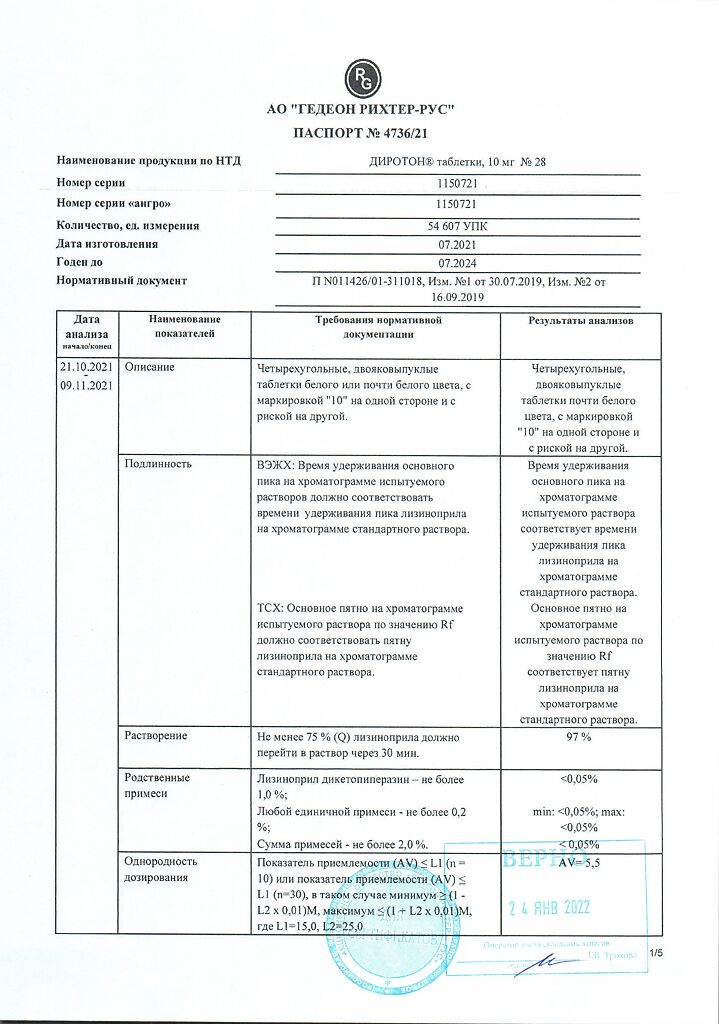
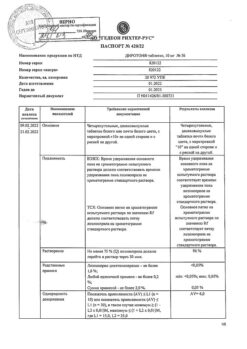
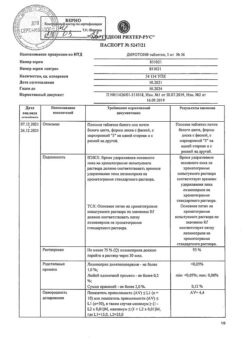
No products in the cart.
Diroton, tablets 10 mg 28 pcs
€5.85 €5.12
Description
Diroton has pronounced hypotensive (lowers blood pressure) and peripheral vasodilator properties.
Indications
Indications
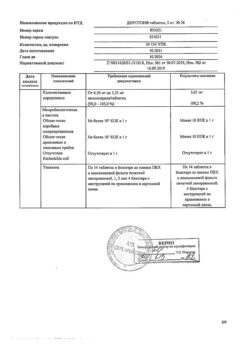
Essential and renovascular arterial hypertension (as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Diroton has pronounced hypotensive (lowers blood pressure) and peripheral vasodilator properties.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Most often, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure occurs with a decrease in fluid volume caused by diuretic therapy, reducing the salt content in food, dialysis, diarrhea or vomiting. In chronic heart failure with or without simultaneous renal failure, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure is possible. More often, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure is detected in patients with severe chronic heart failure, as a result of the use of diuretics in high doses, hyponatremia or impaired renal function. In such patients, treatment with Diroton should be started under the strict supervision of a physician (with caution in selecting the dose of the drug and diuretics).
Similar rules should be followed when prescribing Diroton to patients with coronary artery disease or cerebrovascular insufficiency, in whom a sharp decrease in blood pressure can lead to myocardial infarction or stroke.
A transient hypotensive reaction is not a contraindication for taking the next dose of the drug.
When using Diroton, some patients with chronic heart failure, but with normal or low blood pressure, may experience a decrease in blood pressure, which is usually not a reason to stop treatment.
Before starting treatment with Diroton, if possible, the sodium concentration should be normalized and/or the lost fluid volume should be replaced, and the effect of the initial dose of Diroton on the patient’s blood pressure should be carefully monitored.
In case of renal artery stenosis (especially with bilateral stenosis or in the presence of stenosis of the artery of a single kidney), as well as with circulatory failure due to lack of sodium and/or fluid, the use of Diroton can lead to impaired renal function, acute renal failure, which is usually irreversible after discontinuation of the drug.
In acute myocardial infarction, the use of standard therapy (thrombolytics, acetylsalicylic acid, beta-blockers) is indicated. It is possible to use Diroton in conjunction with intravenous administration or with the use of therapeutic transdermal nitroglycerin systems.
During extensive surgical interventions, as well as when using other drugs that cause a decrease in blood pressure, lisinopril, by blocking the formation of angiotensin II, can cause a pronounced, unpredictable decrease in blood pressure.
In elderly patients, the use of standard doses leads to higher concentrations of the drug in the blood, so special care is required when determining the dose, despite the fact that no differences in the antihypertensive effect of Diroton were identified in elderly and young patients.
Since the potential risk of agranulocytosis cannot be excluded, periodic monitoring of the blood picture is required.
When using the drug under dialysis conditions with a polyacrylonitrile membrane, anaphylactic shock may occur, so either a different type of dialysis membrane or the prescription of other antihypertensive drugs is recommended.
There is no data on the effect of lisinopril on the ability to drive vehicles and machines, however, it must be borne in mind that dizziness may occur, so caution should be exercised.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Lisinopril
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains
lisinopril 10 mg.
Excipients:
magnesium stearate,
talc,
mannitol,
corn starch,
calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of Diroton during pregnancy is contraindicated. Lisinopril penetrates the placental barrier. If pregnancy is established, the drug should be stopped as soon as possible.
Taking ACE inhibitors in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy has an adverse effect on the fetus (a marked decrease in blood pressure, renal failure, hyperkalemia, cranial hypoplasia, and intrauterine death are possible). There is no data on the negative effects of the drug on the fetus when used in the first trimester.
For newborns and infants who have been exposed in utero to ACE inhibitors, it is recommended to establish careful monitoring for the timely detection of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, oliguria, and hyperkalemia.
There is no data on the penetration of lisinopril into breast milk.
If it is necessary to prescribe the drug during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to lisinopril and other components of the drug, a history of angioedema, including that associated with the use of ACE inhibitors, idiopathic angioedema, hereditary angioedema, age under 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the cardiovascular system: possible arterial hypotension, chest pain.
Interaction
Interaction
When used concomitantly with antihypertensive agents, additive antihypertensive effects are possible.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: marked decrease in blood pressure.
Treatment: if necessary, carry out symptomatic therapy (iv fluid administration, control and normalization of blood pressure, water and electrolyte balance).
Lisinopril can be removed from the body through dialysis.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At 15–30 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter-RUS, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At 15-30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Gedeon Richter Rus, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Gedeon Richter Rus |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Diroton, tablets 10 mg 28 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.