Subtotal: €5.03
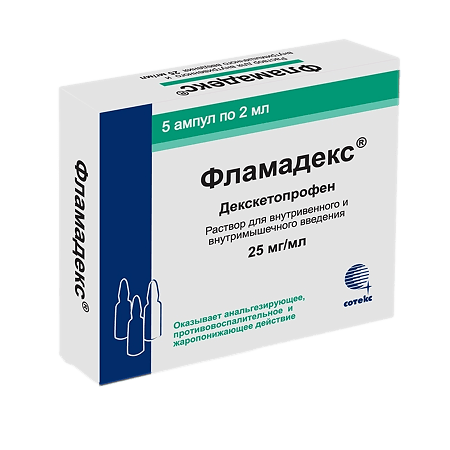
Flamadex, 25 mg/ml 2 ml 5 pcs
€6.66 €5.83
Pharmaceutical effects:
A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), propionic acid derivative. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. The mechanism of action is related to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis at the level of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2.
The analgesic effect comes 30 minutes after parenteral administration. Duration of analgesic effect after administration at a dose of 50 mg is about 4-8 hours.
In combined therapy with opioid analgesics dexectoprofen significantly (up to 30-45%) reduces the need for opioids.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption After intramuscular (i/m) administration of dexketoprofen the maximum concentration (Cmax) in blood serum is reached on average in 20 min (10-45 min). The area under the curve “concentration-time” (AUC) after a single administration at a dose of 25-50 mg is proportional to the dose, both when administered v/m and intravenous (IV). The corresponding pharmacokinetic parameters are similar after single and repeated v/m or v/v administration, indicating that there is no cumulation of the drug.
Distribution Dexketoprofen is characterized by high level of binding to plasma proteins (99%). The average value of Vd is less than 0.25 l/kg, the half-distribution time is about 0.35 h.
Elimation Metabolism of dexketoprofen mainly occurs by conjugation with glucuronic acid with subsequent excretion by the kidneys. The elimination half-life (T1/2) of dexketoprofen trometamol is about 1-2.7 hours. Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases In elderly people, an increase in T1/2 duration (both after a single injection and after repeated intravenous or intravenous administration) of up to 48% on average and a decrease in total clearance of the drug are observed.
Indications
Flamadex® is used in adults over 18 years of age for the symptomatic treatment of acute pain of severe and moderate intensity (for example, postoperative pain, low back pain and renal colic) when oral therapy is inappropriate.
If there is no improvement or you feel worse, contact your doctor.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmaceutical action:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), a derivative of propionic acid. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. The mechanism of action is associated with inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis at the level of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2.
The analgesic effect occurs 30 minutes after parenteral administration. The duration of the analgesic effect after administration at a dose of 50 mg is about 4-8 hours.
When combined with opioid analgesics, dexketoprofen significantly (up to 30-45%) reduces the need for opioids.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption After intramuscular (IM) administration of dexketoprofen, the maximum concentration (Cmax) in the blood serum is achieved on average after 20 minutes (10-45 minutes). The area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) after a single dose of 25-50 mg is proportional to the dose, both with IM and intravenous (IV) administration. The corresponding pharmacokinetic parameters are similar after single and repeated intramuscular or intravenous administration, indicating the absence of drug accumulation.
Distribution Dexketoprofen is characterized by a high level of binding to plasma proteins (99%). The average Vd value is less than 0.25 l/kg, the half-life of distribution is about 0.35 hours.
Excretion The metabolism of dexketoprofen occurs primarily through conjugation with glucuronic acid followed by excretion by the kidneys. The half-life (T1/2) of dexketoprofen trometamol is about 1-2.7 hours. Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases In elderly people, an increase in the duration of T1/2 (both after a single and after repeated IM or IV administration) is observed on average up to 48% and a decrease in the overall clearance of the drug.
Special instructions
Special instructions and precautions
Before using Flamadex®, consult your doctor.
Be sure to tell your doctor and use Flamadex® with caution:
if you have previously had allergic reactions;
if you are an elderly patient;
if you have ever had diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) (gastritis, esophagitis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis);
if you use hormonal drugs that reduce the severity of inflammation and swelling (oral glucocorticosteroids), drugs that reduce blood clotting (anticoagulants, including warfarin or other derivatives of coumarin and heparin), drugs that prevent the formation of blood clots (antiplatelet agents, including acetylsalicylic acid);
if you use antidepressants (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), diuretics (diuretics);
if you have kidney disease;
if you have recently had major surgery or are dehydrated;
if you have liver disease;
if you have high blood pressure (hypertension), heart disease (mild to moderate heart failure, coronary heart disease), diseases of the peripheral arteries and/or cerebral vessels, high levels of lipids in the blood (hyperlipidemia), diabetes mellitus or you smoke;
if you have a hereditary disorder of porphyrin metabolism (including acute intermittent porphyria);
if you have hematopoietic disorders, systemic lupus erythematosus or mixed connective tissue disease;
You should not use Flamadex® in combination with other NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors. Undesirable side effects can be minimized by using the drug at the lowest effective dose for the minimum duration of use necessary to relieve symptoms.
