itopride hydrochloride increases gastric motility due to antagonism of D2-dopamine receptors and inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. Itopride activates the release of acetylcholine and inhibits its degradation.
Itopride hydrochloride also gives antiemetic effect due to interaction with D2-receptors located in the trigger zone. Itopride causes dose-dependent suppression of apomorphine-induced vomiting.
Itopride hydrochloride activates gastric propulsive motility through antagonism of D2 receptors and dose-dependent inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity.
Itopride hydrochloride has a specific effect on the upper gastrointestinal tract, accelerating the transit through the stomach and improving its emptying. Itopride hydrochloride has no effect on serum levels of gastrin.
Pharmacokinetics
Intake. Itopride hydrochloride is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Its relative bioavailability is 60%, which is due to metabolism during the first passage through the liver. Food has no effect on bioavailability.
After oral administration of 50 mg of itopride hydrochloride Cmax is reached after 0.5-0.75 hours and is 0.28 µg/ml. When the drug was repeatedly administered at a dose of 50-200 mg 3 times/day for 7 days, the pharmacokinetics of the drug and its metabolites were linear and cumulation was minimal.
Distribution. Binds to plasma proteins (mainly to albumin) by 96%. Binding to α1-acid glycoprotein is less than 15% of total binding.
Actively distributed in tissues (Vd is 6.1 L/kg) and found in high concentrations in the kidneys, small intestine, liver, adrenal glands and stomach. Penetrates into the brain and spinal cord in minimal amounts. Penetrates into breast milk.
Metabolism. Itopride undergoes active biotransformation in the liver. Three metabolites have been identified, only one of which has little activity that has no pharmacological significance (about 2-3% of that of itopride). The primary metabolite is N-oxide, which is formed by oxidation of the quaternary amino-N-dimethyl group.
Itopride is metabolized by flavin-dependent monooxygenase (FMO3). The number and efficiency of FMO3 isoenzymes in humans can vary depending on the genetic polymorphism, which in rare cases leads to the development of an autosomal recessive condition known as trimethylaminuria (the “smell of fish” syndrome). In patients with trimethylaminuria, the T1/2 of ithopride is prolonged.
According to in vivo pharmacokinetic studies, itoprid has no inhibitory or inducing effect on CYP2C19 and CYP2E1. Therapy with itopride has no effect on CYP or uridine diphosphate glucuronidyltransferase activity.
Elimination. Itopride hydrochloride and its metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine. Renal excretion of ithopride and its N-oxide after a single oral administration of the drug in therapeutic doses in healthy subjects was 3.7% and 75.4%, respectively.
The terminal T1/2 of itopride hydrochloride is about 6 h.
Indications
Indications
Symptomatic treatment of functional non-ulcer dyspepsia (chronic gastritis), in particular relief of:
Bloating.
Feelings of quick satiety.
Pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen.
Anorexia.
Heartburn.
Nausea.
Vomiting.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Ganaton – stimulating the tone and motility of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pharmacodynamics
Mechanism of action. Itopride hydrochloride enhances gastric motility by antagonizing D2-dopamine receptors and inhibiting acetylcholinesterase. Itopride activates the release of acetylcholine and inhibits its destruction.
Itopride hydrochloride also provides an antiemetic effect due to interaction with D2 receptors located in the trigger zone. Itopride causes dose-dependent suppression of apomorphine-induced vomiting.
Itopride hydrochloride activates propulsive gastric motility through antagonism of D2 receptors and dose-dependent inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity.
Itopride hydrochloride has a specific effect on the upper gastrointestinal tract, accelerates gastric transit and improves gastric emptying. Itopride hydrochloride does not affect serum gastrin levels.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction. Itopride hydrochloride is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Its relative bioavailability is 60%, which is associated with first-pass metabolism through the liver. Food has no effect on bioavailability.
After taking 50 mg of itopride hydrochloride orally, Cmax is reached after 0.5–0.75 hours and is 0.28 mcg/ml. When the drug was repeated at a dose of 50–200 mg 3 times a day for 7 days, the pharmacokinetics of the drug and its metabolites were linear, and accumulation was minimal.
