No products in the cart.
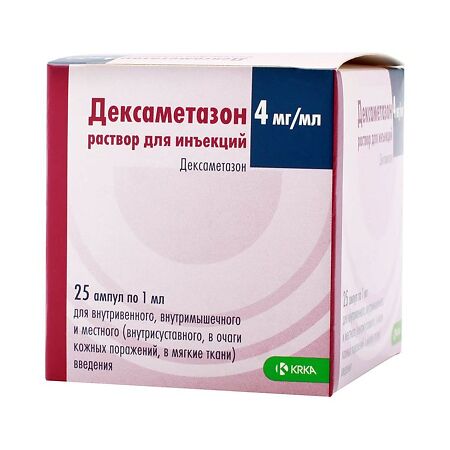
Dexamethasone, 4 mg/ml 1 ml 25 pcs
€6.84 €5.98
Description
Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticoid drug containing fluorine atom.
It has pronounced anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and desensitizing effect, has immunosuppressive activity.
It slightly retains sodium and water in the body. These effects are associated with inhibition of release of inflammatory mediators by eosinophils; induction of lipocortin formation and reduction of the number of mast cells producing hyaluronic acid; reduction of capillary permeability and stabilization of cell membranes (especially lysosomal) and organelle membranes.
The immunosuppressive effect is due to inhibition of release of cytokinins (interleukin 1, 2, gamma interferon) from lymphocytes and macrophages. The main effect on metabolism is connected with protein catabolism, increased gluconeogenesis in liver and decreased utilization of glucose by peripheral tissues.
The drug inhibits vitamin D activity, which leads to decreased calcium absorption and increased calcium excretion. Dexamethasone suppresses the synthesis and secretion of ACTH and secondary to the synthesis of endogenous glucocorticoids.
The peculiarity of action of the drug is significant inhibition of pituitary function and complete absence of mineralocorticoid activity.
Indications
Indications
Taking into account the indications and prescribed doses, they are recommended for the treatment of all those diseases that are amenable to systemic treatment with glucocorticoids (if necessary as an additional treatment to the main one), if local treatment or oral administration is impossible or ineffective:
shock of various origins (anaphylactic, post-traumatic, postoperative, cardiogenic, blood transfusion, etc.);
cerebral edema (with a brain tumor, traumatic brain injury, neurosurgical intervention, cerebral hemorrhage, encephalitis, meningitis, radiation injury);
status asthmaticus;
severe allergic reactions (Quincke’s edema, bronchospasm, dermatosis, acute anaphylactic reaction to drugs, serum transfusion, pyrogenic reactions);
acute hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis;
acute lymphoblastic leukemia;
severe infectious diseases (in combination with antibiotics);
acute adrenal insufficiency;
acute croup;
acute (or exacerbation) rheumatic diseases, systemic connective tissue diseases and joint diseases (humeral periarthritis, epicondylitis, styloiditis, bursitis, tenosynovitis, compressive neuropathy, osteochondrosis, arthritis of various etiologies, osteoarthritis);
diagnosis of adrenocortical insufficiency, pituitary short stature (in children), affective disorders, incl. for depression.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticoid drug that contains a fluorine atom.
It has a pronounced anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and desensitizing effect, and has immunosuppressive activity.
Slightly retains sodium and water in the body. These effects are associated with inhibition of eosinophil release of inflammatory mediators; inducing the formation of lipocortins and reducing the number of mast cells that produce hyaluronic acid; with a decrease in capillary permeability; stabilization of cell membranes (especially lysosomal) and organelle membranes.
The immunosuppressive effect is due to inhibition of the release of cytokinins (interleukin 1, 2, interferon gamma) from lymphocytes and macrophages. The main effect on metabolism is associated with protein catabolism, increased gluconeogenesis in the liver and decreased glucose utilization by peripheral tissues.
The drug inhibits the activity of vitamin D, which leads to a decrease in calcium absorption and an increase in its excretion. Dexamethasone suppresses the synthesis and secretion of ACTH and, secondarily, the synthesis of endogenous glucocorticoids.
A peculiarity of the drug’s action is significant inhibition of pituitary function and the complete absence of mineralocorticoid activity.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Dexamethasone
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
dexamethasone sodium phosphate 4 mg;
Excipients:
methylparaben – 1.5 mg;
propylparaben – 0.2 mg;
sodium metabisulfite – 2 mg;
disodium edetate – 1 mg;
sodium hydroxide – up to pH 7–8.5;
water for injection – up to 1 ml.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Arterial hypertension,
Itsenko-Cushing’s disease,
psychoses,
renal failure,
osteoporosis,
peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum,
bacterial endocarditis,
syphilis,
tuberculosis,
diabetes mellitus,
pregnancy,
systemic mycoses,
infectious joint lesions,
obesity grade III-IV,
hypersensitivity to dexamethasone.
