No products in the cart.
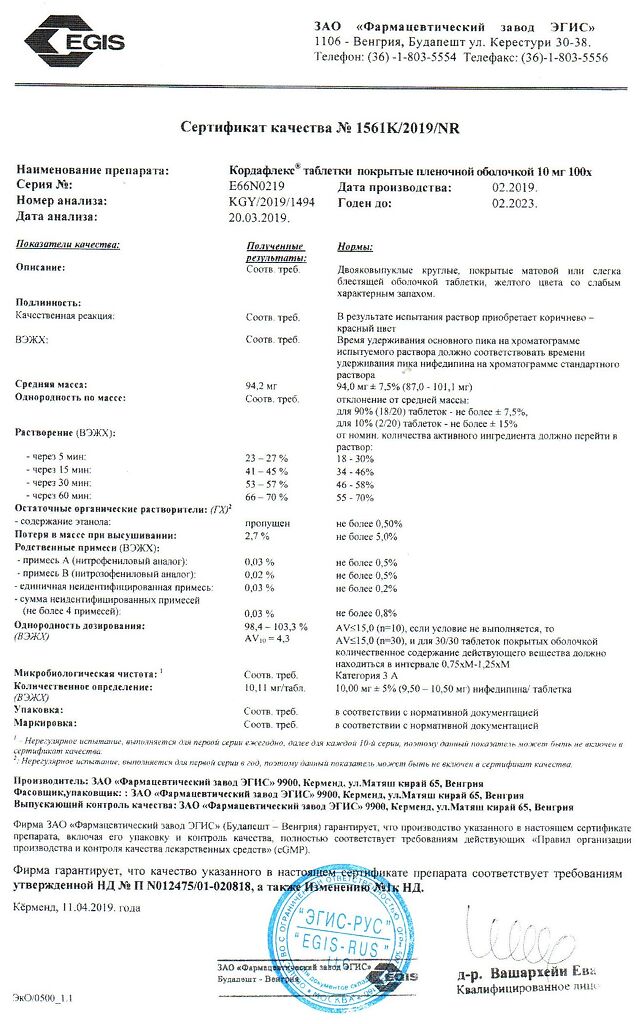
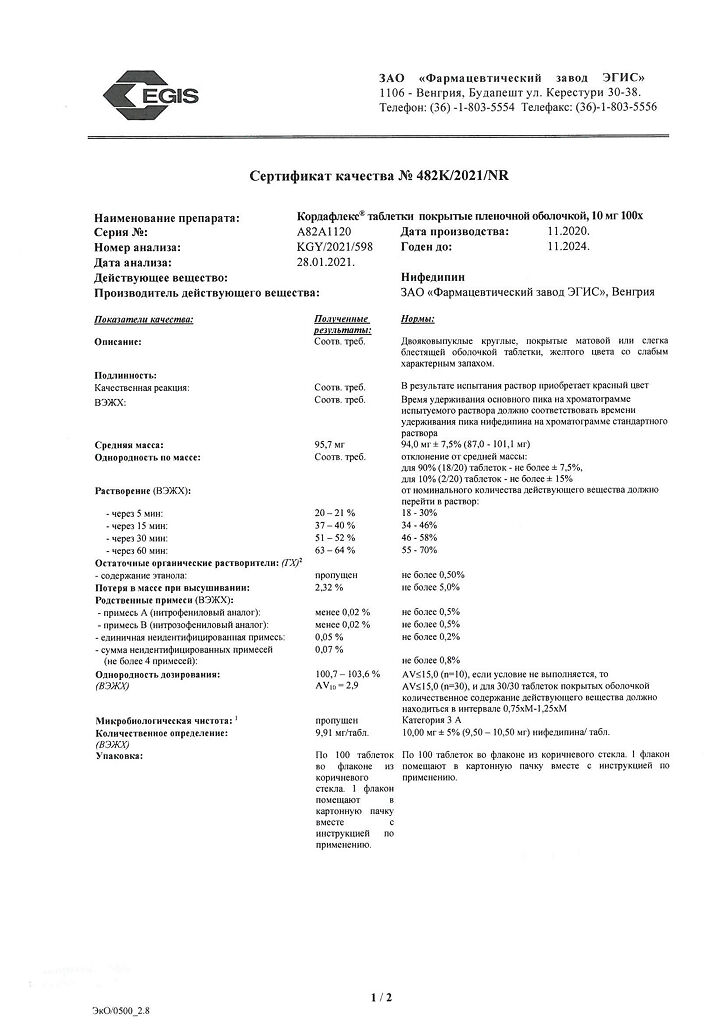
Cordaflex, 10 mg 100 pcs
€4.95 €4.12
Description
Pharmgroup:
Slow calcium channel blocker.
