No products in the cart.
Ciprofloxacin-Teva, 500 mg 10 pcs
€4.32 €3.84
Description
Urinary tract infections, Bronchitis, Adnexitis, Salmonellosis, Otitis media, Lung inflammation (pneumonia), Infectious diseases, Respiratory tract infections, Skin infections, Eye infections, Intestinal infections
Uncomplicated and complicated infections caused by microorganisms sensitive to
ciprofloxacin.
For adult patients
- Respiratory tract infections. Ciprofloxacin is recommended for
Pneumonias caused by Klebsiella spp, Enterobacter spp., Proteus spp., Esherichia coli,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus spp., Moraxella catarrhalis, Legionella spp. and
Staphylococci;
- infections of the middle ear (otitis media), especially if these infections are caused by
Gram-negative microorganisms, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- eye infections;
- Kidney infections and/or complicated urinary tract infections;
- gender organ infections, including adnexitis, gonorrhea, prostatitis;
- infections of the abdomen (bacterial infections of the gastrointestinal tract,
biliary tract, peritonitis;
- Skin and soft tissue infections;
- bone and joint infections;
- sepsis;
- infections or prevention of infections in immunocompromised patients
(immunosuppressed patients or patients with neutropenia);
- Selective intestinal decontamination in immunocompromised patients;
- prevention and treatment of inhalational anthrax (infection with Bacillus
anthracis);
- prevention of invasive infections caused by Neisseria meningitides.
To treat the following infectious and inflammatory diseases, ciprofloxacin
can only be used as an alternative to other antimicrobial
drugs:
- acute sinusitis;
- uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
The current official guidelines for the use of antibacterial agents must be taken into consideration.
Children
- Treating complications caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in children with cystic fibrosis
Lungs from 5 to 17 years of age;
- prevention and treatment of inhalational anthrax (infection with Bacillus
anthracis) from 3 to 18 years (for this dosage form).
The use of ciprofloxacin in children should be initiated only after a benefit/risk assessment due to possible adverse effects on joints and periarticular tissues.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
The tablets should be taken orally, regardless of meals, without chewing, with a small amount of liquid.
If the drug is taken on an empty stomach, the active ingredient is absorbed more quickly. In this case, do not wash the tablets with dairy products or calcium-rich drinks (e.g., milk, yogurt, juices with high calcium content). Calcium in regular foods has no effect on absorption of ciprofloxacin.
If because of the severity of the patient’s condition or for other reasons the patient is unable to take tablets, parenteral therapy with ciprofloxacin infusion solution is recommended, and after the patient’s condition improves, the patient should switch to tablet form of the drug.
In the absence of other prescriptions, the following dosing regimen is recommended:
Adults
Table 1. Depending on the severity of the infection and the patient’s condition)
from 2Ã500 mg to 2Ã750 mg
Infections of the urogenital system:
– acute, uncomplicated
2Ã250 mg to 2Ã500 mg
– cystitis in women (before menopause)
1Ã500 mg
– complicated
from 2Ã500 mg to 2Ã750 mg
– adnexitis, prostatitis, orchitis, epididymitis
/p>
2Ã500 mg to 2Ã750 mg
Gonorrhea
– extragenital
1Ã500 mg
p> – acute, uncomplicated
Diarrhea
2Ã500 mg
Other infections (see
The indications for
2Ã500 mg
Extremely severe, life-threatening
Life-threatening, includingÑ.
– streptococcal pneumonia
– recurrent infections in
pulmonary cystic fibrosis
– bone and joint infections
– septicemia
– peritonitis
Especially in the presence of Pseudomonas,
Staphylococcus or Streptococcus
2Ã750 mg
Pulmonary anthrax
(post-exposure)
2Ã15 mg/kg body weight (maximum dose
500 mg)
The dosing regimen for inhalational anthrax (treatment and prevention) see.
Table 1 and Table 2
The drug should be started immediately after suspected or confirmed infection.
The total duration of ciprofloxacin therapy for inhalational anthrax is 60 days.
