No products in the cart.
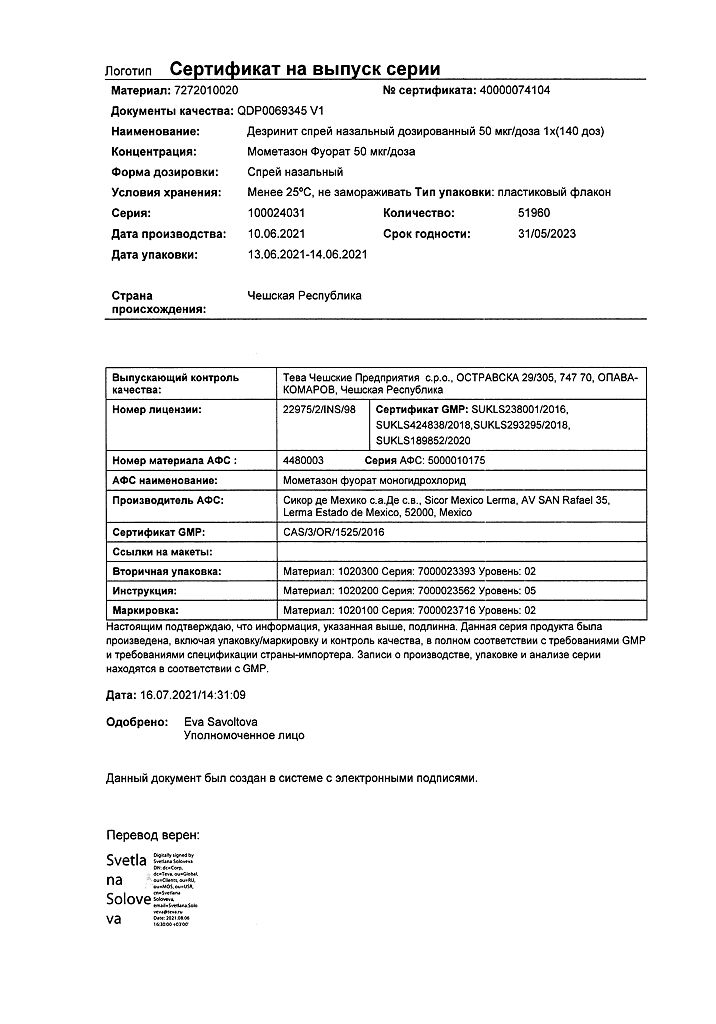
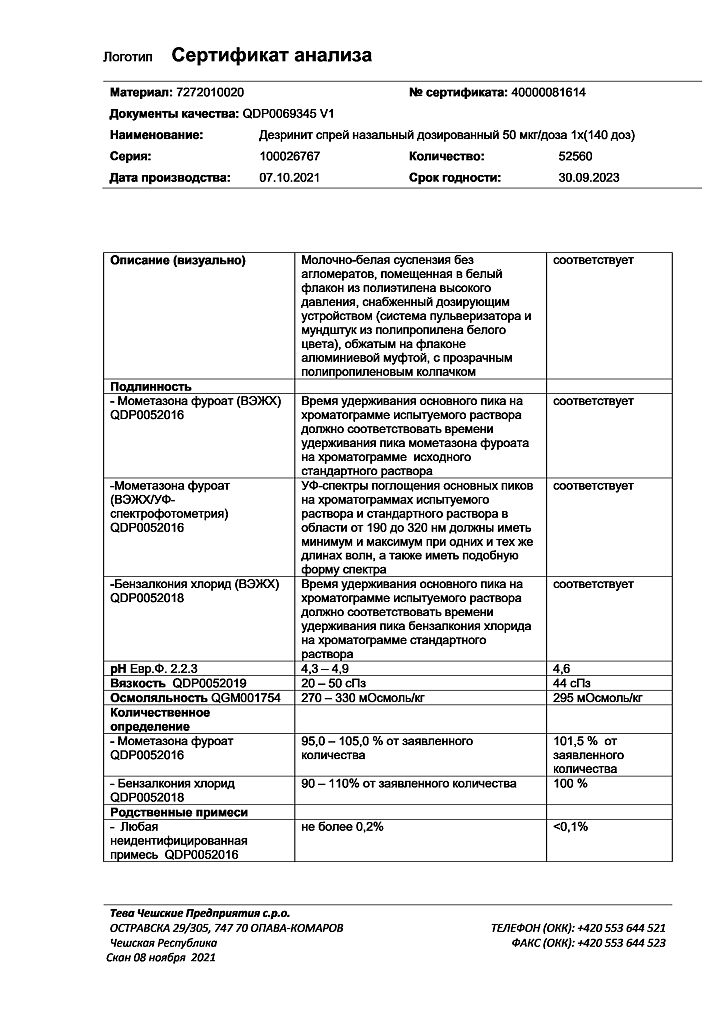
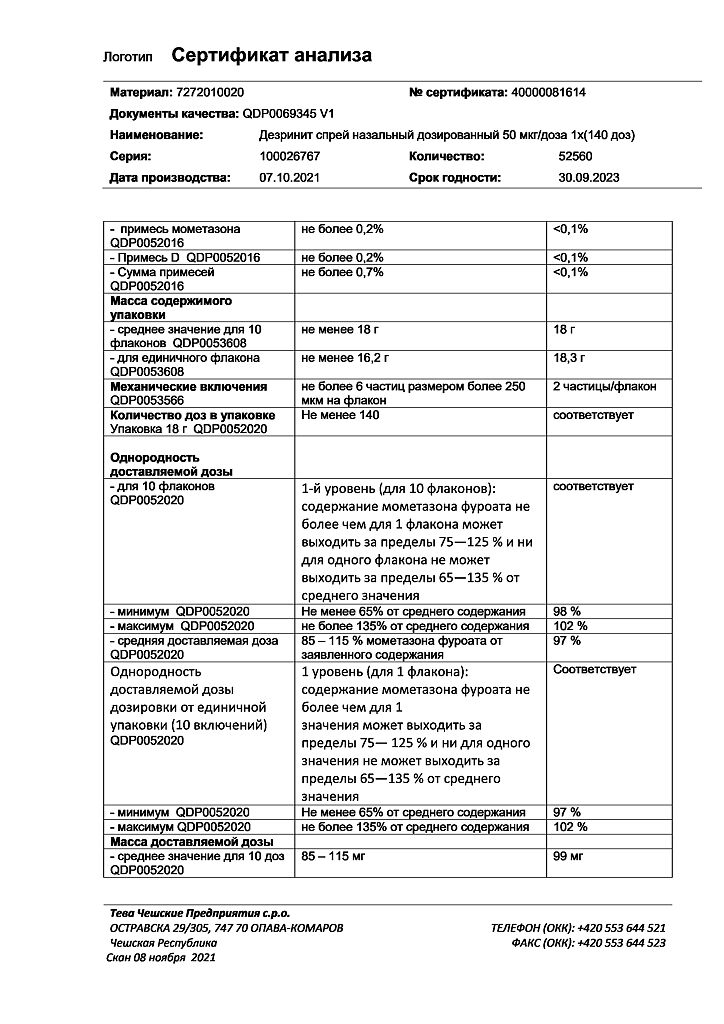
Desrinit, spray 50 mcg/dose 18 g 140 doses
€17.42 €14.51
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: glucocorticosteroid for topical use
ATX code: R01AD09
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Mometasone is a synthetic glucocorticosteroid (GCS) for topical use. It has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects. The local anti-inflammatory effect of the drug is seen when it is used in doses at which there are no systemic effects.
Inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators. It increases production of lipomodulin, which is an inhibitor of phospholipase A, which causes reduction of release of arachidonic acid and, accordingly, inhibition of synthesis of products of arachidonic acid metabolism – cyclic endoperoxides, prostaglandins. It prevents marginal accumulation of neutrophils, which reduces inflammatory exudate and lymphokine production, inhibits macrophage migration, leads to a decrease in infiltration and granulation processes. It reduces inflammation due to decrease in formation of chemotaxis substance (effect on late allergic reactions), inhibits development of allergic reaction of immediate type (due to inhibition of formation of arachidonic acid metabolites and reduction of release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells).
