No products in the cart.
Description
Antianallergic agent – H1-histamine receptor blocker.
Pharmacodynamics
Loratadine – the active ingredient of Claritin®, is a tricyclic compound with pronounced antihistamine action and is a selective blocker of peripheral H1-histamine receptors. It has a fast and prolonged antiallergic effect. Onset of action is within 30 minutes after oral administration of Claritin®. Antihistamine effect reaches its maximum after 8-12 hours from the beginning of action and lasts for more than 24 hours.
Loratadine does not penetrate through the blood-brain barrier and has no effect on the central nervous system. It has no clinically significant anticholinergic or sedative effect, i.e. it does not cause drowsiness and does not affect the speed of psychomotor reactions when used in the recommended doses. Administration of Claritin® drug does not lead to prolongation of QT interval on ECG.
Long-term treatment showed no clinically significant changes in vital signs, physical examination data, laboratory results or electrocardiography. Loratadine has no significant selectivity for H2-histamine receptors. It does not inhibit norepinephrine reuptake and has practically no effect on the cardiovascular system or rhythm driver function.
Pharmacokinetics
Loratadine is rapidly and well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Time to reach maximum concentration (Tmax) of loratadine in blood plasma is 1-1.5 hours, and its active metabolite desloratadine – 1.5-3.7 hours. Eating increases the time to reach the maximum concentration (Tmax) of loratadine and desloratadine by approximately 1 hour, but has no effect on the effectiveness of the drug.
The maximum concentration (Cmax) of loratadine and desloratadine is independent of food intake. In patients with chronic renal disease the maximum concentration (Cmax) and area under the curve “concentration-time” (AUC) of loratadine and its active metabolite are increased compared to patients with normal renal function. Half-lives of loratadine and its active metabolite do not differ from those of healthy patients. In patients with alcoholic liver damage Cmax and AUC of loratadine increased twice as much as these indexes in patients with normal liver function, while pharmacokinetics of its active metabolite did not change significantly.
Loratadine has a high degree (97-99%) and its active metabolite a moderate degree (73-76%) of binding to plasma proteins. Loratadine is metabolized to desloratadine via the cytochrome P450 3A4 system and, to a lesser extent, the cytochrome P450 2D6 system. It is excreted through the kidneys (about 40% of the oral dose taken) and the intestines (about 42% of the oral dose) for more than 10 days, mainly as conjugated metabolites. Approximately 27% of the ingested dose is excreted through the kidneys within 24 hours after drug administration. Less than 1% of active substance is excreted unchanged through the kidneys within 24 hours after drug intake.
The bioavailability of loratadine and its active metabolite is dose-dependent.
The pharmacokinetic profiles of loratadine and its active metabolite in adult and elderly healthy volunteers were comparable.
The elimination half-life of loratadine ranged from 3 to 20 hours (mean 8.4 hours) and that of desloratadine from 8.8 to 92 hours (mean 28 hours); in older patients, from 6.7 to 37 hours (mean 18.2 hours) and 11 to 39 hours (mean 17.5 hours), respectively. The half-life increases with alcoholic liver damage (depending on the severity of the disease) and does not change in the presence of chronic renal failure.
Hemodialysis in patients with chronic renal failure has no effect on the pharmacokinetics of loratadine and its active metabolite.
Indications
Indications
Seasonal (hay fever) and year-round allergic rhinitis and allergic conjunctivitis – elimination of symptoms associated with these diseases – sneezing, itching of the nasal mucosa, rhinorrhea, burning and itching sensation in the eyes, lacrimation.
Chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
Antiallergic agent – H1-histamine receptor blocker.
Pharmacokinetics:
Loratadine is quickly and well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The time to reach the maximum concentration (Tmax) of loratadine in the blood plasma is 1-1.5 hours, and its active metabolite desloratadine is 1.5-3.7 hours. Eating food increases the time to reach maximum concentration (Tmax) of loratadine and desloratadine by approximately 1 hour, but does not affect the effectiveness of the drug. The maximum concentration (Cmax) of loratadine and desloratadine is independent of food intake. In patients with chronic kidney disease, the maximum concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of loratadine and its active metabolite are increased compared to patients with normal renal function. The half-lives of loratadine and its active metabolite do not differ from those in healthy patients. In patients with alcoholic liver damage, the Cmax and AUC of loratadine are doubled compared to these values in patients with normal liver function, while the pharmacokinetics of its active metabolite do not change significantly.