Dosing regimen for renal or hepatic impairment in adults
Table 3. Recommended doses for patients with renal impairment
.Creatinine clearance (ml /
min / 1.73 m2 )
Plasma creatinine
(mg/100 ml)
/p>
Maximal daily dose
ciprofloxacin at
oral administration
30 to 60
1.4 to 1.9
1000 mg maximum
below 30 > 2.0
500 mg maximum
/p>
Patients with renal impairment on hemodialysis
deficiency) or its plasma concentration of 1.4 to 1.9 mg/100 ml
The maximum oral dose of ciprofloxacin should be 1000 mg per
day.
failure) or its plasma concentration of 2 mg/100 ml or more,
The maximum oral dose of ciprofloxacin should be 500 mg per
day. On hemodialysis days, ciprofloxacin is taken after
the procedure.12
Ambulatory patients with renal failure who are on
continuous peritoneal dialysis
. The maximum daily dose of ciprofloxacin should be 500 mg (1 tablet of
Ciprofloxacin-Teva 500 mg or 2 tablets of Ciprofloxacin-
Teva 250 mg).
Patients with hepatic impairment
Dose adjustment is not required.
Patients with renal and hepatic impairment
The dosing regimen is similar to that described in items 1 and 2.
Children with renal and/or hepatic impairment
The dosing regimen in children with renal and hepatic impairment has not been studied.
The duration of therapy
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease, clinical and
bacteriological control. It is important to continue treatment systematically for at least 3
days after fever or other clinical symptoms disappear.
The average duration of treatment:
– 1 day for acute uncomplicated gonorrhea and cystitis;
– up to 7 days for kidney, urinary tract, and abdominal infections;
– The entire period of neutropenia in immunocompromised patients;
– no more than 2 months in osteomyelitis;
– 7 to 14 days in other infections.
Infections caused by Streptococcus spp., because of the risk of late complications, treatment should continue for at least 10 days.
Infections caused by Chlamydia spp.,the treatment should also be continued for at least 10 days.
Interaction
Interaction
Drugs that cause QT interval prolongation
Patients receiving medications that cause QT interval prolongation should be treated with caution when using ciprofloxacin as well as other fluoroquinolones simultaneously./p>
QT interval prolongation (e.g. antiarrhythmic drugs of class I A or class III, tricyclic antidepressants, macrolides, neuroleptics) (see section “Special indications”). See section “Special Indications”).
Chelate compound formation
. Concomitant administration of tablet forms of ciprofloxacin and cationic products, mineral supplements containing calcium, magnesium, aluminum, iron,
sucralfate, antacids, polymeric phosphate compounds (such as sevelamer, lanthanum carbonate) and drugs with high buffering capacity (such as didanosine tablets) containing magnesium, aluminum or calcium reduce absorption of ciprofloxacin. In these cases, ciprofloxacin should be taken either 1-2 hours before,
or 4 hours after taking these drugs.
This restriction does not apply to drugs belonging to the class of
H2-histamine receptor blockers.
Eating food and dairy products
. Simultaneous use of ciprofloxacin and dairy products or mineral-rich beverages (e.g., milk, yogurt, calcium-rich orange juice) should be avoided because absorption of ciprofloxacin may be decreased. However, calcium in other foods has no significant effect on absorption of ciprofloxacin.
Metoclopramide
. Metoclopramide accelerates absorption of ciprofloxacin (when taken orally), which leads to a shorter time to reach maximum plasma concentrations of ciprofloxacin. No effect on the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin has been found.
Omeprazole
. When ciprofloxacin and preparations containing omeprazole are used concomitantly, a slight decrease in the maximum plasma concentration of the drug and a decrease in the area under the pharmacokinetic curve “concentration-time” may be observed.
Theophylline
The concomitant use of ciprofloxacin and drugs containing theophylline may cause an undesirable increase in plasma concentration of theophylline and
Theophylline-induced adverse events may occur accordingly; in very rare cases these adverse events may be life-threatening. If concomitant use of the two drugs is unavoidable, continuous monitoring of plasma theophylline concentrations and, if necessary, reducing the dose of theophylline is recommended (see Special Precautions, Cytochrome P450).