There have been reports of gastrointestinal bleeding, ulcers or perforations (in some cases fatal) during the use of any NSAIDs at different stages of treatment, both with and without the appearance of warning symptoms, and regardless of the presence of serious gastrointestinal complications in the anamnesis.
Stop taking the drug and seek immediate medical attention if gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcers occur. Possible symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding: increasing weakness, pallor, significant darkening of stool, blood in the stool, vomiting streaked with blood.
Tell your doctor about any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially possible symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding) if you have had gastrointestinal side effects in the past, especially if you are older. In elderly patients, the incidence of side effects associated with the use of NSAIDs, especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforated ulcers, which can be life-threatening, increases. If you are an elderly patient, your doctor may start treatment with the lowest possible dose of the drug.
Before taking Flamadex®, tell your doctor if you have ever had an ulcer, bleeding in the stomach or intestines, ulcerative colitis, or Crohn’s disease, as exacerbation of these diseases is possible.
If you are taking medications that may increase your risk of ulcers or bleeding, your doctor may also prescribe you medications that have gastrointestinal protective properties (such as misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors).
Use caution when taking Flamadex® if you are taking medications that may increase the risk of ulcers or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids, anticoagulants such as warfarin, antidepressants (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), or antiplatelet agents such as acetylsalicylic acid.
Children and teenagers
Do not give the drug to children aged 0 to 18 years due to the risk of ineffectiveness and possible unsafety (the safety and effectiveness of Flamadex® in children under 18 years of age have not been established).
Driving vehicles and working with machinery
Attention! This drug may affect your reaction time and ability to drive. Due to possible dizziness and drowsiness while using Flamadex®, the ability to concentrate and the speed of psychomotor reactions may decrease.
Flamadex® contains ethanol
This medicinal product contains 12.7 vol. % ethanol (alcohol), that is, up to 200 mg per dose, which is equal to 5 ml of beer, 2 ml of wine per dose. Harmful for persons with alcoholism. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, children and high-risk groups such as patients with liver disease and epilepsy should be considered.
Flamadex® contains sodium metabisulfite
In some cases, especially in predisposed patients with bronchial asthma with increased sensitivity to sulfites, severe hypersensitivity reactions and bronchospasm may develop.
Active ingredient
Dexketoprofen
Composition
The drug Flamadex® contains
The active ingredient is dexketoprofen.
Flamadex®, 25 mg/ml, solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration.
1 ml of solution contains 25 mg of dexketoprofen (in the form of dexketoprofen trometamol).
One 2 ml ampoule contains 50 mg of dexketoprofen (as dexketoprofen trometamol).
Other ingredients (auxiliary substances) are:
ethanol, sodium chloride, sodium metabisulfite, sodium hydroxide, water for injection.
Pregnancy
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning a pregnancy, consult your doctor before starting to use the drug.
Pregnancy
The use of Flamadex® during pregnancy is contraindicated.
Suppression of prostaglandin synthesis may adversely affect pregnancy and/or embryonic and fetal development. The results of epidemiological studies indicate that drugs that suppress the synthesis of prostaglandins, used in the early stages of pregnancy, can increase the risk of spontaneous abortion, as well as the development of heart defects and cleft of the anterior abdominal wall in the fetus, so the absolute risk of developing abnormalities of the cardiovascular system increased from approximately less than 1% to 1.5%. The risk is believed to increase with increasing dose and duration of use.
The use of NSAIDs by women from the 20th week of pregnancy can lead to the development of oligohydramnios and/or kidney pathology in newborns (neonatal renal dysfunction).
In the third trimester of pregnancy, all inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis can lead to the development of cardiopulmonary pathology in the fetus (premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and hypertension in the pulmonary artery system) and renal dysfunction, which can progress and lead to the development of renal failure with the development of oligohydramnios. In addition, even when used in low doses, in the mother at the end of pregnancy and in the newborn, there may be an increase in bleeding time associated with the antiplatelet effect, as well as suppression of uterine contractility, leading to a delay in labor or prolonged labor in the mother.
In animals, the use of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor increased the risk of intra- and post-implantation losses and increased embryofetal mortality. In addition, in animals receiving prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors during the period of organogenesis, the incidence of fetal malformations, including abnormalities of the cardiovascular system, increased. However, animal studies of dexketoprofen have not revealed any signs of reproductive toxicity.
Breastfeeding period
There is no information about the penetration of dexketoprofen into breast milk.