In studies with provocation tests with application of antigens to the nasal mucosa high anti-inflammatory activity of the drug was demonstrated both in the early and late stages of the allergic reaction. When compared to placebo, a decrease in histamine levels and eosinophil activity as well as a decrease (compared to baseline) in the number of eosinophils, neutrophils and epithelial cell proteins was found.
Pharmacokinetics
In intranasal administration, the systemic bioavailability of mometasone furoate is <1% (with a sensitivity of 0.25 pg/mL detection method). Mometasone suspension is very poorly absorbed in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and the small amount of mometasone suspension that may enter the GI tract after nasal aspiration undergoes active primary metabolism before being excreted with urine or bile.
Indications
Indications
seasonal and year-round allergic rhinitis in adults, adolescents and children from 2 years of age;
acute sinusitis or exacerbation of chronic sinusitis in adults (including the elderly) and adolescents over 12 years of age – as an auxiliary therapeutic agent in treatment with antibiotics;
acute rhinosinusitis with mild to moderate symptoms without signs of severe bacterial infection in patients aged 12 years or more.
preventive treatment of moderate and severe seasonal allergic rhinitis in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age (recommended 2-4 weeks before the expected start of the dusting season);
nasal polyposis, accompanied by impaired nasal breathing and sense of smell, in adults (over 18 years of age).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: glucocorticosteroid for local use
ATX code: R01AD09
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Mometasone is a synthetic glucocorticosteroid (GCS) for topical use. Has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects. The local anti-inflammatory effect of the drug is manifested when it is used in doses at which systemic effects do not occur.
Inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators. Increases the production of lipomodulin, which is an inhibitor of phospholipase A, which causes a decrease in the release of arachidonic acid and, accordingly, inhibition of the synthesis of arachidonic acid metabolic products – cyclic endoperoxides, prostaglandins. Prevents the marginal accumulation of neutrophils, which reduces inflammatory exudate and the production of lymphokines, inhibits the migration of macrophages, and leads to a decrease in the processes of infiltration and granulation. Reduces inflammation by reducing the formation of a chemotaxis substance (impact on late allergy reactions), inhibits the development of an immediate allergic reaction (by inhibiting the formation of arachidonic acid metabolites and reducing the release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells).
In studies with provocative tests with the application of antigens to the nasal mucosa, high anti-inflammatory activity of the drug was demonstrated, both in the early and late stages of the allergic reaction. When compared with placebo, a decrease in the level of histamine and eosinophil activity was found, as well as a decrease (compared to the baseline) in the number of eosinophils, neutrophils and epithelial cell proteins.
Pharmacokinetics
When administered intranasally, the systemic bioavailability of mometasone furoate is <1% (with a sensitivity of the detection method of 0.25 pg/ml). The mometasone suspension is very poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), and the small amount of mometasone suspension that can enter the GIT after injection into the nasal passage undergoes active primary metabolism even before excretion in the urine or bile.
Special instructions
Special instructions
As with any treatment, patients using mometasone in dosed nasal spray dosage form for several months or longer should be periodically examined by a doctor for possible changes in the nasal mucosa.
It is necessary to monitor patients receiving intranasal corticosteroids for a long time. Possible development of growth retardation in children. If growth retardation is detected in children, it is necessary to reduce the dose of intranasal corticosteroids to the lowest that allows for effective control of symptoms. In addition, the patient should be referred to a pediatrician for consultation.
If a local fungal infection of the nose or pharynx develops, it may be necessary to discontinue therapy with mometasone in dosage form – dosed nasal spray and carry out special treatment. Irritation of the mucous membrane of the nose and pharynx that persists for a long time can also serve as a reason to discontinue treatment with mometasone in dosage form – dosed nasal spray.
In placebo-controlled clinical studies in children, when mometasone in dosage form – a nasal spray dosed was used in a daily dose of 100 mcg for a year, no growth retardation was observed in children.
With long-term treatment with mometasone in the dosage form – nasal spray, no signs of suppression of the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system were observed.
