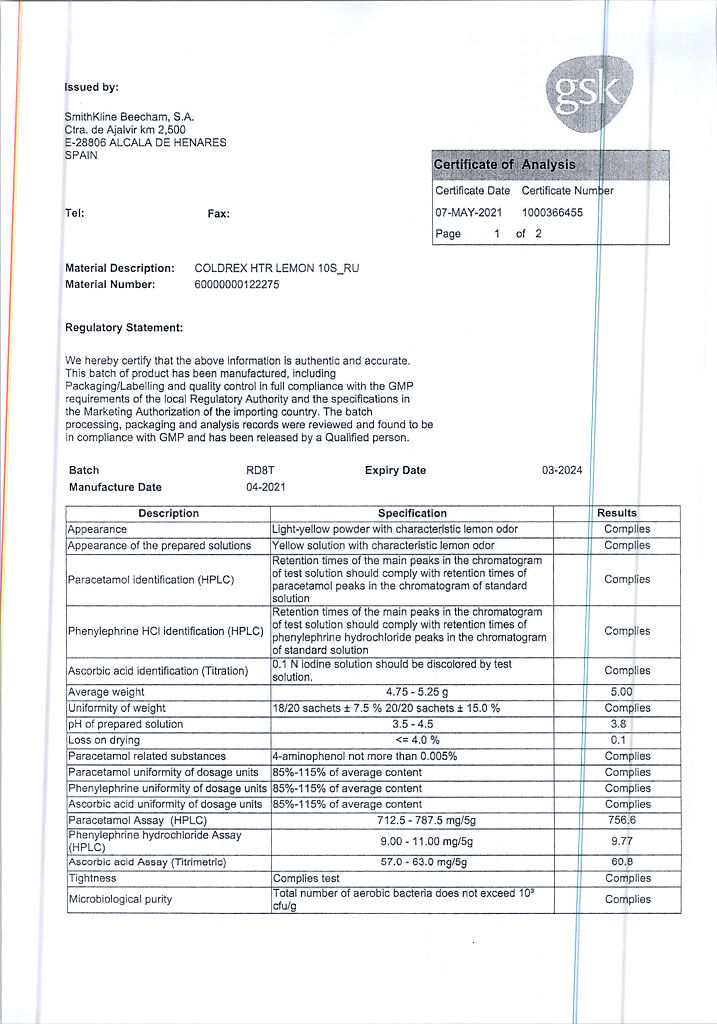
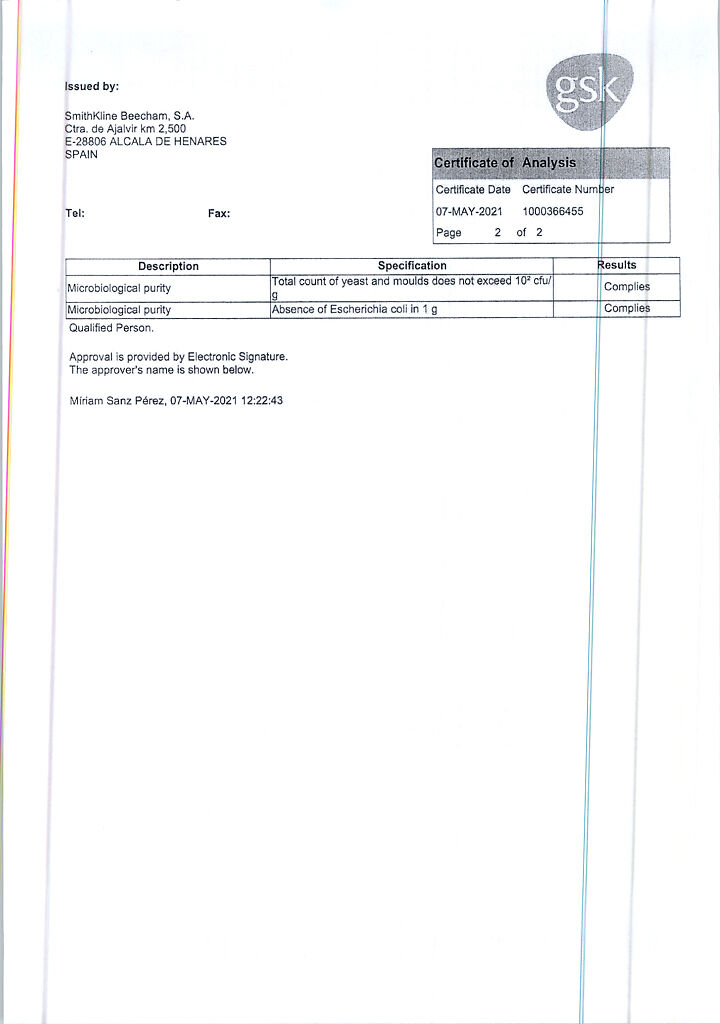
No products in the cart.