Pharm Action:
Cordaflex is a selective slow calcium channel blocker, 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative. It has antihypertensive and antianginal action. Nifedipine reduces flow of extracellular calcium ions inside cardiomyocytes and smooth muscle cells of coronary and peripheral arteries. In therapeutic doses it normalizes the transmembrane flow of calcium ions disturbed in a number of pathological conditions, especially in arterial hypertension. It reduces spasm and dilates coronary and peripheral arterial vessels, decreases PPS, reduces postload and myocardial oxygen demand. At the same time, it improves the blood supply to ischemic areas of the myocardium without the development of “bypass” syndrome, as well as increases the number of functioning collaterals.
Nifedipine has almost no effect on the sinoatrial and AV nodes and has neither pro- nor antiarrhythmic action. It has no effect on venous tone. Nifedipine increases renal blood flow, causing moderate natriuresis. At high doses, it inhibits the release of calcium ions from intracellular depots. Reduces the number of functioning calcium channels without affecting the time of their activation, inactivation and recovery.
After single administration of Cordaflex in the form of sustained release tablets the clinical effect develops in 20 minutes, the duration of clinical effect is 12-24 h.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption
When administered orally it is quickly and almost completely (more than 90%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability is 40-70%.
After oral administration of Cordaflex 10 mg tablet Cmax in blood is reached 0.5-1 hour after administration.
After oral administration of 1 sustained release tablet 20 mg therapeutic concentration of nifedipine in plasma is reached after 1 hour and remains constant till 6 hours (sustained release plateau), and during the next 30-36 hours it gradually decreases.
Distribution
Binding to plasma proteins (albumin) is 94-97%. Unbound nifedipine is distributed in all organs and tissues.
It penetrates through the BET (less than 5%), through the placental barrier, excreted with breast milk.
It does not cumulate.
Metabolism
Nifedipine is extensively metabolized in the liver to form 3 metabolites with no pharmacological activity.
Excretion
After oral administration of Cordaflex in tablet form 10 mg, the T1/2 of nifedipine is 2 h, after administration of 20 mg sustained-release tablet – about 3.8-16.9 h.
60-80% of the oral dose of the drug is excreted in the urine as inactive metabolites, the remainder in the bile and feces.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases
In elderly patients the metabolism of nifedipine in the liver is reduced.
In patients with hepatic impairment, total clearance is decreased and T1/2 of nifedipine is increased.
Chronic renal failure, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis have no effect on the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine.
Indications
Indications
– arterial hypertension of various origins, including hypertensive crises (for 10 mg tablets);
— IHD: for the prevention of attacks in various forms of angina, incl. angiospastic (Prinzmetal’s angina);
– Raynaud’s syndrome (for extended-release tablets).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmaceutical group:
blocker of “slow” calcium channels.
Pharmaceutical action:
Cordaflex is a selective blocker of slow calcium channels, a 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative. Has antihypertensive and antianginal effects. Nifedipine reduces the flow of extracellular calcium ions into cardiomyocytes and smooth muscle cells of the coronary and peripheral arteries. In therapeutic doses, it normalizes the transmembrane current of calcium ions, which is disturbed in a number of pathological conditions, primarily in arterial hypertension. Reduces spasm and dilates coronary and peripheral arterial vessels, reduces peripheral vascular resistance, reduces afterload and myocardial oxygen demand. At the same time, it improves blood supply to ischemic areas of the myocardium without the development of “steal” syndrome, and also increases the number of functioning collaterals.
Nifedipine has virtually no effect on the sinoatrial and AV nodes and does not have either pro- or antiarrhythmic effects. Does not affect the tone of the veins. Nifedipine increases renal blood flow, causing moderate natriuresis. In high doses, it inhibits the release of calcium ions from intracellular stores. Reduces the number of functioning calcium channels without affecting the time of their activation, inactivation and recovery.
After a single dose of Cordaflex in the form of extended-release tablets, the clinical effect develops within 20 minutes, the duration of the clinical effect is 12-24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics:
Suction
When taken orally, it is quickly and almost completely (more than 90%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability – 40-70%.
After oral administration of Cordaflex in tablet form, 10 mg Cmax in the blood is achieved 0.5-1 hour after administration.
