No products in the cart.
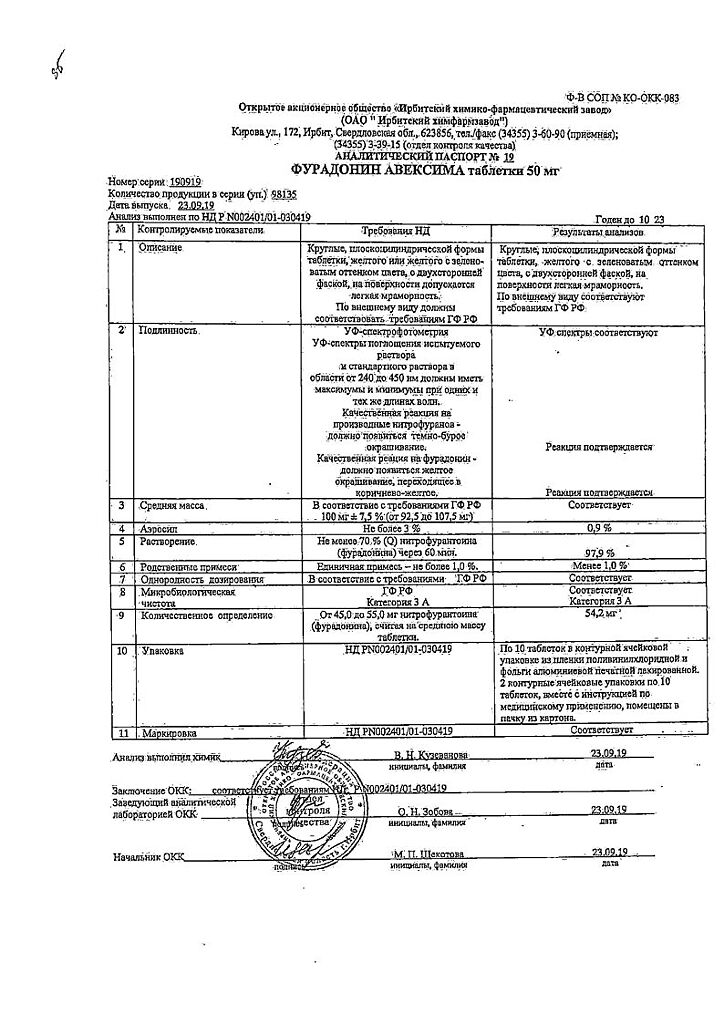
Furadonin Avexima, tablets 50 mg 20 pcs
€6.34 €5.55
Description
Pharmgroup:
An antimicrobial agent – nitrofuran.
Pharmic action:
Synthetic broad spectrum antimicrobial agent. Acts bactericidal.
The mechanism of action is associated with the reduction of furadonin into the active intermediate, which damages ribosomal proteins, disrupts the synthesis of protein, DNA, RNA. In high doses it disrupts permeability of the cell membrane of bacteria.
It is active against Gram-positive aerobic bacteria: Staphylococcus spp, Streptococcus spp; against Gram-negative aerobic bacteria: Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp, Klebsiella spp, Shigella spp.
Weakly active against Enterococcus spp., fungi of the genus Candida.
It is not active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp.
Most strains of Proteus and Serratia are resistant to furadonin.
Indications
Indications
– uncomplicated urinary tract infections (acute cystitis, asymptomatic bacteriuria, urethritis, pyelitis, pyelonephritis);
– prevention of infections during urological operations and examinations (cystoscopy, catheterization).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmaceutical group:
antimicrobial agent – nitrofuran.
Pharmaceutical action:
A synthetic broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. Acts bactericidal.
The mechanism of action is associated with the restoration of furadonin into an active intermediate that damages ribosomal proteins and disrupts the synthesis of protein, DNA, and RNA. In high doses, it disrupts the permeability of the bacterial cell membrane.
Active against gram-positive aerobic bacteria: Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp.; gram-negative aerobic bacteria: Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp., Klebsiella spp., Shigella spp.
Weakly active against Enterococcus spp., fungi of the genus Candida.
Not active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp.