Coldrex HotRem, lemon 5 g 10 pcs
€14.21 €11.84
Description
Paracetamol is an analgesic and antipyretic.
Indications
Indications
To eliminate symptoms of acute respiratory infections and flu, including:
— increased body temperature;
– headache;
– chills;
– pain in joints and muscles;
– nasal congestion;
– pain in the throat and sinuses.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
A combined product whose effect is determined by its constituent components.
Paracetamol is an analgesic and antipyretic.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The patient should be informed that if symptoms persist after 5 days of using the drug, they should stop taking it and consult a doctor.
The drug should be taken only in recommended doses.
The patient should stop taking the drug and consult a doctor immediately if the following side effects occur:
allergic reactions: itching or redness of the skin, difficulty breathing or swelling of the lips, tongue, throat or face;
rash or peeling on the skin, formation of ulcers on the oral mucosa;
bruising or bleeding;
loss of vision. This may be a consequence of increased intraocular pressure. Very rarely, but most likely, this side effect occurs in patients with glaucoma;
feeling of a strong heartbeat or an increase in heart rate or heart rhythm disturbances;
difficulty urinating. This side effect is most often observed in patients with prostatic hypertrophy.
You should not take the drug if you have previously experienced breathing problems when taking acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs.
The drug should not be taken concomitantly with other drugs containing paracetamol, as well as other non-narcotic analgesics (metamizole sodium), NSAIDs (acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen), barbiturates, anticonvulsants, rifampicin and chloramphenicol, sympathomimetics (such as decongestants, appetite suppressants, amphetamine-like psychostimulants), with other drugs to relieve cold and flu symptoms.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Paracetamol, Phenylephrine, [Ascorbic Acid]
Composition
Composition
Paracetamol;
Phenylephrine;
Ascorbic acid
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The drug should not be used during pregnancy without first consulting a doctor!
Animal and human studies have not shown any risk of using paracetamol during pregnancy or adverse effects on intrauterine development.
There is no sufficient data on the effect of drugs containing phenylephrine on the course of pregnancy.
Breastfeeding period
The drug should not be used during breastfeeding without first consulting a doctor!
Paracetamol penetrates the placental barrier and into breast milk. Studies conducted on humans have not shown any negative effects on the baby’s body during breastfeeding.
Phenylephrine may pass into breast milk.
Contraindications
Contraindications
— Severe liver dysfunction;
– severe renal dysfunction;
— hyperthyroidism (including thyrotoxicosis);
— diabetes mellitus;
– sucrase/isomaltase deficiency, fructose intolerance, glucose/galactose malabsorption syndrome, because the drug contains sucrose;
– heart disease (severe stenosis of the aortic mouth, acute myocardial infarction, tachyarrhythmias);
— arterial hypertension;
– simultaneous use of tricyclic antidepressants, beta-blockers, MAO inhibitors and a period of up to 14 days after their withdrawal;
– simultaneous use of other paracetamol-containing drugs and drugs to relieve symptoms of colds, flu and nasal congestion;
– benign prostatic hyperplasia;
— angle-closure glaucoma;
– children up to 12 years of age;
— hypersensitivity to the components of the drug
Side Effects
Side Effects
Determination of the frequency of side effects: very often (≥1/10), often (≥1/100 and <1/10), infrequently (≥1/1000 and <1/100), rarely (≥1/10,000 and <1/1000), very rarely (≥1/100,000 and <1/10,000).At recommended doses, the drug is usually well tolerated.Paracetamol rarely has side effects.From the hematopoietic system: very rarely – thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis.Allergic reactions: very rarely – anaphylactic shock, skin rash, urticaria, angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.From the respiratory system: very rarely – bronchospasm in patients sensitive to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs.
From the liver and biliary tract: very rarely – impaired liver function.
With long-term use in excess of the recommended dose, hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic effects may occur.
Phenylephrine
From the nervous system: often – increased excitability, headache, dizziness, insomnia; very rarely – irritability, nervous tension.
From the cardiovascular system: often – increased blood pressure; rarely – tachycardia, palpitations.
From the digestive system: often – nausea, vomiting.
From the sensory organs: rarely – mydriasis, acute attack of glaucoma in most cases in patients with angle-closure glaucoma.
Allergic reactions: rarely – skin rash, urticaria, allergic dermatitis.
From the urinary system: rarely – dysuria, urinary retention in patients with obstruction of the bladder outlet due to prostatic hypertrophy.
Ascorbic acid
The incidence of side effects has not been established.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, skin hyperemia.
From the digestive system: irritation of the gastrointestinal mucosa.
From the hematopoietic system: thrombocytosis, hyperprothrombinemia, erythropenia, neutrophilic leukocytosis.
Other: hypokalemia.
When taking ascorbic acid more than 600 mg/day, moderate pollakiuria is possible.