Side Effects
Side Effects
With short-term therapy: nausea, vomiting, bradycardia, arrhythmias, ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosa, decreased immunity.
With long-term use: Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, hyperglycemia, pancreatitis, myocardial dystrophy, headache, convulsions, psychosis.
Local reactions: immediately after instillation of the drug, a quickly passing burning sensation is possible.
With prolonged use, intraocular pressure may increase (therefore, when using drugs containing corticosteroids for more than 10 days, intraocular pressure should be measured regularly).
When used for more than 3 months, posterior capsular cataracts may develop. Regeneration processes may slow down.
Interaction
Interaction
There may be pharmaceutical incompatibility of dexamethasone with other IV drugs – it is recommended to administer it separately from other drugs (IV bolus, or through another dropper, as a second solution). When mixing a solution of dexamethasone with heparin, a precipitate forms.
Simultaneous administration of dexamethasone with:
inducers of hepatic microsomal enzymes (phenobarbital, rifampicin, phenytoin, theophylline, ephedrine) leads to a decrease in its concentration;
diuretics (especially thiazide and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors) and amphotericin B – can lead to increased excretion of K+ from the body and an increased risk of developing heart failure;
with sodium-containing drugs – to the development of edema and increased blood pressure;
cardiac glycosides – their tolerability worsens and the likelihood of developing ventricular extrasytolia increases (due to caused hypokalemia);
indirect anticoagulants – weakens (less often enhances) their effect (dose adjustment required);
anticoagulants and thrombolytics – the risk of bleeding from ulcers in the gastrointestinal tract increases;
ethanol and NSAIDs – increases the risk of erosive and ulcerative lesions in the gastrointestinal tract and the development of bleeding (in combination with NSAIDs in the treatment of arthritis, it is possible to reduce the dose of glucocorticosteroids due to the summation of the therapeutic effect);
paracetamol – the risk of developing hepatotoxicity increases (induction of liver enzymes and the formation of a toxic metabolite of paracetamol);
acetylsalicylic acid – accelerates its elimination and reduces its concentration in the blood (when dexamethasone is discontinued, the level of salicylates in the blood increases and the risk of side effects increases);
insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs, antihypertensive drugs – their effectiveness decreases;
vitamin D – its effect on the absorption of Ca2+ in the intestine is reduced;
somatotropic hormone – reduces the effectiveness of the latter, and spraziquantel – its concentration;
M-anticholinergics (including antihistamines and tricyclic antidepressants) and nitrates – helps increase intraocular pressure;
isoniazid and mexiletine – increases their metabolism (especially in “slow” acetylators), which leads to a decrease in their plasma concentrations.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and loop diuretics may increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Indomethacin, displacing dexamethasone from its association with albumin, increases the risk of developing its side effects.
ACTH enhances the effect of dexamethasone.
Ergocalciferol and parathyroid hormone prevent the development of osteopathy caused by dexamethasone.
Cyclosporine and ketoconazole, by slowing down the metabolism of dexamethasone, can in some cases increase its toxicity.
The simultaneous administration of androgens and steroidal anabolic drugs with dexamethasone promotes the development of peripheral edema and hirsutism, and the appearance of acne.
Estrogens and oral contraceptives containing estrogen reduce the clearance of dexamethasone, which may be accompanied by an increase in the severity of its action.
Mitotane and other inhibitors of adrenal function may necessitate an increase in the dose of dexamethasone.
When used simultaneously with live antiviral vaccines and against the background of other types of immunization, it increases the risk of viral activation and the development of infections.
Antipsychotics (neuroleptics) and azathioprine increase the risk of developing cataracts when dexamethasone is prescribed.
When used simultaneously with antithyroid drugs, the clearance of dexamethasone decreases and with thyroid hormones increases.
Overdose
Overdose
The side effects described above may increase.
It is necessary to reduce the dose of Dexamethasone. Treatment is symptomatic.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
KRKA dd Novo Mesto, Slovenia
Additional information
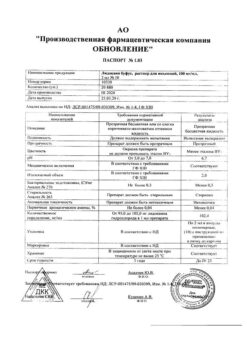
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | KRKA dd Novo mesto, Slovenia |
| Medication form | solution for injection |
| Brand | KRKA dd Novo mesto |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Dexamethasone, 4 mg/ml 1 ml 25 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.