Patients who switch to treatment with mometasone in dosage form – a dosage nasal spray after long-term therapy with systemic glucocorticosteroids require special attention. Withdrawal of systemic corticosteroids in such patients can lead to adrenal insufficiency, the subsequent recovery of which may take up to several months. If signs of adrenal insufficiency appear, systemic corticosteroids should be resumed and other necessary measures taken.
When using intranasal corticosteroids, systemic side effects may develop, especially with long-term use in high doses. The likelihood of developing these effects is much less than with the use of oral corticosteroids.
Systemic side effects may vary in individual patients and depending on the glucocorticosteroid drug used. Potential systemic effects include Cushing’s syndrome, Cushingoid features, adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, cataracts, glaucoma, and less commonly a number of psychological or behavioral effects including psychomotor hyperactivity, sleep disturbance, anxiety, depression, or aggression (especially in children).
During the transition from treatment with systemic glucocorticosteroids to treatment with mometasone nasal spray, some patients may experience initial symptoms of systemic glucocorticosteroid withdrawal (for example, joint and/or muscle pain, fatigue and depression), despite a decrease in the severity of symptoms associated with damage to the nasal mucosa. If these signs appear, you should resume taking systemic glucocorticosteroids and take other necessary measures. Switching from systemic to topical glucocorticosteroids may also reveal pre-existing allergic diseases such as allergic conjunctivitis and eczema that were masked by systemic glucocorticosteroid therapy.
Patients treated with glucocorticosteroids have a potentially reduced immune responsiveness and should be warned about their increased risk of infection in case of contact with patients with certain infectious diseases (for example, chicken pox, measles), as well as the need for medical advice if such contact occurs.
If signs of a severe bacterial infection appear (for example, fever, persistent and sharp pain on one side of the face or toothache, swelling in the orbital or periorbital area), immediate medical consultation is required.
When using mometasone in dosage form – dosed nasal spray for 12 months, there were no signs of atrophy of the nasal mucosa. In addition, mometasone furoate tended to promote normalization of the histological picture when examining biopsy specimens of the nasal mucosa.
The effectiveness and safety of mometasone have not been studied in the treatment of unilateral polyps, polyps associated with cystic fibrosis, and polyps that completely occlude the nasal cavity.
If unilateral polyps of an unusual or irregular shape are detected, especially those that are ulcerated or bleeding, additional medical examination is necessary.
Visual disturbances have been reported with systemic and topical corticosteroid use. If a patient develops symptoms such as blurred vision or other visual disturbances, consider referring the patient to an ophthalmologist to evaluate possible causes, which may include cataracts, glaucoma, or rare diseases such as central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
There is no data on the effect of the drug Dezrinit on the ability to drive vehicles or drive machinery.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Mometasone
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
mometasone furoate monohydrate (in terms of mometasone furoate) 0.052 mg (0.050 mg);
Excipients:
Avicel RC-591 (microcrystalline cellulose, sodium carmellose) – 2 mg,
glycerol – 2.1 mg,
benzalkonium chloride solution 500 g/l – 40 mcg,
polysorbate 80 – 10 mcg,
citric acid monohydrate – 200 mcg,
sodium citrate dihydrate – 280 mcg,
water d/i – q.s. up to 100 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
No special studies have been conducted on the safety of mometasone during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
As with the use of other nasal corticosteroids, Dezrinit should be prescribed during pregnancy and breastfeeding only if the expected benefit from its use outweighs the potential risk to the fetus and newborn. Newborns whose mothers used corticosteroids during pregnancy should be carefully examined to identify possible adrenal hypofunction.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to mometasone or any of the components of the drug; children’s age (for seasonal and year-round allergic rhinitis – up to 2 years; for acute sinusitis or exacerbations of chronic sinusitis – up to 12 years; for nasal polyposis – up to 18 years); recent surgery or trauma to the nose with damage to the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity – before the wound heals (due to the inhibitory effect of GCS on the healing processes).