Other xanthine derivatives
The simultaneous use of ciprofloxacin and caffeine or pentoxifylline (oxpentifylline) may increase the serum concentration of xanthine derivatives.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
. The combination of very high doses of quinolones (DNA gyrase inhibitors) and some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (excluding acetylsalicylic acid) may provoke seizures.
Cyclosporine
In the simultaneous use of ciprofloxacin and drugs containing ciclosporine, a transient transient increase in plasma creatinine concentration was observed. In such cases, creatinine blood concentrations should be determined twice a week.
Peroral hypoglycemic agents
. When using ciprofloxacin concomitantly with oral hypoglycemic agents, primarily sulfonylureas (e.g., glibenclamide, glimepiride), hypoglycemia is presumably caused by potentiation of the oral hypoglycemic agents (see “Side effects”). see section “Side effects”).
Probenecid
Probenecid slows the rate of renal excretion of ciprofloxacin. Concomitant use of ciprofloxacin and drugs containing probenecid leads to increased concentrations of ciprofloxacin in the blood plasma.
Phenytoin18
Concomitant use of ciprofloxacin and phenytoin has resulted in changes (increased or decreased) in plasma phenytoin. To prevent a decrease in the anticonvulsant effect of phenytoin due to decreased concentrations, and to prevent adverse events associated with phenytoin overdose when stopping ciprofloxacin, it is recommended that
Monitor phenytoin therapy in patients taking both medications, including determination of plasma phenytoin levels throughout the period
of concurrent use of both medications and for a short time after completion of combined therapy.
Methotrexate
. Concomitant use of methotrexate and ciprofloxacin may inhibit renal-channel transport of methotrexate, which may be accompanied by increased plasma concentrations of methotrexate. This may increase the likelihood of side effects of methotrexate. Therefore, patients receiving concomitant therapy with methotrexate and ciprofloxacin should be closely monitored.
Tizanidine
A clinical study in healthy volunteers with concomitant use of ciprofloxacin and drugs containing tizanidine showed increased tizanidine serum concentrations: 7-fold increase in maximum concentration (Cmax) (4 to 21 times), 10-fold increase in AUC (area under the pharmacokinetic curve “concentration-time”) (6 to 24 times). Increased serum concentration of tizanidine may cause decreased blood pressure and drowsiness. Thus, concomitant use of ciprofloxacin and drugs containing tizanidine is contraindicated.
Duloxetine
In clinical studies it has been shown that simultaneous
use of duloxetine and potent CYP450 1A2 isoenzyme inhibitors (such as fluvoxamine), may result in increased AUC and Cmax of duloxetine. Although there are no clinical data on possible interaction with ciprofloxacin, one can foresee the possibility of such interaction when ciprofloxacin and duloxetine are used simultaneously.
Ropinirol
. Concomitant use of ropinirole and ciprofloxacin, a moderate inhibitor of the CYP450 1A2 isoenzyme, results in a 60 and 84% increase in Cmax and AUC of ropinirole,19 respectively. The adverse effects of ropinirole should be monitored during its co-administration with ciprofloxacin and for a short period of time after completion of combined therapy.
Lidocaine
. In a study in healthy volunteers, concomitant use of drugs containing lidocaine and ciprofloxacin, a moderate inhibitor of the CYP450 1A2 isoenzyme, was found to decrease lidocaine clearance by 22%
when administered intravenously. Although lidocaine is well tolerated when used concomitantly with ciprofloxacin, there may be increased side effects due to the interaction (see section “Special Precautions”, Cytochrome P450).
Clozapine
. When clozapine and ciprofloxacin were used concomitantly at a dose of 250 mg for 7 days, there was a 29% and 31% increase in serum concentrations of clozapine and N-desmethylclozapine, respectively. The patient’s condition should be monitored and, if necessary, the dosing regimen of clozapine should be adjusted during its co-administration with ciprofloxacin and for a short time after completion of combined therapy (see section “Special Precautions”, Cytochrome P450).
