No products in the cart.
Enalapril Hexal, tablets 10 mg 20 pcs
€2.84 €2.58
Description
An angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor.
ATC code: C09AA02
Pharmacological action
Pharmacodynamics
ACE inhibitor. Enalapril, a metabolite of enalapril, has pharmacological activity. It suppresses the formation of angiotensin II and eliminates its vasoconstrictor effect. It decreases total peripheral vascular resistance, systolic and diastolic blood pressure (BP), post- and preload on myocardium.
Dilates the arteries to a greater extent than the veins, and there is no reflex increase in heart rate.
It also reduces preload, decreases right atrial pressure in the small circulatory circle, reduces left ventricular hypertrophy. Reduces the tone of the renal tubular arterioles, thus reducing intra-column hemodynamics and prevents diabetic nephropathy. It does not affect the metabolism of glucose, lipoproteins and sexual function.
The maximum effect develops in 6-8 hours and lasts for 24 hours. Therapeutic effect is achieved after several weeks of treatment.
Indications
Indications
Arterial hypertension;
Chronic heart failure (as part of combination therapy)
Left ventricular dysfunction
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor.
ATX code: C09AA02
Pharmacological action
Pharmacodynamics
ACE inhibitor. Enalapril’s metabolite, enalaprilat, has pharmacological activity. Suppresses the formation of angiotensin II and eliminates its vasoconstrictor effect. At the same time, total peripheral vascular resistance, systolic and diastolic blood pressure (BP), post- and preload on the myocardium decrease.
It dilates arteries to a greater extent than veins, while there is no reflex increase in heart rate.
It also reduces preload, reduces pressure in the right atrium in the pulmonary circulation, and reduces left ventricular hypertrophy. Reduces the tone of the efferent arterioles of the glomeruli of the kidneys, thereby reducing intraglomerular hemodynamics and preventing diabetic nephropathy. Does not affect the metabolism of glucose, lipoproteins or sexual function.
The maximum effect develops after 6-8 hours and lasts for 24 hours. The therapeutic effect is achieved after several weeks of treatment.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Caution must be exercised when prescribing Enalapril Hexal to patients with reduced circulating blood volume (as a result of diuretic therapy, limiting salt intake, hemodialysis, diarrhea and vomiting) – there is an increased risk of a sudden and pronounced decrease in blood pressure after using even the initial dose of an ACE inhibitor. Transient arterial hypotension is not a contraindication for continuing treatment with the drug after stabilization of blood pressure. If blood pressure decreases again, the dose should be reduced or the drug discontinued.
Enalapril should not be used in patients undergoing dialysis using AN 69 polyacrylonitrone membranes due to the likelihood of developing anaphylactic reactions.
Kidney function should be checked before starting the drug. Patients with impaired renal function should reduce the single dose or increase the intervals between doses of the drug.
Before and during treatment, blood pressure levels should be monitored and laboratory parameters analyzed, especially in cases of salt and/or fluid loss, impaired renal function, severe or renal hypertension, heart failure and over the age of 65 years.
In the case of previous treatment with diuretics, in particular in patients with chronic heart failure, the risk of developing orthostatic hypotension increases, therefore, before starting treatment with enalapril, it is necessary to compensate for the loss of fluids and salts.
In some patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or solitary kidney stenosis, increases in blood urea and serum creatinine were observed. The changes were reversible and the indicators returned to normal after cessation of treatment.
For newborns and infants who have been exposed in utero to ACE inhibitors, it is recommended to conduct careful monitoring for timely detection of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, oliguria, hyperkalemia and neurological disorders that may be due to a decrease in renal and cerebral blood flow with a decrease in blood pressure caused by ACE inhibitors. In oliguria, it is necessary to maintain blood pressure and renal perfusion by administering appropriate fluids and vasoconstrictors.
If angioedema of the face, extremities, lips or larynx develops, you should immediately stop taking the drug and consult a doctor. A cough may appear, which stops after stopping the drug.
Sudden cessation of treatment does not lead to withdrawal syndrome (a sharp rise in blood pressure).
Before studying the functions of the parathyroid glands, the drug should be discontinued.
Before surgery (including dentistry), the surgeon/anesthesiologist must be warned about the use of ACE inhibitors.
The drug should be prescribed with caution to patients with diabetes mellitus due to the risk of developing hyperkalemia.
