No products in the cart.
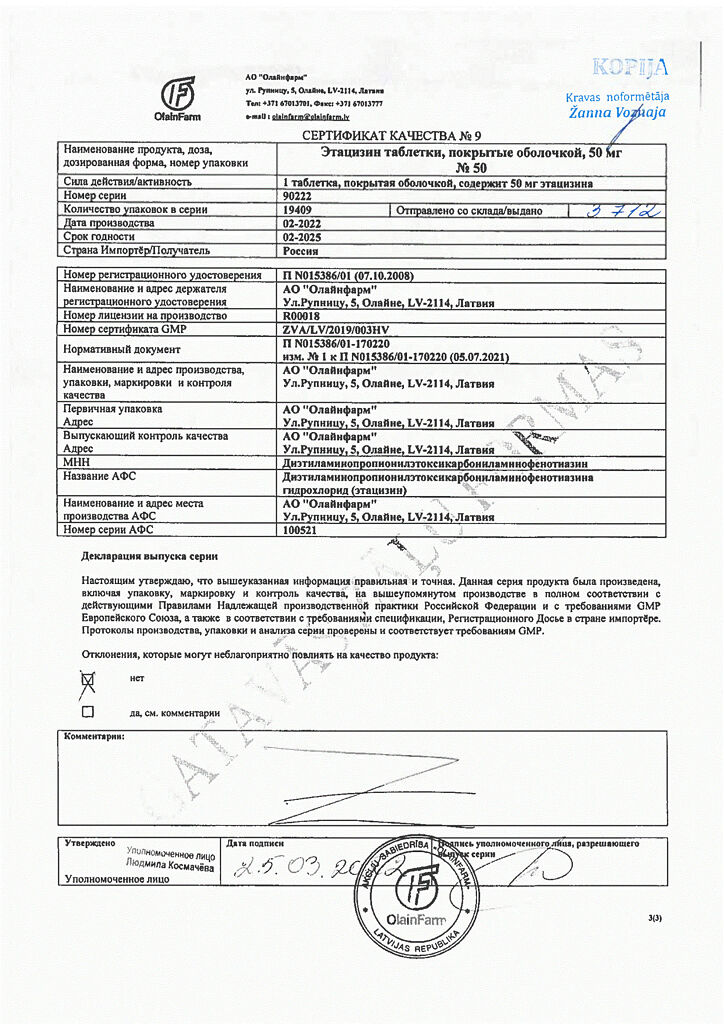
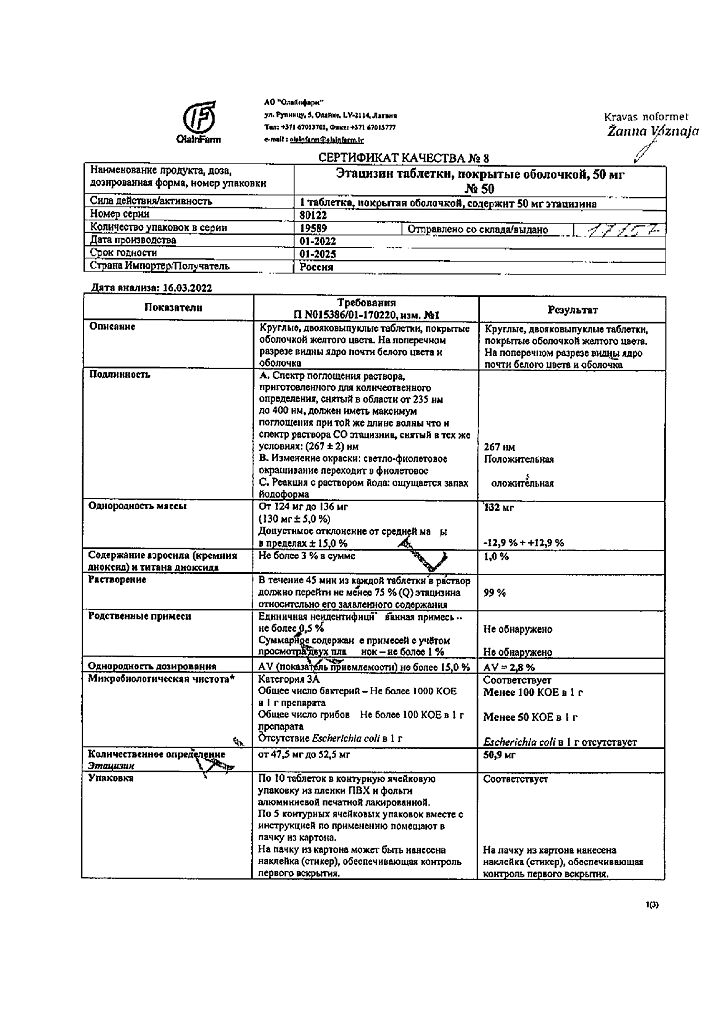
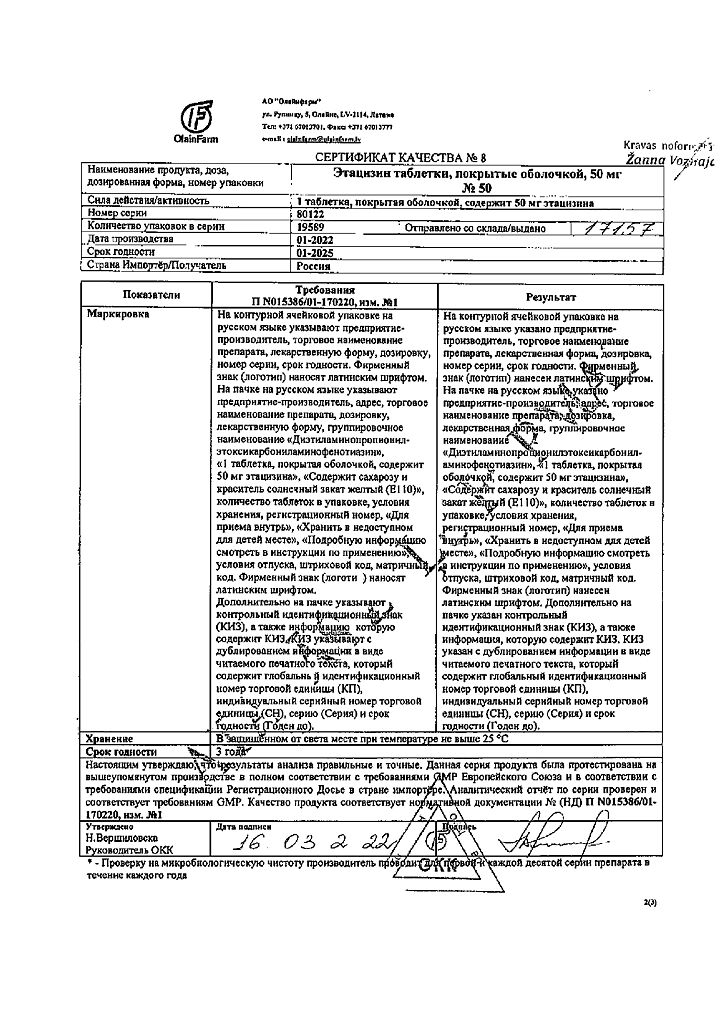
Etacizin, 50 mg 50 pcs.
€94.39 €88.65
Description
Tetracyzine is a class IC antiarrhythmic agent with long-lasting antiarrhythmic action. It inhibits the rate of rise of the action potential front (Vmax), does not change the resting potential. Depending on the dose, it may decrease the duration of action potential. Does not significantly change the effective refractory periods of the ventricles and atria. Inhibits the fast incoming sodium current and, to a lesser extent, the slow incoming calcium current.
Tetracyzine slows the conduction of excitation through the myocardial conduction system. ECG shows prolongation of PR interval and QRS complex; ST interval, reflecting ventricular repolarization, is unchanged or tends to be shortened.
Tetracyzine increases myocardial fibrillation threshold. Unlike many antiarrhythmic agents, Etacizin does not cause a significant decrease in heart rate or prolongation of QT interval duration on ECG.
The antiarrhythmic effect usually develops on day 1 or 2 when taken orally; the duration of treatment depends on the form of arrhythmia and the effectiveness and tolerability of the drug.
Pharmacokinetics
In oral administration, it is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and determined in the blood after 30-60 minutes. Cmax in blood plasma is reached after 2.5-3 hours. Bioavailability is 40%. 90% is bound to plasma proteins. T1/2 is 2.5 hours.
Parameters of pharmacokinetics of Etacizin are subject to significant individual fluctuations and require individual study in individual patients to determine the optimal blood plasma concentration of the drug. The drug is intensively metabolized during “first passage” through the liver. Some of the resulting metabolites have antiarrhythmic activity. Etacizine is excreted from the body by the kidneys as metabolites. Etacizine penetrates the placental barrier. It is excreted with breast milk.