Sildenafil
When used concomitantly in healthy volunteers with ciprofloxacin at a dose of 500 mg
warfarin, acenocoumarol, phenprocoumon, fluindone) may lead to strengthening of their anticoagulant effect. The magnitude of this effect may vary depending on the
compatient infections, age and general condition of the patient, so it is difficult to estimate
the effect of ciprofloxacin on MHO (international normalized ratio) increase. MHO should be monitored quite frequently during co-administration of ciprofloxacin and vitamin K antagonists, and for a short time after completion of combined therapy.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Severe infections, staphylococcal infections and infections due to .Gram-positive and anaerobic bacteria
.In the treatment of severe infections, staphylococcal infections and infections caused by anaerobic bacteria, ciprofloxacin should be used in combination with appropriate antibacterial agents.
Infections due to Streptococcus pneumoniae
Ciprofloxacin is not recommended for the treatment of infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae because of its limited effectiveness against the pathogen.
Genital tract infections
.In genital infections suspected to be caused by strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae.resistant to fluoroquinolones, information about local resistance to ciprofloxacin should be considered and sensitivity of the pathogen should be confirmed with laboratory tests.
Urinary tract infections
Fluoroquinolone resistance to Escherichia coli., the most common pathogen causing urinary tract infections, varies by region of the Russian Federation. When prescribing, it is recommended to take into account the local prevalence of resistance of Escherichia coli to fluoroquinolones.
Cardiac disorders
Ciprofloxacin has an effect on QT interval prolongation (see section “Adverse effects”). Given that women are characterized by longer average QT interval duration compared to men, they are more sensitive to drugs that cause QT interval prolongation. Elderly patients also have increased sensitivity to the action of drugs that cause prolongation of the interval
Application in children
Ciprofloxacin, like other drugs in this class, has been found to cause arthropathy of large joints in animals. In a review of current data on the safety of ciprofloxacin use in children under 18 years of age, most of whom have pulmonary fibrosis, no association between cartilage or joint damage and the use of the drug has been established. Ciprofloxacin in children is not recommended for the treatment of diseases other than the treatment of complications of pulmonary cystic fibrosis (in children 5 to 17 years old) associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and for the treatment and prevention of inhalational anthrax (after suspected or proven infection with Bacillus anthracis).
Hypersensitivity
Sometimes already after the first dose of ciprofloxacin, hypersensitivity to the drug may develop (see “Side effects” section). Side effects”), including allergic reactions, which should be immediately reported to the attending physician. In rare cases, after the first use, anaphylactic reactions up to and including anaphylactic shock may occur. In these cases the use of ciprofloxacin should be stopped immediately and appropriate treatment should be carried out.
Gastrointestinal tract
.If severe and prolonged diarrhea occurs during or after ciprofloxacin treatment, the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis should be excluded, which requires immediate drug withdrawal and appropriate treatment (oral vancomycin 250 mg 4 times daily). Drugs which inhibit intestinal peristalsis are contraindicated in this situation.
Hepatobiliary system
Hepatic necrosis and life-threatening liver failure have been reported with ciprofloxacin. In the presence of the following signs of liver disease, such as anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, itching, painful abdomen, ciprofloxacin administration should be stopped (see section “Side effects”).
In patients taking ciprofloxacin who have had liver disease, a temporary increase in liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase activity or cholestatic jaundice may be observed.
Motor system
Patients with severe myasthenia gravis should use ciprofloxacin with caution because exacerbation of symptoms is possible.
At the first signs of tendinitis (painful swelling of the joint area, inflammation) the use of ciprofloxacin should be stopped, physical activity should be avoided, because there is a risk of tendon rupture, and a physician should be consulted.
In cases of tendonitis and tendon rupture (mainly Achilles tendon) may occur while taking ciprofloxacin, sometimes bilaterally, during the first 48 hours after starting therapy. Inflammation and tendon rupture may occur even several months after ciprofloxacin treatment termination. Elderly patients, patients with renal insufficiency, patients after organ transplantation receiving concomitant treatment with corticosteroids have an increased risk of tendinopathy.
Ciprofloxacin should be used with caution in patients with a history of quinolone-related tendon disease.