After oral administration of 1 tablet of prolonged action 20 mg, the therapeutic concentration of nifedipine in the blood plasma is achieved after 1 hour and remains at a constant level for up to 6 hours (prolonged action plateau), and gradually decreases in the next 30-36 hours.
Distribution
Binding to blood plasma proteins (albumin) is 94-97%. Unbound nifedipine is distributed in all organs and tissues.
Penetrates through the BBB (less than 5%), through the placental barrier, and is excreted in breast milk.
Does not cumulate.
Metabolism
Nifedipine is extensively metabolized in the liver with the formation of 3 metabolites that do not have pharmacological activity.
Removal
After oral administration of Cordaflex in the form of a 10 mg tablet, T1/2 of nifedipine is 2 hours, after taking a prolonged-release tablet 20 mg – about 3.8-16.9 hours.
60-80% of the dose of the drug taken orally is excreted in the urine in the form of inactive metabolites, the remaining part is excreted in bile and feces.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In elderly patients, the metabolism of nifedipine in the liver is reduced.
In patients with liver failure, total clearance decreases and T1/2 of nifedipine increases.
Chronic renal failure, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis do not affect the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The antihypertensive effect of Cordaflex is enhanced by hypovolemia. A decrease in pulmonary artery pressure and hypovolemia after dialysis may also enhance the effects of the drug, and therefore a dose reduction is recommended.
In rare cases, at the beginning of a course of treatment with Cordaflex or when its dose is increased, chest pain (angina due to paradoxical ischemia) may occur soon after taking the drug. If a causal relationship is found between taking the drug and angina pectoris, treatment should be discontinued.
In case of arterial hypertension or coronary vascular disease, abrupt withdrawal of nifedipine can cause a hypertensive crisis or myocardial ischemia (rebound phenomenon).
If during therapy the patient requires surgery under general anesthesia, it is necessary to inform the anesthesiologist about the Cordaflex therapy being performed.
Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased cerebral blood flow due to acute peripheral vasodilation.
During a course of treatment with Cordaflex, the consumption of alcoholic beverages is not recommended due to the risk of an excessive decrease in blood pressure.
Use in pediatrics
Due to the lack of sufficient clinical data, the drug is not recommended for use in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the initial, individually determined period of use of Cordaflex, driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require rapid psychomotor reactions are not allowed. In the process of further treatment, the degree of restrictions is determined depending on the patient’s individual response to the drug.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Nifedipine
Composition
Composition
1 tab.:
– nifedipine 10 mg
Excipients:
polyvinyl butyral,
magnesium stearate,
talc,
hydroxypropylcellulose,
sodium croscarmellose,
lactose monohydrate,
microcrystalline cellulose,
titanium dioxide,
iron oxide yellow,
hypromellose.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Cordaflex® is contraindicated for use in the first trimester of pregnancy.
The use of Cordaflex in pregnant women is indicated only in cases where normalization of blood pressure is impossible with the use of other antihypertensive drugs.
Since nifedipine is excreted in breast milk, you should avoid using Cordaflex during lactation or stop breastfeeding during treatment with the drug.
Contraindications
Contraindications
— acute stage of myocardial infarction;
— cardiogenic shock;
— severe arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure below 90 mm Hg);
– severe aortic or mitral stenosis, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis;
– severe heart failure;
— I trimester of pregnancy;
– period of lactation (breastfeeding);
– children and adolescents up to 18 years of age;
– hypersensitivity to nifedipine and other components of the drug Cordaflex.
Cordaflex® should be used with caution in chronic heart failure, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, severe cerebrovascular accidents, CVS, severe tachycardia, severe liver and/or renal dysfunction, malignant arterial hypertension, in patients on hemodialysis (due to the risk of severe arterial hypotension due to peripheral vasodilation), with lactose intolerance, as well as in patients elderly.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the cardiovascular system: facial skin flushing, severe arterial hypotension, peripheral edema, tachycardia; rarely – increased angina attacks (drug discontinuation required), increased heart failure, fainting.
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: headache, dizziness, increased fatigue, sleep disturbances (drowsiness or insomnia); in isolated cases – mood lability, visual impairment; with long-term use in high doses – paresthesia in the limbs, tremor.
From the digestive system: diarrhea, constipation, nausea, heartburn; rarely (with long-term use of the drug) – dry mouth, flatulence, intrahepatic cholestasis, increased activity of liver transaminases; in some cases – gum hyperplasia, gingivitis, anorexia.
From the hematopoietic system: rarely – thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, leukopenia; in some cases – anemia.
From the urinary system: increased daily diuresis; rarely – deterioration of renal function in patients with chronic renal failure.
