No products in the cart.
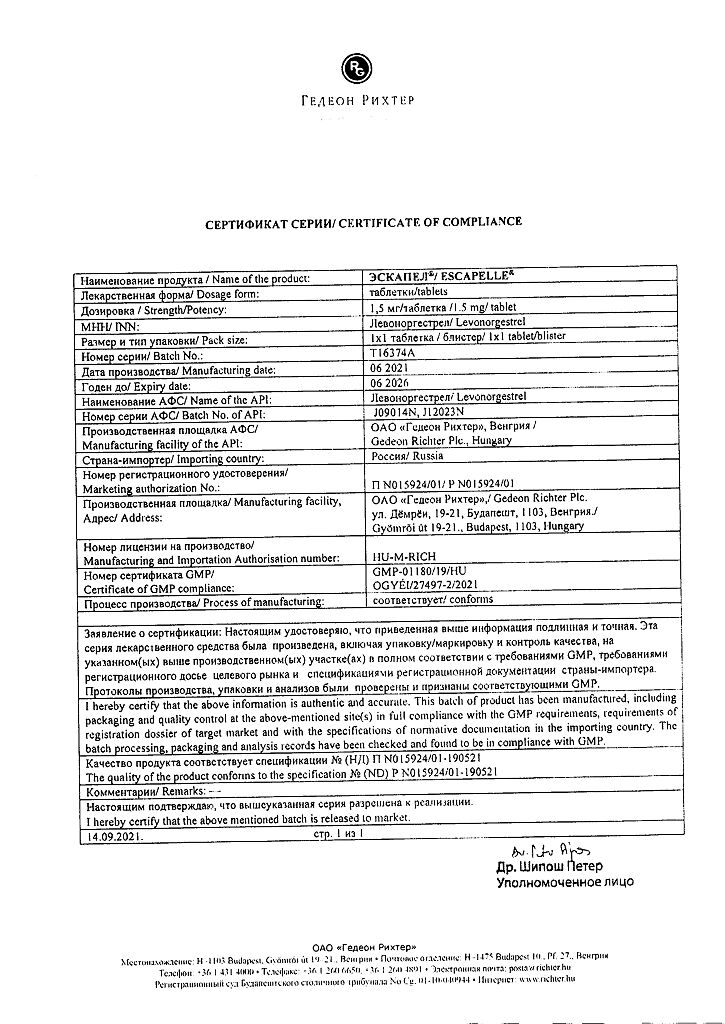
Escapel, 1.5 mg tablets
€23.00 €20.61
EAN: 5997001360484
SKU: 207825
Categories: Contraceptive, Gynecology and Obstetrics, Hormonal, Medicine
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group:Emergency contraceptive.
ATX code: G03AD01
Pharmacodynamics
Levonorgestrel is a synthetic gestagen with contraceptive action, pronounced gestagenic and anti-estrogenic properties. The main mechanism of action is inhibition and/or delay of ovulation as a result of suppression of peak luteinizing hormone. Under the recommended dosing regimen, levonorgestrel suppresses ovulation and fertilization if sexual intercourse occurred in the pre-ovulatory phase, when
the possibility of fertilization is greatest. Levonorgestrel is not effective if implantation of a fertilized egg has already occurred.
Effectiveness: According to a previous clinical study, two doses of levonorgestrel 0.75 mg at 12-hour intervals prevented pregnancy in 85% of cases. Its efficacy decreases with time following intercourse (95% if used within 24 hours, 85% between 24 and 48 hours, and 58% between 48 and 72 hours).
The results of another clinical study showed that a single levonorgestrel dose of 1.5 mg (within 72 hours of unprotected intercourse) prevents pregnancy in 84% of cases.
There is limited data, requiring further confirmation, on the effect of excess body weight/high body mass index (BMI) on contraceptive efficacy. Two clinical trials (CIs) found decreased efficacy of levonorgestrel and increased pregnancy rates in women with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 compared with women with normal BMI (5.19% and 0.96%, respectively). However, no decrease in the contraceptive efficacy of levonorgestrel was confirmed in other studies (pregnancy rates were 1.17% in obese women and
0.99% in women with normal BMI).
With the recommended dosing regimen, levonorgestrel has no significant effect on clotting factors, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
Adolescent girls under 18 years
In a prospective observational study, it was shown that of 305 cases of levonorgestrel as an emergency contraceptive, seven resulted in pregnancy. Thus, the overall failure rate was 2.3%.
The failure rate in adolescent girls younger than 18 years (2.6% or 4/153) was comparable to the failure rate in women 18 years and older (2.0% or 3/152).
Pharmacokinetics
Assimilation
Levonorgestrel is rapidly and almost completely absorbed when taken orally. After taking levonorgestrel at a dose of 1.5 mg, the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) is 18.5 ng/ml and is reached after 2 hours. After reaching the maximum values, the concentration of levonorgestrel decreases. Absolute bioavailability is 100%.
