No products in the cart.
Flamax, 50 mg/ml 2 ml 10 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmgroup:
NSAIDs.
Pharmic action:
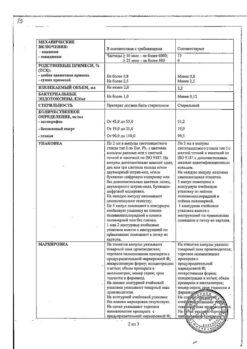
Flamax is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, a propionic acid derivative.
It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects, inhibits platelet aggregation.
By affecting cyclooxygenase and lipooxygenase link of arachidonic acid metabolism, ketoprofen inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes.
The analgesic effect is due to both central and peripheral mechanisms.
It has anti-bradykinin activity, stabilizes lysosomal membranes.
Pharmacokinetics:
Distribution.
Up to 99% of absorbed ketoprofen is bound to plasma proteins, mainly to albumin. The maximum concentration of the drug in plasma (Cmax) is reached quickly due to the low volume of distribution (0.1-0.2 l/kg). The equilibrium concentration of ketoprofen is reached 24 hours after the start of its regular administration. Ketoprofen penetrates well into the synovial fluid and connective tissues.
Significant levels of concentrations in synovial fluid are reached as early as 15 minutes after a single intramuscular injection of 100 mg of ketoprofen. Although ketoprofen concentrations in synovial fluid are somewhat lower than in plasma, they are more stable (persisting for up to 30 hours), resulting in long-term reduction of pain and joint stiffness.
Metabolism, excretion.
Ketoprofen is mainly metabolized in the liver, where it undergoes glucuronization to form glucuronic acid esters, excreted mainly by the kidneys. Excretion with feces is less than 1%. The half-life of ketoprofen varies from 1.6 to 1.9 hours. It does not cumulate.
Indications
Indications
Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system:
– rheumatoid arthritis;
– seronegative arthritis: ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew’s disease), psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis (Reiter’s syndrome);
– gout, pseudogout;
– osteoarthritis.
Pain syndrome:
– tendinitis, bursitis, myalgia, neuralgia, radiculitis;
– migraine;
– post-traumatic and postoperative pain syndrome;
– pain syndrome in cancer;
– algodismenorrhea.
Flamax is intended for symptomatic therapy, reducing pain and inflammation at the time of use, and does not affect the progression of the disease.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmaceutical group:
NSAIDs.
Pharmaceutical action:
Flamax is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, a derivative of propionic acid.
It has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effect, suppresses platelet aggregation.
By acting on the cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase components of arachidonic acid metabolism, ketoprofen inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes.
The analgesic effect is due to both central and peripheral mechanisms.
It has anti-bradykinin activity and stabilizes lysosomal membranes.
Pharmacokinetics:
Distribution.
Up to 99% of absorbed ketoprofen is bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. The maximum concentration of the drug in plasma (Cmax) is achieved quickly due to the low volume of distribution (0.1-0.2 l/kg). The equilibrium concentration of ketoprofen is achieved 24 hours after the start of its regular use. Ketoprofen penetrates well into synovial fluid and connective tissue.
Significant concentration levels in the synovial fluid are achieved within 15 minutes after a single intramuscular injection of 100 mg of ketoprofen. Although the concentrations of ketoprofen in synovial fluid are slightly lower than in plasma, they are more stable (lasting up to 30 hours), resulting in a long-term reduction in pain and joint stiffness.
Metabolism, excretion.
Ketoprofen is mainly metabolized in the liver, where it undergoes glucuronidation to form esters with glucuronic acid, which are excreted mainly by the kidneys. Excretion in feces is less than 1%. The half-life of ketoprofen ranges from 1.6 to 1.9 hours. Does not cumulate.
Special instructions
Special instructions
When using Flamax® and warfarin or lithium drugs simultaneously, patients should be under strict medical supervision. Caution must be exercised when prescribing the drug to patients with a history of peptic ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract, renal or liver failure, and those receiving coumarin anticoagulants. Like other drugs in this group, it can mask the symptoms of infectious diseases.