Instructions for road users:
As a result of treatment with enalapril, individual reactions may develop that may impair the patient’s ability to actively participate in road traffic, which should also be kept in mind when servicing cars and when working with devices that require increased attention. These phenomena intensify with increasing doses and with alcohol intake.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Enalapril
Composition
Composition
10 mg tablets:
active substance:
enalapril maleate – 10.0 mg;
excipients:
sodium bicarbonate,
lactose monohydrate,
corn starch,
talc,
magnesium stearate,
iron oxide red.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Enalapril Hexal should not be used for
hypersensitivity to the drug and to other angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors;
history of angioedema, including while taking ACE inhibitors;
stenosis (unilateral or bilateral) of the renal arteries;
liver or kidney diseases;
pregnancy, breastfeeding;
age under 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
Side Effects
Side Effects
Most side effects are temporary and do not require discontinuation of the drug.
From the cardiovascular system:
At the beginning of therapy, rarely: arterial hypotension (including orthostatic), dizziness, weakness, blurred vision, and very rarely – chest pain, angina pectoris, palpitations, thromboembolism of the branches of the pulmonary artery.
From the respiratory system:
Non-productive dry cough, interstitial pneumonitis, bronchospasm, shortness of breath, rhinorrhea, pharyngitis.
From the digestive tract:
Dry mouth, anorexia, dyspeptic disorders (nausea, diarrhea or constipation, vomiting. Abdominal pain), intestinal obstruction, pancreatitis, impaired liver function and biliary excretion, hepatitis, jaundice.
From the nervous system:
In rare cases, headache, dizziness, weakness, increased fatigue, drowsiness, and confusion may occur; extremely rarely (when taken in high doses) – depression, sleep disturbance, peripheral neuropathy and paresthesia, muscle cramps, nervousness, tinnitus and blurred vision. These disturbances are temporary and normalize after discontinuation of the drug.
From the side of kidney function:
Rarely – renal dysfunction, proteinuria, the development of hyperkalemia and hyponatremia, as well as taste changes (the phenomena are temporary and normalize after discontinuation of the drug).
From the reproductive system:
Very rarely, when used in high doses – impotence.
Allergic reactions:
Skin rash, angioedema of the face, extremities, lips, tongue, glottis and/or larynx, dysphonia, exfoliative dermatitis, exudative erythema multiforme (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis, pemphigus, pruritus, urticaria, photosensitivity, serosis, vasculitis, myositis, arthralgia, arthritis, stomatitis.
Laboratory indicators:
There may be a decrease in hemoglobin levels, hematocrit and platelet count. In very rare cases, especially in patients with impaired renal function, diffuse connective tissue diseases, or during simultaneous therapy with allopurinol, procainamide or immunosuppressants, anemia, thrombocytopenia, neuropathy, increased urea concentrations, hypercreatininemia, eosinophilia may develop; in isolated cases – increased activity of “liver” transaminases, agranulocytosis or pancytopenia.
It is necessary to regularly monitor the values of the above laboratory parameters before and during treatment, especially in patients at risk.
Interaction
Interaction
Allopurinol: decrease in the number of leukocytes in the blood, leukopenia.
Analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (for example, acetylsalicylic acid, indomethacin): the hypotensive effect of enalapril may be weakened.
Antihypertensive drugs: increased hypotensive effect of enalapril, especially when taken simultaneously with diuretics.
Anesthetics and narcotics: increased blood pressure reduction.
Potassium, potassium-sparing diuretics (especially spironolactone, amiloride, triamterene), and other agents such as heparin: increased serum potassium levels.
Table salt: weakening of the antihypertensive effect.
Lithium: increased levels of lithium in the blood serum (regular monitoring of lithium levels is necessary).
Oral antidiabetic agents, insulin: in rare cases, the hypoglycemic effect of oral hypoglycemic agents (for example, sulfonyl urea / biguanidine) and insulin may be enhanced. In such cases, a reduction in the dose of glucose-lowering drugs is required.
Novocainamide: decrease in the number of leukocytes in the blood, leukopenia.
Cytostatics, immunosuppressants, systemic corticosteroids: decrease in the number of leukocytes in the blood, leukopenia.
Alcohol: enhances the effects of alcohol.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: pronounced decrease in blood pressure, up to the development of collapse, myocardial infarction, acute cerebrovascular accident or thromboembolic complications, convulsions, stupor.
Treatment: the patient is transferred to a horizontal position with a low headboard. In mild cases, gastric lavage and ingestion of saline solution are indicated; in more severe cases, measures aimed at stabilizing blood pressure are indicated: intravenous administration of saline, plasma substitutes, if necessary, administration of angiotensin II, hemodialysis (the elimination rate of enalaprilat is on average 62 ml/min).