The use of Flamadex® during breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Fertility
Dexketoprofen, like other NSAIDs, can reduce female fertility, so it is not recommended for women planning pregnancy. In women having problems conceiving or undergoing evaluation for infertility, discontinuation of dexketoprofen should be considered.
Contraindications
Do not use Flamadex®:
if you are allergic to dexketoprofen or any of the other ingredients of the medicine listed in section 6 of the leaflet;
if you have a complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs (including those previously observed);
if you have ever developed attacks of asthma, bronchospasm, acute rhinitis or nasal polyps, urticaria or angioedema when using drugs with similar effects (for example, acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and other NSAIDs);
if you have previously had skin hypersensitivity reactions to light (photoallergic or phototoxic reactions) while being treated with ketoprofen or fibrates (a class of drugs that have a positive effect on blood fat levels by lowering triglyceride levels, increasing high-density lipoprotein (“good” cholesterol) levels and reducing low-density lipoprotein (“bad” cholesterol) levels);
if you have had gastrointestinal bleeding, ulcers or perforations, including those associated with previous use of NSAIDs;
if you have chronic digestive disorders (chronic dyspepsia);
if you have erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract;
if you have gastrointestinal bleeding; other active bleeding (including suspected intracranial hemorrhage);
if you have Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis;
if you have severe liver dysfunction (10-15 points on the Child-Pugh scale);
if you have active liver disease;
if you have progressive kidney disease, a confirmed high level of potassium in the blood (hyperkalemia);
if you have chronic kidney disease: (glomerular filtration rate (GFR) < 59 ml/min/1.73 m2);
if you have chronic heart failure in the decompensation stage;
if you have a period before and after coronary bypass surgery;
if you have bleeding disorders (hemorrhagic diathesis and other coagulation disorders);
if you are severely dehydrated (from vomiting, diarrhea, or not drinking enough fluids).
Flamadex® is contraindicated for neuraxial anesthesia (epidural or intrathecal administration) as it contains ethanol.
Side Effects
Like all medicines, Flamadex® can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them.
You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following adverse reactions that occur:
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
abdominal pain;
bloody vomiting;
fever.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people):
swelling of the larynx;
low glucose levels (hypoglycemia);
fainting;
heart rhythm disturbance (extrasystole);
increased heart rate (tachycardia);
increased blood pressure (arterial hypertension);
peptic ulcer, gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation of a peptic ulcer;
impaired renal function (acute renal failure);
increased amount of urine (polyuria);
renal colic, the presence of ketone (acetone) bodies in the urine (ketonuria);
presence of protein in the urine (proteinuria).
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
sudden, widespread, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reactions (anaphylactic reactions, including anaphylactic shock);
narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi (bronchospasm), shortness of breath;
inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis);
kidney inflammation (nephritis or nephrotic syndrome);
a serious allergic reaction that may start as a rash in one area but spread throughout the body (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell’s syndrome);
swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat, which may cause difficulty swallowing or breathing (angioedema).
The most commonly observed side effects are from the gastrointestinal tract. Peptic ulcers, perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding may develop, sometimes with death, especially in elderly patients. According to available data, the use of the drug may cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, constipation, indigestion (dyspeptic symptoms), abdominal pain, black semi-liquid stools with a characteristic unpleasant odor (melena), bloody vomiting, ulcerative stomatitis, exacerbation of colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gastritis is less common. There are also reports of edema, hypertension and heart failure during treatment with NSAIDs.
As with the use of other NSAIDs, the following side effects may develop: aseptic meningitis, which develops mainly in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus or mixed connective tissue disease, hematological disorders (thrombocytopenic purpura, aplastic and hemolytic anemia, in rare cases – agranulocytosis and bone marrow hypoplasia). Bullous reactions are possible, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (very rare).
According to clinical studies and epidemiological data, the use of some NSAIDs, especially in high doses and for a long time, may be accompanied by a slight increase in the risk of developing pathology caused by arterial thrombosis (for example, myocardial infarction or stroke).
Other adverse reactions:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
nausea;
vomit;
pain at the injection site;
reaction at the injection site, including inflammation;
bruise (hematoma);
bleeding;
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
decreased hemoglobin content in the blood (anemia);
headache;
dizziness;
drowsiness;
insomnia;
blurred vision;
decreased blood pressure;
redness of the face and neck;
indigestion (dyspepsia);
diarrhea (diarrhea);
constipation;
dry mouth;
inflammatory skin lesions (dermatitis);
skin itching;
skin rash;
increased sweating;
fatigue;
pain;
a feeling of cold accompanied by muscle tremors (chills).