Distribution
Levonorgestrel binds to plasma albumin and sex hormone-binding globulin (hGBS). Only 1.5% of the total dose is in free form, 65% is bound to HSPH. Passes into breast milk.
Metabolism
Metabolism of levonorgestrel corresponds to that of sex hormones. Levonorgestrel is hydrolysed in the liver and the metabolites are excreted as conjugated glucuronides. Pharmacologically active metabolites of levonorgestrel are unknown.
Elimation
Excreted exclusively as metabolites, approximately equally by the kidneys and through the intestine. The elimination half-life (T1/2) is about 26 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in special groups of patients
Children and adolescents under 18 years:The pharmacokinetics of levonorgestrel have been studied exclusively in adult women; there are limited data on the use of levonorgestrel in adolescent girls under 16 years of age.
Patients with renal and hepatic impairment: Pharmacokinetics of levonorgestrel in patients with hepatic or renal impairment have not been studied.
Patients with obesity
. A pharmacokinetics study showed that levonorgestrel concentrations were significantly reduced in obese women (BMI ≥30 kg/m²) (approximately 50% reduction in Cmax and AUC0-24 was observed) compared with those in women with normal BMI (< 25 kg/m²).
Another study also reported a reduction in levonorgestrel Cmax of approximately 50% in obese women compared with that in women with normal BMI, while doubling the levonorgestrel dose to 3 mg in obese women provided plasma concentrations similar to those observed in women with normal BMI who received 1.5 mg of levonorgestrel. The clinical significance of these
data is unclear.
Indications
Indications
Emergency (postcoital) contraception (after unprotected sexual intercourse or if the contraceptive method used is unreliable).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: emergency contraception.
ATX code: G03AD01
Pharmacodynamics
Levonorgestrel is a synthetic gestagen with a contraceptive effect, pronounced gestagenic and antiestrogenic properties. The main mechanism of action is inhibition and/or delay of ovulation as a result of suppression of the peak of luteinizing hormone. With the recommended dosage regimen, levonorgestrel suppresses ovulation and fertilization if sexual intercourse occurs in the preovulatory phase, when
the possibility of fertilization is greatest. Levonorgestrel is not effective if implantation of a fertilized egg has already occurred.
Efficacy: According to the results of an earlier clinical study, taking two doses of levonorgestrel 0.75 mg every 12 hours prevented pregnancy in 85% of cases. The effectiveness of the drug decreases over time after sexual intercourse (95% when used within 24 hours, 85% when used within 24 to 48 hours, 58% when used within 48 to 72 hours).
Another clinical trial showed that a single dose of levonorgestrel 1.5 mg (within 72 hours after unprotected intercourse) prevented pregnancy in 84% of cases.
There are limited data that require further confirmation on the impact of excess body weight/high body mass index (BMI) on contraceptive effectiveness. In 2 clinical studies (CTs), a decrease in the effectiveness of levonorgestrel and an increase in the incidence of pregnancy in women with a BMI ≥30 kg/m2 was found compared with women with a normal BMI (5.19% and 0.96%, respectively). However, in other clinical trials, a decrease in the contraceptive effectiveness of levonorgestrel was not confirmed (pregnancy rate was 1.17% in obese women and
0.99% in women with normal BMI).
With the recommended dosage regimen, levonorgestrel does not have a significant effect on blood clotting factors, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
Teenage girls under 18
A prospective observational study showed that of 305 cases of levonorgestrel use as emergency contraception, pregnancy occurred in seven cases. Thus, the overall failure rate was 2.3%.
The failure rate for adolescent girls under 18 years of age (2.6% or 4/153) was comparable to the failure rate for women 18 years of age and older (2.0% or 3/152).
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
When taken orally, levonorgestrel is rapidly and almost completely absorbed. After taking levonorgestrel at a dose of 1.5 mg, the maximum concentration (Cmax) in blood plasma is 18.5 ng/ml and is achieved after 2 hours. After reaching maximum values, the concentration of levonorgestrel decreases. Absolute bioavailability is 100%.
Distribution
Levonorgestrel binds to plasma albumin and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). Only 1.5% of the total dose is in free form, 65% is associated with SHBG. Passes into breast milk.
Metabolism
The metabolism of levonorgestrel corresponds to the metabolism of sex hormones. Levonorgestrel is hydroxylated in the liver and metabolites are excreted in the form of conjugated glucuronides. Pharmacologically active metabolites of levonorgestrel are unknown.
Removal
It is excreted exclusively in the form of metabolites, approximately equally by the kidneys and through the intestines. The half-life (T1/2) is approximately 26 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in special groups of patients
Children and adolescents under 18 years of age: The pharmacokinetics of levonorgestrel have been studied exclusively in adult women; Data on the use of levonorgestrel in adolescent girls under 16 years of age are limited.
Patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency: The pharmacokinetics of levonorgestrel in patients with hepatic or renal insufficiency have not been studied.
Obese patients
A pharmacokinetic study showed that levonorgestrel concentrations were significantly reduced in obese women (BMI ≥30 kg/m²) (approximately 50% reduction in Cmax and AUC0-24 was observed) compared with those in women with normal BMI (< 25 kg/m²).
Another study also reported a reduction in levonorgestrel Cmax of approximately 50% in obese women compared with that in women with normal BMI, while doubling the levonorgestrel dose to 3 mg in obese women produced plasma concentrations similar to those observed in women with normal BMI who received 1.5 mg levonorgestrel. Clinical significance of these
data is unclear.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Emergency contraception is a method that can be used occasionally. It should not replace methods of planned contraception.
Emergency contraception does not prevent pregnancy in all cases.
If there is doubt about the timing of unprotected intercourse, or if unprotected intercourse occurred more than 72 hours during the same menstrual cycle, then there is a possibility that conception has already occurred. In this regard, the use of Escapelle® during the second sexual intercourse may not be effective in preventing pregnancy. If your menstrual period is delayed
bleeding for more than 5–7 days and a change in its nature (scanty or heavy bleeding), pregnancy must be excluded.
If pregnancy occurs after using the drug Escapel®, the possibility of developing ectopic pregnancy must be taken into account. The appearance of pain in the lower abdomen and fainting may indicate an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy. The absolute risk of ectopic pregnancy appears to be low because levonorgestrel prevents ovulation and fertilization. Ectopic pregnancy can develop despite the appearance of uterine bleeding. Therefore, the use of Escapelle® is not recommended in women at risk of developing
ectopic pregnancy (history of salpingitis or ectopic pregnancy).
The use of Escapel® is not recommended in patients with severe liver dysfunction.
Severe malabsorption syndromes, such as Crohn’s disease, may reduce the effectiveness of levonorgestrel.
After taking Escapelle®, the menstrual cycle, as a rule, does not change and menstrual bleeding occurs on time. Sometimes menstrual bleeding may start a few days earlier or later. Women should be advised to visit their doctor to select and begin using a method of routine contraception. If the drug Escapel® was taken against the background of regular hormonal contraception, but
the expected “withdrawal” bleeding does not occur in the next 7-day “pill-free” period, pregnancy should be excluded.
Repeated use of the drug during one menstrual cycle is not recommended due to the possibility of cycle disruption.
There is limited evidence that requires further confirmation that the contraceptive effectiveness of Escapelle may decrease with increasing body weight or BMI. All women, regardless of their weight and BMI, should take emergency contraception as soon as possible after unprotected sex.
Escapelle® is not effective as a permanent method of contraception and should only be used as an emergency measure. Levonorgestrel 1.5 mg should be used exclusively for emergency contraception!
Women seeking repeated courses of emergency contraception should be advised to use routine contraceptive methods.
The use of the drug in teenage girls under 16 years of age is possible only in exceptional cases (including rape) and only after consultation with a gynecologist. After emergency contraception, consultation with a gynecologist is recommended.
Fertility
Levonorgestrel increases the risk of developing menstrual irregularities, which in some cases can lead to earlier or later ovulation. These changes may affect fertility, but there are no data on the effects of levonorgestrel on fertility with long-term use.
The use of emergency contraception does not replace necessary precautions related to protection against sexually transmitted diseases.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
The effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery has not been studied.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Levonorgestrel
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
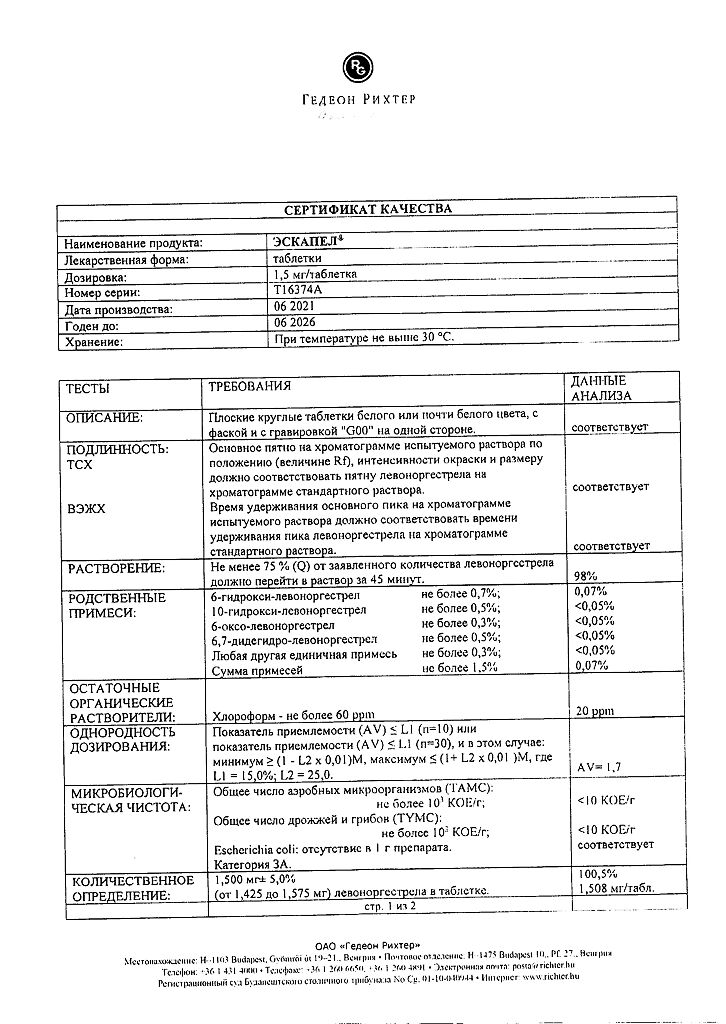
Active ingredient: levonorgestrel 1.5 mg.