Nervous system
Ciprofloxacin, like other fluoroquinolones, may provoke seizures and lower the seizure threshold. In patients with epilepsy and CNS disorders (e.g., decreased seizure threshold, history of seizures, impaired cerebral circulation, organic brain lesions or stroke) due to the risk of CNS adverse reactions, ciprofloxacin should be used only when the expected clinical effect exceeds the possible risk of side effects of the drug.
When using ciprofloxacin, cases of epileptic status have been reported (see section “Adverse effects”).
If seizures occur, the drug should be discontinued.
Mental reactions may occur even after the first use of fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin. In rare cases, depression or psychotic reactions may progress to suicidal thoughts and suicidal completions (see section “Side effects”). In case of development of any side effects on the central nervous system, including mental disorders, it is necessary to immediately cancel the drug Ciprofloxacin-Teva and initiate
appropriate therapy. In these cases, conversion to therapy with an antibiotic other than fluoroquinolones is recommended, if possible.
Patients taking fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, have had cases of sensory or sensorimotor polyneuropathy, hypoesthesia, dysesthesia or weakness. If symptoms such as pain, burning, tingling, numbness, weakness occur, patients should inform their physician before continuing use of the drug.
Skin
A photosensitization reaction may occur when taking ciprofloxacin, so patients should avoid contact with direct sunlight and UV light.
The treatment should be discontinued if photosensitization symptoms are observed (e.g., skin changes similar to sunburns, see section “Side effects.
Cytochrome P450
Ciprofloxacin is known to be a moderate inhibitor of CYP450 1A2 isoenzymes. Caution should be exercised when concomitant use of ciprofloxacin and drugs metabolized by these enzymes, such as theophylline,
methylxanthine, caffeine, duloxetine, ropinirole, clozapine, olanzapine, agomelatine – because the increased serum concentrations of these drugs due to
inhibition of their metabolism by ciprofloxacin may cause specific adverse reactions. Simultaneous use of ciprofloxacin and tizanidine is contraindicated.
The recommended daily dose should not be exceeded to avoid development of crystalluria, and adequate fluid intake and maintenance of acidic urine are also necessary.
In the in vitro setting, ciprofloxacin may interfere with the bacteriological study of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, inhibiting its growth.by inhibiting its growth, which may lead to false-negative results
Ciprofloxacin may interfere with the bacteriological study of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in patients taking ciprofloxacin.
Dysglycemia
As with other fluoroquinolones, changes in blood glucose concentrations, including hypo- and hyperglycemia, are possible with ciprofloxacin. Dysglycemia is more likely to occur with ciprofloxacin therapy in elderly patients and patients with diabetes receiving concomitant therapy with oral
Hypoglycemic agents (such as sulfonylurea preparations) or insulin. When using ciprofloxacin in such patients the risk of hypoglycemia increases, up to hypoglycemic coma. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of hypoglycemia (confusion, dizziness, “wolfish” appetite, headache, nervousness, palpitations or increased pulse rate, pale skin, sweating, trembling, weakness). If the patient develops hypoglycemia, ciprofloxacin treatment should be stopped immediately and appropriate therapy should be started. In these cases, it is recommended to switch to therapy with another antibiotic other than
fluoroquinolones, if possible. When treatment with ciprofloxacin in elderly patients, close monitoring of blood glucose concentrations is recommended in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Aneurysm and aortic dissection
.Epidemiologic studies have reported an increased risk of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection after fluoroquinolones, especially in elderly patients.
In this regard, fluoroquinolones should be used only after careful assessment of the benefit/risk ratio and consideration of other therapy options in patients with a family history of aortic aneurysm or in patients with a diagnosed aneurysm
aortic aneurysm and/or aortic dissection or in the presence of other risk factors or conditions predisposing to the development of an aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection (e.g., Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos vascular syndrome, Takayasu arteritis, giant cell arteritis, Behçet disease, arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis).
In case of sudden pain in the abdomen, chest or back, patients should immediately see a physician in the emergency department.
Influence on driving, operating machinery
Fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, may impair patients’ ability to drive and engage in other potentially dangerous activities requiring increased attention and rapid psychomotor reactions due to the effect on the CNS.