During treatment, monitoring of the peripheral blood picture and the functional state of the liver and kidneys is necessary.
If it is necessary to determine 17-ketosteroids, the drug should be discontinued 48 hours before the study.
If liver or kidney function is impaired, dose reduction and careful monitoring are necessary.
To reduce the risk of developing adverse events from the gastrointestinal tract, the minimum effective dose should be used for the shortest possible short course.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Ketoprofen
Composition
Composition
1 ampoule (2 ml) contains ketoprofen 100 mg;
excipients:
propylene glycol;
ethanol (ethyl alcohol 95% calculated as 100% substance);
benzyl alcohol;
sodium hydroxide;
water for injections.
Contraindications
Contraindications
“Aspirin” asthma, gastric and duodenal ulcers (exacerbation), ulcerative colitis (exacerbation), Crohn’s disease, diverticulitis, peptic ulcers, blood coagulation disorders (including hemophilia), renal and liver failure, children and adolescents under 18 years of age, pregnancy (III trimester).
Side Effects
Side Effects
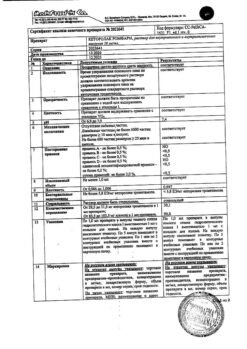
During clinical trials, the following side effects were noted (possibly related to the use of ketoprofen):
From the gastrointestinal tract: dyspepsia (11%); 3–9% – nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea/constipation, flatulence; >1% – anorexia, vomiting, stomatitis;
From the nervous system and sensory organs: 3–9% – headache, agitation (including insomnia, nervousness, unusual dreams); >1% – dizziness, central nervous system depression (including drowsiness, malaise), ringing in the ears, blurred vision;
From the cardiovascular system and blood (hematopoiesis, hemostasis):
From the respiratory system: >1% – dyspnea, hemoptysis, nosebleeds, pharyngitis, rhinitis, bronchospasm, laryngeal edema.
From the genitourinary system: 3–9% – impaired renal function (edema, increased blood urea nitrogen); >1% – symptoms and signs of urinary tract irritation;
From the skin: >1% – rash, alopecia, eczema, pruritis, urticaria, bullous rash, exfoliative dermatitis, photosensitivity, skin discoloration, onycholysis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Interaction
Interaction
With the simultaneous use of Flamax® and loop diuretics, the nephrotoxic effect of both drugs is enhanced. Reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs, enhances the effect of anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, fibrinolytics, ethanol, side effects of glucocorticosteroids and mineralocorticosteroids, estrogens; reduces the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs and diuretics.
Simultaneous use with other NSAIDs, glucocorticosteroids, ethanol, corticotropin can lead to the formation of ulcers and the development of gastrointestinal bleeding, increasing the risk of developing renal dysfunction. Concomitant use with oral anticoagulants, heparin, thrombolytics, antiplatelet agents, cefaperazone, cefamandole and cefotetan increases the risk of bleeding.
Increases the hypoglycemic effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs (dose recalculation is necessary). Inducers of microsomal oxidation in the liver (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants) increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites.
Combined use with sodium valproate leads to a decrease in platelet aggregation.
Increases plasma concentrations of verapamil and nifedipine, lithium drugs, methotrexate.
Antacids and cholestyramine reduce absorption.
Increases the hematotoxicity of myelotoxic drugs.
To avoid sediment, you should not mix Flamax and tramadol in one bottle.
Overdose
Overdose
Cases of overdose have not been described.
Symptoms: dizziness, vomiting, headache, shortness of breath, abdominal pain, bleeding, liver and kidney dysfunction may occur.
Treatment: symptomatic.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
PharmFirma Sotex, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. |
| Manufacturer | PharmFirm Sotex, Russia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | PharmFirm Sotex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Flamax, 50 mg/ml 2 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.