Excipients: colloidal silicon dioxide; potato starch; magnesium stearate; talc; corn starch; lactose monohydrate.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Taking the drug during a known or suspected pregnancy is contraindicated. Based on the available data, no adverse effects on the fetus have been identified in the event of continued pregnancy while using levonorgestrel-containing drugs for emergency contraception.
Breastfeeding period
Levonorgestrel passes into breast milk. The potential exposure of the baby to levonorgestrel can be reduced if the woman takes the drug immediately after feeding. After taking the drug, breastfeeding should be stopped for at least 8 hours.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to levonorgestrel and/or to any of the excipients in the drug.
– Age up to 16 years (due to limited data on the safety and effectiveness of levonorgestrel in this age group).
– Severe liver failure.
– Known or suspected pregnancy.
– Breastfeeding for at least 8 hours after taking the drug.
– Lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
With caution
Diseases of the liver (mild to moderate severity) or biliary tract; jaundice (including history); severe malabsorption syndromes, such as Crohn’s disease; the presence of a hereditary or acquired predisposition to thrombosis.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The most common adverse reaction (ADR) with levonorgestrel was nausea.
ADRs are presented according to systemic organ classes in accordance with the MedDRA classification and with the frequency of occurrence: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100, <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100), rare (≥1/10000, <1/1000), very rare (<1/10000), including individual reports. Within each group, HPs are distributed in decreasing order of their importance.
Nervous system disorders
Very common: headache.
Common: dizziness.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Very common: nausea, pain in the lower abdomen.
Common: diarrhea, vomiting.
Disorders of the genital organs and breast
Very common: bleeding not associated with menstruation.
Common: delay of menstruation by more than 7 days, irregular menstrual bleeding, engorgement of the mammary glands.
General and administration site disorders
Very common: increased fatigue.
The nature of menstrual bleeding may vary slightly, but for most women, the next menstruation begins within 5 days of the expected due date.
If the onset of the next menstruation is delayed by more than 5 days, pregnancy should be excluded.
The following adverse events were observed in clinical practice during the post-registration period:
Gastrointestinal disorders
Very rare: abdominal pain.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Very rare: skin rash, urticaria, itching.
Disorders of the genital organs and breast
Very rare: pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea.
General and administration site disorders
Very rare: swelling of the face.
Interaction
Interaction
When used simultaneously with drugs that induce microsomal liver enzymes (mainly inducers of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme), the metabolism of levonorgestrel is accelerated.
Concomitant use of efavirenz reduces plasma concentrations of levonorgestrel by approximately 50%.
The following liver enzyme inducing drugs may reduce the effectiveness of levonorgestrel: barbiturates (including primidone), phenytoin and carbamazepine, drugs containing St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum), and rifampicin, ritonavir, rifabutin and griseofulvin.
Drugs containing levonorgestrel may increase the risk of cyclosporine toxicity due to inhibition of its metabolism.
Levonorgestrel may reduce the effectiveness of ulipristal acetate by competitively acting on the progesterone receptor, and therefore their simultaneous use is not recommended.
Overdose
Overdose
No serious adverse reactions have been reported following acute overdose of large doses of oral contraceptives.
Symptoms: nausea and withdrawal bleeding.
Treatment: symptomatic. There is no specific antidote.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years.
Do not use after the expiration date indicated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter, Hungary
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 30 ° C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Gedeon Richter, Hungary |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Gedeon Richter |
Related products
Gynecology and Obstetrics
Gynecology and Obstetrics
Buy Escapel, 1.5 mg tablets with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.