Most strains of Proteus and Serratia are resistant to furadonin.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug should be discontinued at the first signs of peripheral neuropathy (paresthesia), because the development of this complication can be life-threatening.
It is necessary to stop treatment with furadonin if unexplained symptoms of impaired pulmonary function, liver function, hematological and neurological disorders occur.
If signs of lung damage appear, furadonin should be stopped immediately. Careful monitoring of pulmonary function is required in patients receiving long-term treatment with furadonin, especially in the elderly.
Careful monitoring of patients receiving long-term therapy with furadonin is necessary to identify signs of hepatitis development.
After taking furadonin, the urine may turn yellow or brown. Patients receiving furadonin may experience false-positive reactions when determining glucose in the urine.
Furadonin should be discontinued if signs of hemolysis appear in patients with suspected glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Reactions from the gastrointestinal tract can be minimized when taking the drug with food, milk or by reducing the dose.
Pregnancy and lactation period. The use of furadonin during pregnancy is contraindicated. If it is necessary to use it during lactation, the child should be weaned from the breast for the entire period of treatment.
Use in pediatrics. Not recommended for use in children under 6 years of age.
Caution when prescribing should be observed in persons with diabetes mellitus, anemia, electrolyte disturbances, deficiency of B vitamins, because the neurotoxic effect of the drug may be enhanced.
Furadonin should not be used to treat diseases of the renal cortex (glomerulonephritis), purulent paranephritis, or prostatitis. Especially for the treatment of parenchymal infection of one non-functioning kidney. In cases of recurrent or severe infection, surgical causes must be excluded.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and work with moving mechanisms. Furadonin may cause dizziness and drowsiness. The patient should not drive a car or operate moving machinery while taking the medicine.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Nitrofurantoin
Composition
Composition
1 tab:
– nitrofurantoin 50 mg
excipients:
potato starch,
Aerosil,
calcium stearate.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– hypersensitivity to nitrofurantoin or nitrofurans;
– severe renal dysfunction, renal failure, oliguria (creatine clearance less than 60 ml/min);
– children under 6 years of age;
– liver cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis;
– chronic heart failure (NYHA class III-IV);
– deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
– acute porphyria.
– pregnancy and lactation due to possible hemolytic anemia in the fetus or newborn due to the immaturity of erythrocyte enzyme systems.
Side Effects
Side Effects
– nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, hepatitis, cholestatic syndrome, pancreatitis, pseudomembranous enterocolitis.
– dizziness, headache, asthenia, nystagmus, drowsiness, peripheral neuropathy.
– interstitial changes in the lungs (interstitial pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis), bronchospasm, cough, flu-like syndrome, chest pain.
– leukopenia, granulocytopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, megaloblastic anemia.
– lupus-like syndrome, arthralgia, myalgia, anaphylactic reactions, fever, eosinophilia, rash, erythema multiforme exudative (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), exfoliative dermatitis.
– superinfection of the genitourinary tract, most often caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Interaction
Interaction
The absorption of furadonin is increased when taken with food or with medications that cause delayed gastric emptying.
Magnesium trisilicate reduces the absorption of furadonin.
Probenecid and sulfinpyrazone reduce the renal excretion of furadonin.
Corboanhydrase inhibitors and agents that cause an alkaline reaction in urine reduce the antibacterial activity of furadonin.
Furadonin and antimicrobial agents from the fluoroquinolone group are antibacterial antagonists.
Furadonin can suppress intestinal flora, which leads to a decrease in estrogen absorption and the effectiveness of estrogen-containing contraceptives. Patients are recommended to use non-hormonal methods of contraception.
Furadonin may inactivate the oral typhoid vaccine.
Nitrofurantoin weakens the antibacterial effect of norfloxacin in the urinary tract; simultaneous use is not recommended.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: when high doses are administered, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting may occur.
Treatment: discontinuation of the drug, taking large amounts of fluid to increase excretion of the drug in the urine, hemodialysis, symptomatic therapy. There is no specific antidote.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
4 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Irbitsky Chemical Plant, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 4 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Irbit Chemical Plant, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Irbit Chemical Plant |
Related products
Buy Furadonin Avexima, tablets 50 mg 20 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.