No products in the cart.
Cordinic, tablets 10 mg 60 pcs
€16.99 €14.16
Description
Pharmacodynamics
Nicorandil has antianginal action, which is based on a combination of nitrate-like properties and the ability to open potassium channels. By opening potassium channels, nicorandil causes hyperpolarization of the cell membrane, and the nitrate-like
effect is to increase the intracellular content of cyclic guanylmonophosphate.
These pharmacological effects lead to relaxation of smooth muscle cells and cellular protection of the myocardium during ischemia. The hemodynamic effects are expressed as a balanced decrease in pre- and post-load (in contrast to nitrates and slow calcium channel blockers (SCBs), which act primarily on pre- or post-load, respectively).
In view of selective vasodilation of coronary arteries, the resulting load on the ischemic myocardium is minimal. Nicorandil does not affect myocardial contractility and practically does not change heart rate (HR).
Limits systemic blood pressure (BP) by less than 10%, has a beneficial positive effect on cerebral circulation in patients with ischemic stroke. Nicorandil does not affect indexes of lipid metabolism and glucose metabolism. Nicorandil stops an attack of angina pectoris with reduction of pain syndrome within 4-7 minutes after the intake under the tongue and its complete cessation within 12-17 minutes.
Pharmacokinetics
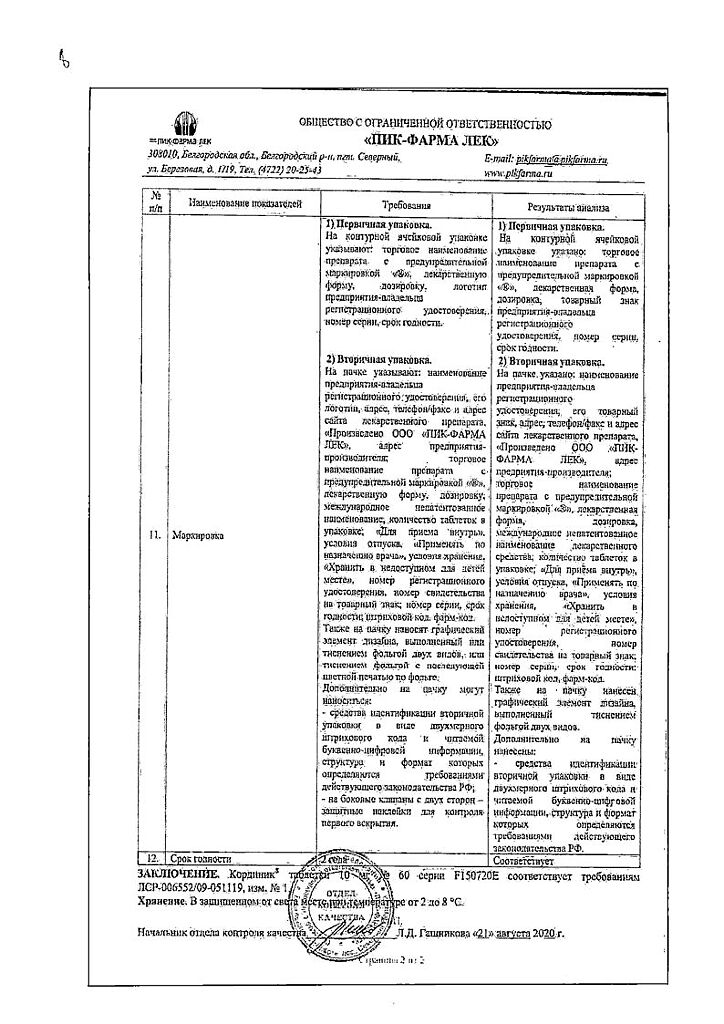
Nicorandil is rapidly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, reaching maximum plasma concentration in 0.5-1 hours. It is not subject to intensive metabolism in the liver and has a half-life of 50 minutes. It is mainly excreted by the kidneys.
Nicorandil slightly binds with blood plasma proteins.
The free fraction in blood plasma is about 75%.
Pharmacokinetic parameters have little dependence on the patient’s age, presence of concomitant liver or renal pathology, prescription of concomitant therapy.
Indications
Indications
Symptomatic treatment of stable angina in adult patients in case of insufficient effectiveness, contraindications to use or intolerance to first-line antianginal drugs (such as beta-blockers and/or slow calcium channel blockers).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological action
Pharmacological action – vasodilating, antianginal.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Ulcerations and ulcers. When using nicorandil preparations, the occurrence of ulcerations (ulcers) of the gastrointestinal tract, skin and mucous membranes has been described.
Ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. Ulcerations associated with nicorandil may occur in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract in the same patient. The ulcers are resistant to treatment and in most cases heal only after discontinuation of nicorandil. In the event of ulcerations (ulcers) of the gastrointestinal tract, taking Cordinic® should be stopped immediately. Health care providers should be aware of the importance of prompt diagnosis of nicorandil-induced ulcers and prompt discontinuation of the drug if such ulcers occur. According to available information, ulcerations (ulcers) may appear either soon after starting nicorandil or several years after starting treatment. There are reports of the development of gastrointestinal bleeding as a complication of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract when taking nicorandil. Patients concomitantly taking acetylsalicylic acid or NSAIDs have an increased risk of developing severe complications such as gastrointestinal bleeding. Therefore, extreme caution is recommended when using acetylsalicylic acid or NSAIDs concomitantly with nicorandil. As ulcers progress, perforations, fistulas, or abscesses may occur. Patients with diverticular disease have a particularly high risk of developing fistulas or bowel perforation when taking nicorandil medications. Cases of perforation of the gastrointestinal tract have been described with the simultaneous use of nicorandil and glucocorticosteroids. Therefore, the combined use of these drugs should be carried out with extreme caution.
Ulcerations of the eyes. Very rare cases of conjunctivitis, conjunctival ulcers and corneal ulcers associated with the use of nicorandil have been described. Patients should be warned about symptoms of corneal damage and the need to monitor their eye condition. If ulcerations (ulcers) of the cornea occur, Cordinic® should be discontinued.
Arterial hypotension. Nicorandil in therapeutic doses has an antihypertensive effect. Nicorandil should be used with caution in combination with other drugs that lower blood pressure.
Chronic heart failure. Due to the lack of experience in clinical use, the administration of nicorandil to patients with chronic heart failure of NYHA class III–IV is contraindicated.
Hyperkalemia. Very rare cases of severe hyperkalemia have been reported with the use of nicorandil. Nicorandil should be used with caution in combination with other drugs that may increase blood potassium levels, especially in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment.
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Cordinic® should be used with caution in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. The pharmacological action of nicorandil is partly due to the presence of an organic nitrate group. As a result of the metabolism of organic nitrates, nitrites may be formed, which can cause methemoglobinemia in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery. Nicorandil, like other vasodilators, can reduce blood pressure, cause dizziness and a feeling of weakness and, thus, affect the ability to drive vehicles and machines. These effects may be enhanced when used concomitantly with other drugs that lower blood pressure (eg, vasodilators, tricyclic antidepressants). Care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Nikorandil
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
active ingredient:
nicorandil 10/20 mg,
excipients:
potato starch – 5/10 mg;
MCC 102 – 84/168 mg;
calcium stearate – 1/2 mg
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
There is limited or no experience with the use of nicorandil in pregnant women. Animal studies have not demonstrated direct or indirect reproductive harm. As a precaution, Cordinic® should not be used during pregnancy.
Animal studies have shown that nicorandil is excreted in small amounts into breast milk. It is unknown whether nicorandil is excreted into human breast milk, and therefore the use of Cordinic® during breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to nicorandil or any of the components of the drug;
patients in shock (including cardiogenic shock), with severe hypotension or left ventricular failure with low filling pressure, or cardiac decompensation;
simultaneous use with phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil);
simultaneous use with soluble guanylate cyclase inhibitors (such as riociguat);
hypovolemia;
pulmonary edema;
pregnancy and breastfeeding (see “Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding”);
children under 18 years of age (efficacy and safety have not been established).
With caution: arterial hypotension; heart rhythm disturbances; atrioventricular block of the first degree; Prinzmetal’s angina; liver and/or kidney dysfunction; angle-closure glaucoma; anemia; hyperkalemia; simultaneous use with tricyclic antidepressants, glucocorticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including acetylsalicylic acid) and drugs that can increase the content of potassium in the blood; diverticular bowel disease; deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Adverse reactions are listed according to damage to organs and systems and frequency of occurrence. The frequency of occurrence is determined as follows: very often very often (≥1/10); often (≥1/100, <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100); rare (≥1/10000, <1/1000); very rare (< 1/10000); frequency unknown (cannot be estimated from available data).
