No products in the cart.
Eralfon 10000 IU 0.25 ml syringe without needle protection device. 10000 me 0,25 ml 6 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Recombinant human erythropoietin, a purified glycoprotein. It stimulates erythropoiesis. It is synthesized in mammalian cells, in which the gene encoding human erythropoietin is integrated. Biologically and immunologically it is identical to human erythropoietin excreted from urine. Endogenous erythropoietin is synthesized in kidneys and depends on the level of blood oxygenation.
Pharmacokinetics
After p/k injection the concentration of active substance in plasma increases slowly, reaching a maximum level after 12-18 hours.
After repeated intravenous administration T1/2 in healthy adults is 4 hours, in patients with renal insufficiency – about 6 hours; in children – about 6 hours.
Indications
Indications
The treatment of anemia associated with chronic renal failure in adult patients on hemo- or peritoneal dialysis or for whom dialysis is indicated; in children on hemodialysis.
The treatment of anemia in cancer patients (receiving or not receiving chemotherapy) with nonmyeloid tumors.
The prevention of anemia in cancer patients with non-myeloid tumors receiving long-term chemotherapy.
The treatment of anemia in HIV patients receiving zidovudine therapy (when endogenous erythropoietin levels ⤠500 IU/mL).
In a preoperative program before major surgery in patients with hematocrit levels of 33-39%, to facilitate the collection of autologous blood and to reduce the risks associated with the use of allogeneic hemotransfusions (when the expected need for transfused blood is higher than the amount that can be obtained without epoetin alfa).
Before major surgery with expected average blood loss (2-4 units or 900-1800 mL) in adult patients with mild to moderate anemia (hemoglobin >10 and ⤠13 g/dL) to reduce the need for allogeneic hemotransfusions and improve erythropoiesis recovery.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
The solution for intravenous and percutaneous administration is clear, colorless.
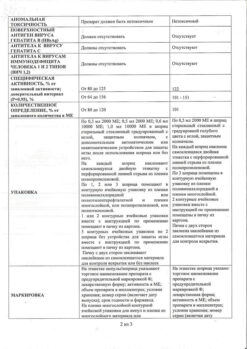
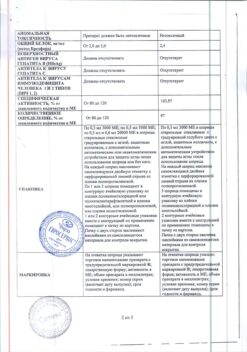
Auxiliary substances: sodium chloride – 3.
Solvent: sodium chloride – 3.504 mg, sodium citrate pentasquihydrate – 3.48 mg or sodium citrate dihydrate – 2.8656 mg, albumin solution (in terms of dry albumin) – 1.5 mg, citric acid monohydrate – 0.0342 mg, water d / i – to 0.6 ml.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Interaction
Interaction
The action of epoetin alfa may be enhanced with concomitant administration of blood products.
In concomitant use of epoetin alfa with cyclosporine, plasma concentrations of the latter may decrease due to increased binding to red blood cells (when using this combination it is necessary to monitor the concentration of cyclosporine in plasma and increase its dose, if necessary).
Epoetin alfa should not be mixed with solutions of other drugs.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
With caution, use in patients with a history of seizure reactions; patients at increased risk of thrombosis or other vascular complications require close medical monitoring.
With caution, use with gout.
Be sure that patients with arterial hypertension have received effective antihypertensive therapy before initiating use.
At the time of use, BP should be monitored, paying attention to the occurrence or worsening of unusual headaches. In this case, correction of the current therapy or prescription of antihypertensive agents may be required. If BP does not decrease despite adequate therapy, epoetin alfa should be discontinued.
Before starting epoetin alfa, the state of iron depot in the body should be evaluated. In most patients with chronic renal failure, cancer and HIV-infected patients plasma ferritin levels decrease simultaneously with an increase in hematocrit. Ferritin levels should be determined throughout the course of treatment. If it is less than 100 ng/ml, replacement therapy with iron preparations is recommended. Patients who donate autologous blood and are in the pre- or postoperative period should also receive an additional adequate amount of iron.