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
List B.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
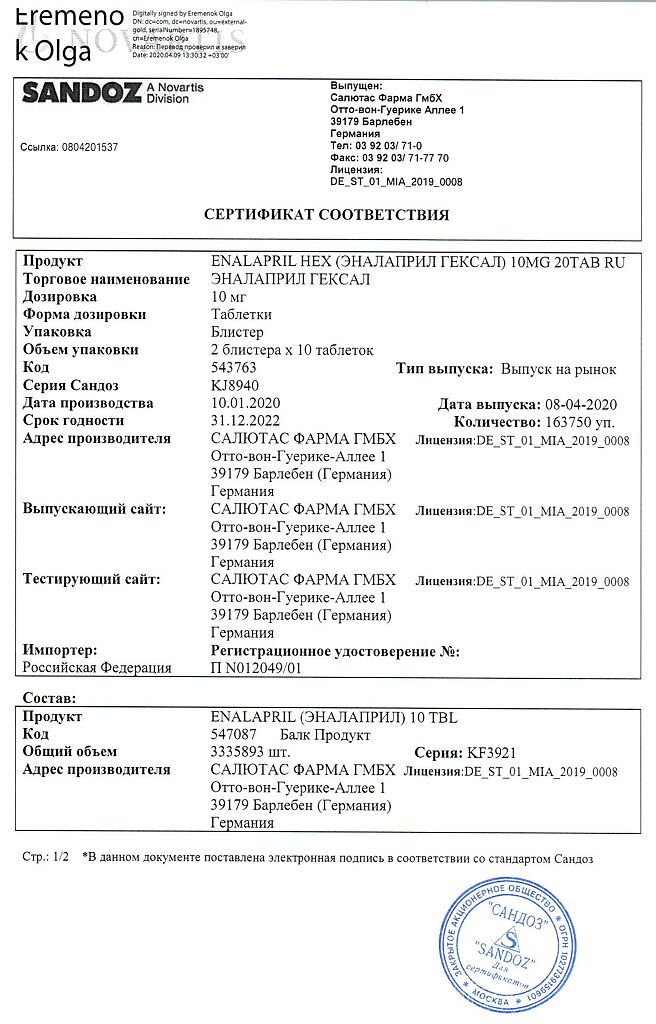
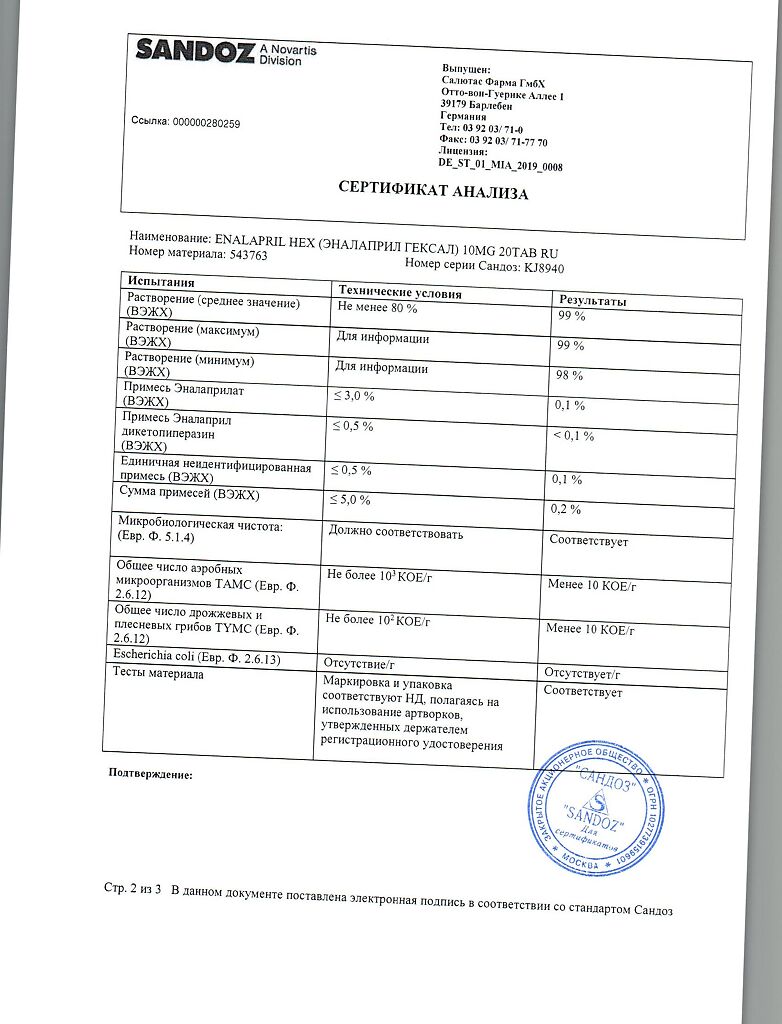
Salutas Pharma GmbH, Germany
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Salutas Pharma GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Salutas Pharma GmbH |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Enalapril Hexal, tablets 10 mg 20 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.