Indications
Indications
Prevention and treatment of heart rhythm disturbances: supraventricular and ventricular extrasystole, paroxysms of atrial fibrillation and flutter, ventricular and supraventricular tachycardia, including Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) in adult patients without organic heart disease.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Ethacizine is a class IC antiarrhythmic agent (membrane stabilizers). Ethacizine inhibits the rapid influx of sodium through sodium channels of the cell membrane, affecting sodium channels on both the outer and inner surfaces of the cell membrane. These additional binding sites provide longer-lasting activity for etacizine. To a lesser extent, etacizin inhibits the slow influx of calcium. The negative inotropic effect of etacizine is associated with blockade of slow calcium flux.
Ethacizine slows down the conduction of excitation along atrial fibers, ventricular fibers, Purkinje fibers, as well as the AV node and additional conduction pathways, for example, the Kent bundle.
The ECG shows prolongation of the PQ, PR intervals and the QRS complex; the ST interval, reflecting ventricular repolarization, does not change or tends to shorten. Ethacizine inhibits the rate of rise of the action potential front (Vmax) and does not change the resting potential.
Ethacizine does not significantly reduce heart rate or prolong the QT interval on the ECG. Does not significantly affect blood pressure.
Ethacizine has anticholinergic properties and is therefore effective in the treatment of arrhythmias associated with activation of the vagus nerve.