Loratadine has a high degree (97-99%), and its active metabolite has a moderate degree (73-76%) of binding to plasma proteins.
Loratadine is metabolized to desloratadine via the cytochrome P450 3A4 system and, to a lesser extent, the cytochrome P450 2D6 system. Excreted through the kidneys (approximately 40% of the oral dose) and intestines (approximately 42% of the oral dose) for more than 10 days, mainly in the form of conjugated metabolites. Approximately 27% of an oral dose is excreted through the kidneys within 24 hours of taking the drug. Less than 1% of the active substance is excreted unchanged through the kidneys within 24 hours after taking the drug.
The bioavailability of loratadine and its active metabolite is dose-dependent. The pharmacokinetic profiles of loratadine and its active metabolite in adults and elderly healthy volunteers were comparable.
The half-life of loratadine ranges from 3 to 20 hours (average 8.4 hours), and that of desloratadine ranges from 8.8 to 92 hours (average 28 hours); in elderly patients, respectively, from 6.7 to 37 hours (average 18.2 hours) and from 11 to 39 hours (average 17.5 hours). The half-life increases with alcoholic liver damage (depending on the severity of the disease) and does not change in the presence of chronic renal failure.
Hemodialysis in patients with chronic renal failure does not affect the pharmacokinetics of loratadine and its active metabolite.
Pharmacodynamics:
Loratadine, the active substance of the drug Claritin®, is a tricyclic compound with a pronounced antihistamine effect and is a selective blocker of peripheral H1-histamine receptors. Has a quick and long-lasting antiallergic effect. The onset of action is within 30 minutes after taking the drug Claritin® orally. The antihistamine effect reaches its maximum 8-12 hours after the onset of action and lasts more than 24 hours.
Loratadine does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier and has no effect on the central nervous system. Does not have a clinically significant anticholinergic or sedative effect, i.e. does not cause drowsiness and does not affect the speed of psychomotor reactions when used in recommended doses. Taking the drug Claritin® does not lead to prolongation of the QT interval on the ECG.
No clinically significant changes in vital signs, physical examination findings, laboratory results, or electrocardiography were observed during long-term treatment.
Loratadine does not have significant selectivity for histamine H2 receptors. Does not inhibit norepinephrine reuptake and has virtually no effect on cardiovascular or pacemaker function.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Claritin® should be discontinued 48 hours before skin testing, as antihistamines may interfere with diagnostic test results.
With caution:
Severe liver dysfunction.
Pregnancy
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Loratadine
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
active ingredient: loratadine 10 mg;
excipients: lactose monohydrate 71.3 mg, corn starch 18 mg, magnesium stearate 0.7 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
A large amount of data on the use of loratadine in pregnant women (more than 1000 cases analyzed) indicate that the drug does not influence the occurrence of malformations or feto- and neonatal toxicity of loratadine.
No reproductive toxicity was observed in animal studies.
As a precaution, it is advisable to avoid using the drug during pregnancy. Loratadine and its active metabolite are excreted into breast milk, therefore, when prescribing the drug during breastfeeding, the issue of stopping breastfeeding should be considered.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Intolerance or hypersensitivity to loratadine or any other component of the drug.
Children under 3 years of age and body weight less than 30 kg.
Breastfeeding period.
Patients with rare hereditary diseases (impaired galactose tolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption).
Side Effects
Side Effects
In clinical studies involving children aged 2 to 12 years, headache (2.7%), nervousness (2.3%), and fatigue (1%) were observed more often than in the placebo group (“dummy”).
In clinical studies in adults, adverse events observed more often than with placebo occurred in 2% of patients taking Claritin®. In adults, when using the drug Claritin®, headache (0.6%), drowsiness (1.2%), increased appetite (0.5%) and insomnia (0.1%) were observed more often than in the placebo group.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), side effects are classified according to their frequency as follows: very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10), uncommon (≥ 1/1000 to < 1/100), rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1000), very rare (< 1/10000); frequency unknown - based on available data, it was not possible to determine the frequency of occurrence.Information on side effects is provided based on the results of observations of the post-registration period.
From the immune system: very rarely – allergic reactions (including angioedema, anaphylaxis).
From the nervous system: very rarely – dizziness, convulsions.
From the cardiovascular system: very rarely – tachycardia, palpitations.
From the digestive system: very rarely – dry mouth, nausea, gastritis.
From the liver and biliary tract: very rarely – liver dysfunction.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: very rarely – rash, alopecia.