From the musculoskeletal system: myalgia; in isolated cases – arthritis.
From the endocrine system: in isolated cases – gynecomastia, hyperglycemia (completely disappear after discontinuation of the drug), changes in body weight, galactorrhea.
Allergic reactions: rarely – urticaria, exanthema, itching; in some cases – autoimmune hepatitis.
Other: feeling of heat; in isolated cases – weakness, sweating, fever, chills, photodermatitis.
Interaction
Interaction
From the point of view of enhancing the antihypertensive and antianginal effect, the combination of Cordaflex with beta-blockers, diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and nitrates is rational. All of the above combinations are safe and effective in most clinical situations, since they lead to summation or potentiation of effects, however, in some cases there is a risk of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure and increased symptoms of heart failure.
The combination of Cordaflex with clonidine, methyldopa, octadine, prazosin is possible according to indications, but can cause severe orthostatic hypotension.
An increase in the hypotensive effect is also observed during combination therapy with cimetidine, ranitidine and tricyclic antidepressants.
Nifedipine increases the concentration of digoxin and theophylline in the blood plasma, and therefore the clinical effect and/or the content of digoxin and theophylline in the blood plasma should be monitored.
Procaine, quinidine and other drugs that cause QT prolongation enhance the negative inotropic effect and increase the risk of QT prolongation. Under the influence of nifedipine, the concentration of quinidine in the blood serum is significantly reduced, which is apparently due to a decrease in its bioavailability, as well as the induction of enzymes that inactivate quinidine. When nifedipine is discontinued, a transient increase in quinidine concentration is observed (approximately 2 times), which reaches a maximum level on days 3-4. Caution should be exercised when using such combinations, especially in patients with impaired left ventricular function.
Nifedipine can displace drugs characterized by a high degree of binding from protein binding (including indirect anticoagulants – derivatives of coumarin and indanedione, NSAIDs), as a result of which their concentrations in the blood plasma may increase.
When administered simultaneously with rifampicin, phenytoin and calcium preparations, the effect of nifedipine is weakened.
Nifedipine inhibits the elimination of vincristine from the body and may cause increased side effects of vincristine; if necessary, the dose of vincristine is reduced.
Diltiazem inhibits the metabolism of nifedipine in the body; if necessary, reduce the dose of nifedipine.
Grapefruit juice, erythromycin and azole antifungals (fluconazole, intraconazole, ketoconazole) may inhibit the metabolism of nifedipine and therefore enhance its effects.
Likewise, the simultaneous use of Cordaflex and cimetidine increases the concentration of nifedipine in the blood plasma and enhances its effects
Since nifedipine is metabolized by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, any inhibitor or inducer of this enzyme may affect the metabolism of nifedipine. Cyclosporine is also a CYP3A4 substrate; therefore, when cyclosporine and nifedipine are used together, each may increase the duration of the effect of the other.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: severe arterial hypotension, tachycardia, chest pain (angina), headache, collapse, loss of consciousness, nodal or ventricular extrasystole due to inhibition of the sinus node, bradycardia, fainting. In severe cases, disturbances of consciousness leading to coma, hyperkalemia, metabolic alkalosis, hypoxia, cardiogenic shock with pulmonary edema are possible.
Treatment: given the lack of a specific antidote, in cases of early detoxification, gastric lavage is performed with the administration of activated charcoal. If necessary, small intestinal lavage can be done, which is more appropriate in case of overdose of controlled-release drugs. When prescribing laxatives, it should be taken into account that taking slow calcium channel blockers suppresses intestinal motility to the point of complete atony.
Since nifedipine is highly bound to plasma proteins, hemodialysis is not effective, but plasmapheresis may be effective.
Symptomatic therapy is indicated. Symptoms of cardiac arrhythmias with bradycardia can be eliminated by administering beta-agonists and/or atropine. For life-threatening bradycardia, an artificial pacemaker should be used. With a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, infusion of usual doses of norepinephrine (norepinephrine) or epinephrine (adrenaline) is indicated; dopamine (maximum dose 25 mcg/kg body weight/min), dobutamine (maximum dose 15 mcg/kg body weight/min), isoprenaline and 10% calcium gluconate solution (10-20 ml i.v.) can be used. If symptoms of heart failure develop, intravenous administration of fast-acting cardiac glycosides is recommended.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature of 15–25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
4 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
EGIS, Hungary
Additional information
| Shelf life | 4 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at 15-25 °C |
| Manufacturer | EGIS, Hungary |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | EGIS |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Cordaflex, 10 mg 100 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.