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people):
increased blood glucose (hyperglycemia);
increased levels of triglycerides in the blood (hypertriglyceridemia);
anorexia;
burning, tingling, or pins and needles sensation on the skin (paresthesia);
tinnitus;
thrombophlebitis of superficial veins;
decreased breathing (bradypnea);
liver cell damage;
the appearance of uneven, itchy, red blisters on the surface of the skin (urticaria);
acne (acne);
increased muscle tone, making it difficult to move (muscle rigidity);
stiffness in the joints;
involuntary muscle contractions of a paroxysmal nature (muscle cramps);
back pain;
menstrual irregularities;
dysfunction of the prostate gland;
frequent convulsive muscle contractions (trembling);
peripheral edema;
deviation from the norm in liver function tests.
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
decrease in the content of neutrophils in the blood (neutropenia);
decreased platelet count in the blood (thrombocytopenia);
increased sensitivity of the skin to light (photosensitization reactions).
Interaction
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken, or may start taking any other medications.
It is not recommended to use Flamadex® in combination with the following drugs:
other NSAIDs, including salicylates in high doses (≥ 3 g/day): simultaneous use of several NSAIDs increases the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcers;
oral anticoagulants (drugs that reduce blood clotting), heparin in doses exceeding prophylactic doses due to the risk of bleeding;
ticlopidine (prevents the formation of blood clots), as the risk of bleeding increases;
lithium preparations (drugs for the treatment of depression and other mental disorders) because NSAIDs increase the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma (decreased excretion of lithium), which can reach toxic levels, so the doctor may order laboratory tests to monitor the level of lithium in the blood;
methotrexate (an antitumor drug) in high (at least 15 mg/week) doses, because the toxicity of methotrexate increases due to a decrease in its excretion when using NSAIDs;
glucocorticosteroids (hormonal drugs prescribed for the treatment of autoimmune rheumatological diseases) because the risk of developing ulcers and gastrointestinal bleeding increases;
hydantoin derivatives (used to treat epilepsy) and sulfonamides (antimicrobial agents) because the severity of their toxic manifestations may increase.
You should be careful when using Flamadex® together with drugs:
diuretics (diuretics), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (drugs to lower blood pressure), aminoglycoside antibacterial drugs and angiotensin II receptor antagonists (drugs to lower blood pressure). Dexketoprofen weakens the effect of diuretics and other antihypertensive (blood pressure-lowering) drugs. Treatment with NSAIDs is associated with a risk of acute renal failure in patients with kidney disease.
methotrexate (antitumor drug) in low (less than 15 mg/week) doses, because the toxicity of methotrexate increases due to a decrease in its excretion when using NSAIDs;
pentoxifylline (a drug that improves blood microcirculation), because the risk of bleeding increases.
zidovudine (an antiviral drug used to treat HIV) – can lead to the development of severe anemia (decreased hemoglobin);
oral hypoglycemic drugs (drugs that lower blood glucose levels) due to a possible increase in hypoglycemic effect.
It must be taken into account that when using Flamadex® together with drugs such as:
β-blockers (drugs used to lower blood pressure) – their effectiveness may be reduced;
cyclosporine (a drug for the treatment and prevention of rejection after bone marrow transplantation and organ transplantation) and tacrolimus (a drug for the treatment and prevention of rejection after organ transplantation) may increase their toxic effect on the kidneys;
thrombolytic drugs (drugs that prevent blood clotting), because the risk of bleeding increases;
probenecid (a drug used to treat gout) may increase the concentration of dexketoprofen in the blood plasma;
cardiac glycosides – NSAIDs can lead to an increase in their concentration in the blood plasma;
mifepristone (abortion drug), because there is a theoretical risk of a change in its effectiveness, NSAIDs should be prescribed no earlier than 8-12 days after taking mifepristone;
quinolone antibiotics – a high risk of developing seizures when using NSAIDs in combination with high doses of quinolones.
tenofovir (antiviral drug for the treatment of HIV): When used concomitantly with NSAIDs, plasma urea and creatinine concentrations may increase, so renal function should be monitored to assess the possible effect of concomitant use of these drugs.
Deferasirox (used for some chronic anemias) may increase the risk of gastrointestinal toxicity when used concomitantly with NSAIDs.
pemetrexed (antineoplastic agent) – when used concomitantly with NSAIDs, the elimination of pemetrexed may be reduced, so special caution should be exercised when using NSAIDs in high doses. In patients with mild renal insufficiency (chronic kidney disease (GFR 60-89 ml/min/1.73 m2), concomitant use of pemetrexed and NSAIDs should be avoided for two days before and two days after taking pemetrexed.
Storage conditions
Keep the drug out of the reach and sight of children so that the child cannot see it.
Do not take the drug after the expiration date indicated on the blister or cardboard pack.
The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated on the package.
Store in the original package. Do not store at temperatures above 25°C.
Manufacturer
PharmFirma Sotex, Russia
| Manufacturer | PharmFirm Sotex, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | PharmFirm Sotex |
Related products
Buy Flamadex, 25 mg/ml 2 ml 5 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.