General disorders: very rarely – fatigue.
Laboratory and instrumental data: frequency unknown – increase in body weight.
If any of these side effects get worse or you notice any other side effects not listed in the instructions, tell your doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
Eating does not affect the effectiveness of Claritin®.
The drug Claritin® does not enhance the effects of alcohol on the central nervous system.
Potential interactions may occur with all known inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2D6, resulting in increased plasma levels of loratadine and an increased risk of side effects.
When loratadine was taken together with ketoconazole and erythromycin (inhibitors of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme) or cimetidine (inhibitor of the CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 isoenzymes), an increase in the concentration of loratadine in plasma was observed, but this increase was not clinically significant, including according to electrocardiography.
When used simultaneously with drugs that inhibit hepatic metabolism, caution should be exercised.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: drowsiness, tachycardia, headache.
In case of overdose, consult a doctor immediately.
Treatment: symptomatic and supportive therapy. It is possible to lavage the stomach, take adsorbents (crushed activated carbon with water).
Loratadine is not eliminated by hemodialysis. After emergency care is provided, it is necessary to continue monitoring the patient’s condition.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Bayer Bitterfeld GmbH, Germany
Additional information
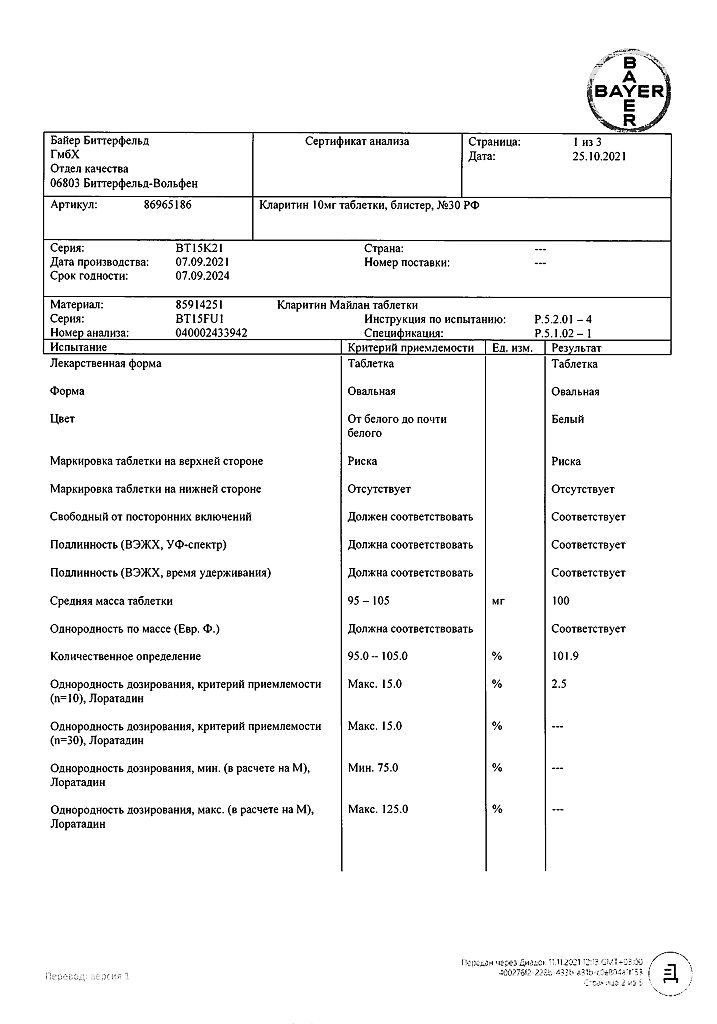
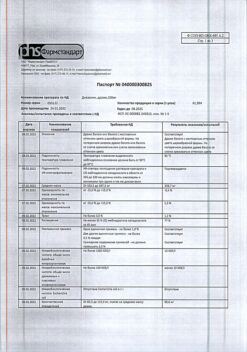
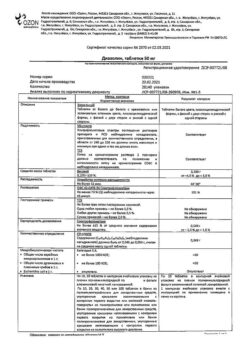
| Shelf life | 4 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Keep out of reach of children at 2° to 30°C. |
| Manufacturer | Bayer Bitterfeld GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Bayer Bitterfeld GmbH |
Related products
Buy Claritin, tablets 10 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.