Metabolism and nutrition: very rarely – hyperkalemia.
From the nervous system: very often – headache; often – dizziness.
From the organ of vision: very rarely – corneal ulcer, conjunctival ulcer, conjunctivitis; frequency unknown – diplopia.
From the heart: often – increased heart rate.
From the side of blood vessels: often – dilatation of skin vessels with a feeling of a rush of heat; infrequently – decreased blood pressure.
From the gastrointestinal tract: often – nausea, vomiting, rectal bleeding*; infrequently – ulcer of the oral mucosa*; rarely – gastrointestinal ulcers (stomatitis, aphthous stomatitis, ulcer of the oral mucosa, tongue ulcer, small intestinal ulcer, large intestinal ulcer, anal ulcer); very rarely – abdominal pain*; frequency unknown – gastrointestinal bleeding.
From the liver and biliary tract: very rarely – liver dysfunction (such as hepatitis, cholestasis or jaundice).
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: rarely – itching, skin rash; uncommon – angioedema*; very rarely – angioedema, ulcerations of the skin and mucous membranes (mainly perianal ulcers, genital ulcers and parastomal ulcers).
From the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue: infrequently*/rarely – myalgia.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site: often – a feeling of weakness.
*Adverse reactions were reported in a clinical study when nicorandil was used in addition to standard antianginal therapy in patients with stable angina and a high risk of cardiovascular complications.
Description of individual adverse reactions. Complications of gastrointestinal ulcers, such as perforation, fistula, or abscess formation, sometimes leading to gastrointestinal bleeding and weight loss, have been reported.
Interaction
Interaction
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors. The simultaneous use of nicorandil with phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil) is contraindicated due to the risk of severe arterial hypotension.
Soluble guanylate cyclase inhibitors. Concomitant use of nicorandil with soluble guanylate cyclase inhibitors (such as riociguat) is contraindicated as it may lead to a significant decrease in blood pressure.
Medicines that lower blood pressure. Nicorandil in therapeutic doses can lower blood pressure. When nicorandil is used simultaneously with antihypertensive drugs or other drugs that lower blood pressure (for example, vasodilators, tricyclic antidepressants, alcohol), the antihypertensive effect may be enhanced.
Dapoxetine should be co-administered with nicorandil with extreme caution due to the potential for orthostatic hypotension.
When nicorandil is used simultaneously with the drug sapropterin, blood pressure may decrease below normal.
Glucocorticosteroids. Cases of perforation of the gastrointestinal tract have been described with the combined use of nicorandil and glucocorticosteroids. If it is necessary to prescribe nicorandil and corticosteroids simultaneously, special caution should be used.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Patients concomitantly taking nicorandil and NSAIDs (including acetylsalicylic acid in both anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective doses) have an increased risk of developing severe complications from the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastrointestinal ulcers, perforation and bleeding.
Medicines that can increase potassium levels in the blood. Caution should be exercised when using nicorandil in combination with drugs that may increase potassium levels in the blood (risk of hyperkalemia).
Other interactions
Cimetidine (inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4/5) and rifampicin (inducer of CYP3A4) do not have a significant effect on the metabolism of nicorandil.
Nicorandil does not affect the pharmacodynamics of warfarin and acenocoumarol.
Clinical studies have not revealed pharmacodynamic and/or pharmacokinetic interactions of nicorandil with beta-blockers, slow calcium channel blockers, digoxin, a combination of digoxin with furosemide, acenocoumarol, rifampicin and cimetidine.
Clinical experience to date suggests that nitrates in the form of extended-release tablets, when used concomitantly with nicorandil, do not affect the clinical tolerability of the latter. However, due to the fact that the nicorandil molecule contains a nitrate group, caution should be exercised when combined with nitrates due to the possibility of potentiation of the antihypertensive effect.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: The expected manifestations of an acute overdose of nicorandil are peripheral vasodilation, a marked decrease in blood pressure and reflex tachycardia.
Treatment: monitoring of cardiovascular parameters and general supportive measures are recommended (for example, placing the patient in a supine position with legs elevated or with the head of the bed lowered). If there is no effect, it is recommended to replenish the volume of circulating plasma with intravenous administration of plasma-substituting solutions. In case of development of life-threatening conditions, the use of vasopressors is possible.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light at a temperature of 2 to 8°C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Pik-Pharma, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Pik-Pharma, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Pik-Pharma |
Related products
Buy Cordinic, tablets 10 mg 60 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.