If side effects occur, the patient should immediately stop taking the drug and consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If any of the above side effects worsen, or any other side effects occur, the patient should inform the doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
Paracetamol, when taken for a long time, enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants (warfarin and other coumarins), which increases the risk of bleeding. Occasional administration of a single dose of the drug does not have a significant effect on the effect of indirect anticoagulants.
Inducers of microsomal oxidation enzymes in the liver (barbiturates, diphenin, carbamazepine, rifampicin, zidovudine, phenytoin, ethanol, flumecinol, phenylbutazone and tricyclic antidepressants) increase the risk of hepatotoxicity in overdoses and concomitant use with paracetamol.
Microsomal oxidation inhibitors (cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity.
Paracetamol reduces the effectiveness of diuretics.
Metoclopramide and domperidone increase, and cholestyramine reduces the rate of absorption of paracetamol.
Paracetamol enhances the effects of MAO inhibitors, sedatives, ethanol.
Phenylephrine when taken with MAO inhibitors can lead to an increase in blood pressure.
Phenylephrine reduces the effectiveness of beta-blockers and antihypertensive drugs, increases the risk of developing arterial hypertension and disorders of the cardiovascular system.
Concomitant use of phenylephrine with sympathomimetic amines may increase the risk of adverse cardiovascular effects.
Tricyclic antidepressants enhance the sympathomimetic effect of phenylephrine and may increase the risk of side effects from the cardiovascular system.
Concomitant use of halothane with phenylephrine increases the risk of developing ventricular arrhythmia.
Phenylephrine reduces the hypotensive effect of guanethidine, which, in turn, enhances the alpha-adrenergic stimulating activity of phenylephrine.
Antidepressants, antiparkinsonian drugs, antipsychotic drugs, phenothiazine derivatives increase the risk of developing urinary retention, dry mouth, constipation.
Concomitant administration of GCS with phenylephrine increases the risk of developing glaucoma.
When used simultaneously with digoxin and cardiac glycosides, the risk of developing heart rhythm disturbances or a heart attack may increase.
Ascorbic acid increases the risk of developing crystalluria during treatment with salicylates and short-acting sulfonamides, slows down the excretion of acids by the kidneys, increases the excretion of drugs that have an alkaline reaction (including alkaloids), and reduces the concentration in the blood of oral contraceptives.
Ethanol contributes to the development of acute pancreatitis.
Myelotoxic drugs enhance the hematotoxicity of the drug.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of overdose of Coldrex® HotRem (even if you feel well), the risk of delayed signs of serious liver damage should be taken into account.
Symptoms caused by paracetamol: within 24 hours – pale skin, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, abdominal pain; within 12-48 hours, signs of liver dysfunction, signs of impaired glucose metabolism and metabolic acidosis may appear.
Clinical pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology
Paracetamol is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, distribution in body fluids is relatively even.
Metabolized primarily in the liver with the formation of several metabolites.
T1/2 when taking a therapeutic dose is 2-3 hours. The main amount of the drug is excreted after conjugation in the liver. No more than 3% of the received dose of paracetamol is excreted unchanged.
Phenylephrine is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and undergoes first-pass metabolism in the intestine and liver under the influence of MAO. When phenylephrine is taken orally, the bioavailability of the drug is limited.
It is excreted almost entirely in the urine as a sulfuric acid conjugate.
Ascorbic acid is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, binding to plasma proteins is 25%. Distribution in body tissues is wide.
Metabolized in the liver, excreted in the urine as oxalate and unchanged.
Ascorbic acid, taken in excessive quantities, is quickly excreted unchanged in the urine.
Short product description
Short product description
Coldrex HotRem is a combined drug, the effect of which is determined by the active components included in its composition:
Paracetamol has an analgesic and antipyretic effect.
Phenylephrine is a vasoconstrictor, relieves nasal congestion (narrows the vessels of the nasal mucosa and paranasal sinuses) and facilitates breathing.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) replenishes the need for vitamin C for colds and flu.
The active ingredients of Coldrex HotRem do not cause drowsiness.*
* Instructions for medical use, RU P N016305/01
Recommendations for use
Recommendations for use
If you have one of the following diseases/conditions/risk factors, be sure to consult your doctor before taking the drug:
Benign hyperbilirubinemia.
Mild to moderate liver and kidney dysfunction.
Alcoholic liver disease.
Cardiovascular diseases, including high blood pressure, occlusive vascular disease (Raynaud’s syndrome).
Pheochromocytoma.
The presence of severe infections, including sepsis, because taking the drug may increase the risk of metabolic acidosis.
Patients with glutathione deficiency (in particular, extremely malnourished patients suffering from anorexia, chronic alcoholism or patients with a low body mass index).
Concomitant use of antihypertensive drugs.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
It is recommended to store the drug out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
SmithKline Beecham S.A., Spain
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | The drug should be kept out of reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | SmithKlein Beecham S.A., Spain |
| Medication form | Powder for preparation of solution for oral administration |
| Brand | SmithKlein Beecham S.A. |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Coldrex HotRem, lemon 5 g 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.