With caution
The drug Dezrinit should be used with caution in case of tuberculosis infection (active or latent) of the respiratory tract, untreated fungal, bacterial, systemic viral infection or infection caused by Herpes simplex with eye damage (as an exception, the drug can be prescribed for these infections as directed by a doctor), the presence of an untreated local infection involving the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Adverse events associated with the use of the drug (≥1%) identified during clinical trials in patients with allergic rhinitis or nasal polyposis and during post-marketing use of the drug, regardless of the indication for use, are presented in Table 1. Adverse reactions are listed in accordance with the MedDRA system-organ class classification. Within each systemic organ class, adverse reactions are classified by frequency of occurrence.
Nosebleeds were generally mild and self-limiting, and their incidence was slightly higher than with placebo (5%), but equal to or less than with other intranasal corticosteroids that were used as active controls (some of which had an incidence of nosebleeds of up to 15%). The incidence of all other adverse events was comparable to that observed with placebo.
The overall incidence of adverse events in patients treated for nasal polyposis was comparable to the incidence in patients with allergic rhinitis.
The overall incidence of adverse events in patients treated for acute rhinosinusitis was comparable to the incidence in patients with allergic rhinitis and placebo.
When using intranasal corticosteroids, the development of systemic side effects is possible, especially with long-term use of intranasal corticosteroids in high doses (see section “Special instructions”).
Table 1
The frequency of adverse reactions is established as follows:
very often (≥1/10); often (≥1/100, < 1/10), rarely (≥1/1000, < 1/100).
For adverse reactions during post-registration surveillance, the frequency has not been established (cannot be determined based on available data).
System-organ class
Very often
Often
Rarely
Frequency not set
Infectious and parasitic diseases
Pharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections*
Immune system disorders
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic reactions, angioedema, bronchospasm, shortness of breath
Nervous system disorders
Headache
Visual disorders
Impaired vision (see section “Special instructions”)
Increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma, cataracts
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Nosebleeds**
Nosebleeds (i.e., obvious bleeding as well as blood-stained mucus or blood clots), burning sensation in the nose, irritation of the nasal mucosa, ulceration of the nasal mucosa
Perforation of the nasal septum
Gastrointestinal disorders
Pharyngeal irritation (feeling of irritation of the pharyngeal mucosa)**
Impaired taste and smell
* detected with a frequency of “rarely” when using the drug twice a day for nasal polyposis
** detected when using the drug twice a day for nasal polyposis
Children
Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: nosebleeds (6%), irritation of the nasal mucosa (2%), sneezing (2%).
From the nervous system: headache (3%).
The incidence of these adverse events in children was comparable to the incidence when using placebo.
Interaction
Interaction
The simultaneous use of mometasone with loratadine did not lead to a change in the concentration of loratadine or its main metabolite in the blood plasma, and the presence of mometasone in the plasma was not detected even at minimal concentrations. In these studies, mometasone furoate was not detected in blood plasma (with a sensitivity of the detection method of 50 pg/ml).
When used concomitantly with CYP3A inhibitors, including cobicistat-containing drugs, the risk of systemic side effects increases. Their simultaneous use should be avoided unless the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the possible risk of systemic side effects of corticosteroids. If used concomitantly, patients should be monitored for systemic side effects of corticosteroids.
Overdose
Overdose
With long-term use of GCS in high doses, as well as with the simultaneous use of several GCS, inhibition of the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system is possible. Due to the low systemic bioavailability of the drug (< 1%, with a sensitivity of the detection method of 0.25 pg/ml), it is unlikely that in case of accidental or intentional overdose, any measures will be required other than observation with the possible subsequent resumption of the drug at the recommended dose.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C, do not freeze.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years.
The shelf life of an opened bottle is 2 months.
Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Teva Czech Enterprises s.r.o., Czech Republic
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. Shelf life of the opened bottle is 2 months. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C, do not freeze. KEEP OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN. |
| Manufacturer | Teva Czech Enterprises s.r.o., Czech Republic |
| Medication form | nasal spray |
| Brand | Teva Czech Enterprises s.r.o. |
Related products
Buy Desrinit, spray 50 mcg/dose 18 g 140 doses with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.