Distribution. Binds to plasma proteins (mainly albumin) by 96%. Binding to α1-acid glycoprotein accounts for less than 15% of total binding.
Actively distributed in tissues (Vd is 6.1 l/kg) and is found in high concentrations in the kidneys, small intestine, liver, adrenal glands and stomach. Penetrates the brain and spinal cord in minimal quantities. Passes into breast milk.
Metabolism. Itopride undergoes active biotransformation in the liver. 3 metabolites have been identified, only one of which exhibits small activity that has no pharmacological significance (approximately 2–3% of that of itopride). The primary metabolite is N-oxide, which is formed as a result of oxidation of the quaternary amino-N-dimethyl group.
Itopride is metabolized by flavin-dependent monooxygenase (FMO3). The amount and effectiveness of FMO3 isoenzymes in humans may vary depending on genetic polymorphisms, which in rare cases lead to the development of an autosomal recessive condition known as trimethylaminuria (fishy odor syndrome). In patients with trimethylaminuria, T1/2 of itopride increases.
According to in vivo pharmacokinetic studies, itopride does not have an inhibitory or inducing effect on CYP2C19 and CYP2E1. Itopride therapy does not affect CYP or uridine diphosphate glucuronyl transferase activity.
Excretion. Itopride hydrochloride and its metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine. Renal excretion of itopride and its N-oxide after a single oral dose of the drug in therapeutic doses in healthy people was 3.7 and 75.4%, respectively.
Terminal T1/2 of itopride hydrochloride is about 6 hours.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Due to the enhancement of the action of acetylcholine by itopride, the drug should be prescribed with caution due to the possible development of cholinergic adverse reactions in patients for whom their occurrence may aggravate the course of the underlying disease.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Itopride
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active ingredient:
itopride hydrochloride – 50 mg;
Excipients:
lactose – 34.975 mg (including excess due to weight loss during production – 2.93%),
corn starch – 15 mg,
carmellose – 20 mg,
anhydrous silicic acid – 4 mg,
magnesium stearate – 1 mg,
hypromellose – 4.4 mg,
macrogol 6000 – 0.4 mg,
titanium dioxide – 0.2 mg,
carnauba wax – 0.025 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of Ganaton during pregnancy and lactation is possible only in cases where there is no safer alternative, and the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus or child.
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to itopride or any auxiliary component of the drug;
gastrointestinal bleeding, mechanical obstruction or perforation of the gastrointestinal tract;
pregnancy;
lactation period;
children under 16 years of age.
With caution: the drug should be used in patients for whom the occurrence of cholinergic adverse reactions (associated with increased action of acetylcholine under the influence of itopride) may aggravate the course of the underlying disease.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the hematopoietic system: leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Allergic reactions: skin hyperemia, itching, rash, anaphylaxis.
From the endocrine system: increased prolactin levels, gynecomastia.
From the side of the central nervous system: dizziness, headache, tremor.
From the digestive system: diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, increased salivation, nausea, jaundice.
Changes in laboratory parameters: increased activity of AST and ALT, GGT, alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin levels.
Interaction
Interaction
Metabolic interaction is hardly possible, because itopride is metabolized by flavin monooxygenase and not by isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system.
With simultaneous use of Ganaton with warfarin, diazepam, diclofenac sodium, ticlopidine hydrochloride, nifedipine and nicardipine hydrochloride, no changes in the binding of itopride to proteins were observed.
Itopride increases gastric motility, so it may affect the absorption of other drugs administered orally at the same time. Particular caution should be exercised when using drugs with a low therapeutic index, as well as forms with a delayed release of the active substance or enteric-coated drugs.
Antiulcer agents such as cimetidine, ranitidine, teprenone and cetraxate do not interfere with the prokinetic action of itopride.
Anticholinergics may reduce the effect of itopride.
Overdose
Overdose
Cases of overdose in humans have not been described.
In case of overdose, gastric lavage and symptomatic therapy are indicated.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Mailan EPD G.K., Japan
Additional information
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Mylan EPD G.K., Japan |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Mylan EPD G.K. |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Ganaton, 50 mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.