Etatsizin has local anesthetic and moderate anti-ischemic activity.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Diethylaminopropionylethoxycarbonylaminophenothiazine
Composition
Composition
active ingredient: etacizine (diethylaminopropionylethoxycarbonylaminophenothiazine hydrochloride) 50.00 mg;
excipients: potato starch 9.57 mg, sucrose 19.30 mg, methylcellulose 0.33 mg, calcium stearate 0.80 mg;
shell composition: sucrose 37.695 mg, povidone K-25 0.753 mg, quinoline yellow dye (E104) 0.025 mg, sunset yellow dye (E110) 0.003 mg, calcium carbonate 6.308 mg, magnesium hydroxycarbonate 3.678 mg, titanium dioxide (E171) 0.665 mg, silicon dioxide 0.827 mg, carnauba wax 0.046 mg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to etacizin or to any of the excipients in the drug.
– Conduction disorders (including sinoatrial block, atrioventricular (AV) block II and III degrees in the absence of a pacemaker), intraventricular conduction disturbances (complete block of the bundle branches).
– Severe hypertrophy of the left ventricular myocardium.
– Acute coronary syndrome (acute myocardial infarction, unstable angina).
– Post-infarction cardiosclerosis.
– Marked expansion of the cardiac cavities.
– Cardiogenic shock.
– Severe arterial hypotension (blood pressure below 90/60 mmHg with the appearance of clinical symptoms such as tachycardia, dizziness, confusion, restlessness, cold, clammy, pale or cyanotic skin, syncope).
– Chronic heart failure of III-IV functional class according to the NYHA classification.
– Decrease in left ventricular ejection fraction.
– Severe dysfunction of the liver (Child-Pugh class C (10-15 points)) and/or kidneys (glomerular filtration rate (GFR) < 30 ml/min/1.73 m2).
– Pregnancy, breastfeeding period.
– Children under 18 years of age.
– Concomitant use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
– When used simultaneously with antiarrhythmic drugs IC (moracizine, propafenone, lappaconitine hydrobromide) and class IA (quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide, ajmaline).
– Organic heart lesions.
– Brugada syndrome
Side Effects
Side Effects
Side effects are indicated according to the MedDRA organ system groups and frequency of occurrence: very often (≥ 1/10); often (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1000 to < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1000); very rare (<1/10,000); unknown (cannot be determined from available data).Nervous system disorders
Often: dizziness, disturbance of accommodation (at the beginning of treatment), disturbance of balance.
Rarely: headache.
Unknown: staggering when walking or turning the head, drowsiness, in some cases diplopia was noted.
Cardiac disorders
Rarely: atrioventricular block, impaired intraventricular conduction, decreased myocardial contractility.
Unknown: sinus node arrest, decreased coronary blood flow, arrhythmia, arrhythmogenic effect.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Rarely: nausea, pain in the upper abdomen.
Laboratory and instrumental data
Unknown: prolongation of the PQ interval, flattening of the P wave on the ECG and prolongation of the QRS complex.
Interaction
Interaction
Contraindicated for use with class IC (moracizine, lappaconitine hydrobromide, propafenone) and class IA antiarrhythmic drugs (quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide, ajmaline).
Ethacizine should not be prescribed concomitantly with MAO inhibitors.
The combination of beta-blockers with Etatsizin can enhance the antiarrhythmic effect, especially in relation to arrhythmias provoked by exercise or stress. This combined use allows you to reduce the dose of etacizine, which reduces the risk of side effects. This combination is desirable for the treatment and prevention of paroxysmal tachycardia.
The combined use of Etatsizin with digoxin increases the antiarrhythmic effect of the drugs and improves myocardial contractility. As a result of this combined use, nausea and loss of appetite are possible, which is caused by an increase in the concentration of digoxin in the blood. In this case, reduce the dose of digoxin.
Ethacizine can be taken together with amiodarone (class III), which allows you to reduce the doses of both drugs.
There is no data on the interaction of etacizin with drugs that cause polymorphic ventricular tachycardia of the “pirouette” type and/or increase the duration of the QT interval on the ECG. Ethacizine does not have a significant effect on the QT interval, but caution should be exercised when coadministering these drugs.
Overdose
Overdose
Etatsizin has a small therapeutic breadth, so severe intoxication can easily occur (especially with simultaneous use of other antiarrhythmic drugs).
Symptoms: prolongation of PR intervals and expansion of the QRS complex, increased amplitude of T waves, bradycardia, sinoatrial and AV block, asystole, paroxysms of polymorphic and monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, decreased myocardial contractility, persistent decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, blurred vision, headache, gastrointestinal disorders.
An overdose of etacizine can impair the patient’s vital functions and cause death, so overdose should be treated in the intensive care unit.
Treatment: symptomatic; for the treatment of ventricular tachycardia, do not use antiarrhythmic drugs of classes IA and IC; sodium bicarbonate can eliminate widening of the QRS complex, bradycardia and arterial hypotension. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Olainfarm, Latvia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Olinefarm, Latvia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Olinefarm |
Related products
Buy Etacizin, 50 mg 50 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.