Hemoglobin levels should be monitored at least once a week during administration until stable levels are achieved, then somewhat less frequently. In the pre- and postoperative period, hemoglobin levels should be checked more frequently if baseline levels were less than 14 g/dL. Hematocrit levels should also be monitored regularly. During the first 8 weeks of therapy, platelet counts should be monitored regularly, since epoetin alfa may cause a moderate dose-dependent increase in platelet counts, which self-adjust to normal during the course of therapy; thrombocytosis rarely develops.
It should be considered that preoperative elevation of hemoglobin levels may be a predisposing factor for the development of thrombotic complications. Patients should receive adequate prophylactic antithrombotic therapy prior to elective surgery.
The use of epoetin alfa at baseline hemoglobin levels greater than 15 g/dL is not recommended in the pre- and postoperative period.
With caution, use in patients with porphyria. In chronic renal insufficiency during therapy with epoetin alfa worsening of porphyria is possible.
The correction of anemia may be accompanied with the improvement of appetite and increase of potassium and protein absorption. It should be borne in mind that periodic correction of dialysis parameters may be necessary to maintain urea, creatinine and potassium levels within normal limits. In patients with chronic renal insufficiency, serum electrolyte levels should be monitored.
Patients on hemodialysis during therapy with epoetin alfa often require an increased dose of heparin during dialysis due to increased hematocrit. In case of inadequate dose of heparin, dialysis system occlusion is possible.
In patients with chronic renal failure and clinically significant CHD or congestive heart failure, maintenance hemoglobin levels should not exceed the upper limit of the optimal recommended level (no more than 10-12 g/dL in adults).
When used in patients with liver dysfunction there may be delayed biotransformation of epoetin alfa and marked enhancement of erythropoiesis. Safety of epoetin alfa use in this category of patients has not been established.
Possible effect of epoetin alfa on growth of some types of tumors, especially bone marrow malignancies, cannot be completely excluded.
All special warnings and precautions associated with the autologous blood collection program must be followed (this applies to all patients receiving epoetin alfa).
Therapeutic efficacy of epoetin alfa may decrease with deficiency of iron, folic acid, vitamin B12, aluminum intoxication, intercurrent illness, hidden bleeding, hemolysis, bone marrow fibrosis.
In experimental animal studies of chronic toxicity of epoetin alfa, subclinical bone marrow tissue fibrosis and anemia with or without signs of bone marrow hypoplasia were observed in several cases. It is believed that this is associated with the appearance of antibodies to epoetin alpha.
No mutagenic effects have been identified.
Impact on ability to drive and operate machinery
When using epoetin alfa until the optimal maintenance dose is established, patients with CKD should avoid potentially hazardous activities because of the increased risk of arterial hypertension at the beginning of therapy.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Uncontrolled arterial hypertension, hypersensitivity to epoetin alfa.
Pending major non-prednisional surgery with autologous blood is contraindicated if there is severe vascular disease (including coronary, carotid, cerebral, peripheral) and recent myocardial infarction or acute cerebral arrhythmias.
Side effects
Side effects
Flu-like syndrome: dizziness, drowsiness, fever, headache, joint and muscle pain are possible (mainly at the beginning of treatment).
Cardiovascular system disorders: dose-dependent increase of BP; worsening of arterial hypertension course is possible (most frequently in patients with chronic renal insufficiency); in single cases – hypertensive crises, malignant arterial hypertension with encephalopathy symptoms (headache, mental confusion) and generalized tonic-clonic convulsions.
Hematopoietic system disorders: rare – thrombocytosis.
coagulation system disorders: in single cases – thrombosis of shunt (in patients on hemodialysis with a tendency to hypotension or in the presence of stenoses, aneurysms).
Ureinary system disorders: hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, increased concentration of urea, creatinine, uric acid in plasma (in patients with chronic renal failure) are possible.
Allergic reactions: in some cases – mild to moderately expressed skin rash, eczema, urticaria, pruritus, angioedema.
Local reactions: redness, burning sensation, mild to moderate pain at the site of injection may occur (more often if administered by injection).
Others: rare – potentially serious complications related to respiratory distress or a decrease in BP; immune reactions (has minimal ability to induce antibody formation).
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Manufacturer | PharmFirm Sotex, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | PharmFirm Sotex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Eralfon 10000 IU 0.25 ml syringe without needle protection device. 10000 me 0,25 ml 6 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.