Synopsis
Synopsis
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin or other drugs from the group of
fluoroquinolones or excipients (see section “Composition”).
significant adverse effects (hypotension, somnolence) associated with increased
Tizanidine plasma concentrations (see section “Interaction with other drugs”). See “Interaction with other
drugs”).
Side effects
Side effects
The adverse reactions listed below are classified as follows:
“very common” (â¥10), “common” (â¥1/100 to < 1/10), “infrequent” (â¥1/1000 to < 1/100),
“rare” (â¥1/10 000 to < 1/1000), “very rare” (⤠10000), “frequency unknown”.
Unwanted reactions that have been reported only in postmarketing
observations and whose frequency has not been evaluated are designated “frequency unknown.
Infectious and parasitic diseases
Infrequent: mycotic superinfections.
Rarely: pseudomembranous colitis (in very rare cases with possible lethal outcome)
.p> Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Infrequent: eosinophilia.
Rarely: leukopenia, anemia, neutropenia, leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, thrombocythemia.
Very rare: hemolytic anemia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia (life-threatening),
Bone marrow suppression (life-threatening).
Immune system disorders
Rarely: allergic reactions, allergic edema/ angioedema.
very rare: anaphylactic reactions, anaphylactic shock (life-threatening),
serum sickness.
Endocrine system disorders
Frequency unknown: syndrome of inadequate antidiuretic hormone secretion.
Disorders of metabolism and nutrition
Infrequent: decreased appetite and the amount of food taken.
Rarely: hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia.
Frequency unknown: severe hypoglycemia, up to the development of hypoglycemic
coma, especially in elderly patients, patients with diabetes mellitus taking
oral hypoglycemic drugs or insulin.
Mental disorders
Infrequent: psychomotor hyperactivity/ agitation.
Rarely: confusion and disorientation, anxiety, disturbed dreams
(nightmares), depression (increased self-harm behaviors such as
suicidal behaviors/thoughts, and attempted or successful suicide),
Hallucinations.
Very rare: psychotic reactions (increased self-harm behavior, such
as suicidal acts/thoughts, and attempted or successful suicide).
Frequency unknown: attention deficits, nervousness, memory impairment, delirium.
Nervous system disorders
Infrequent: headache, dizziness, sleep disturbances, taste disorders.
Rarely: paresthesias and dysesthesias, hypoesthesia, tremors, seizures (including seizures
epilepsy), vertigo.
Very rare: migraine, impaired movement coordination, impaired sense of smell,
hyperesthesia, intracranial hypertension (cerebral pseudotumor symptomatology).
Frequency unknown: peripheral neuropathy and polyneuropathy.
Visual disorders
Rarely: vision disorders.
very rare: disorder of color perception.
Hearing and labyrinth disorders
Rarely: Tinnitus, hearing loss.
very rare: hearing disorders.
Cardiac disorders
Rarely: tachycardia.
Frequency unknown: long QT interval, ventricular arrhythmias (including pirouette type)*.
vascular disorders
Rarely: vasodilation, decreased blood pressure, fainting.
very rare: vasculitis.
Disorders of the respiratory system, thoracic and mediastinal organs
Rarely: respiratory disorders (including bronchospasm).
Gastrointestinal tract disorders
Frequently: nausea, diarrhea.
Infrequent: vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, flatulence.
Very rare: pancreatitis.
Liver and biliary tract disorders
Infrequent: increased activity of “hepatic” transaminases, increased concentration of bilirubin.
Rarely: disorders of liver function, jaundice, hepatitis (non-infectious).
Very rare: necrosis of liver tissue (in extremely rare cases progressing to life-threatening liver failure).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Infrequent: rash, itching, urticaria.
Rarely: photosensitization, blistering.
Very rare: petechia, small erythema multiforme, nodular erythema,
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (malignant exudative erythema), including potentially life-threatening; Lyell syndrome (toxic epidermal necrolysis), including potentially life-threatening.
Frequency unknown: acute generalized pustular exanthema.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Infrequent: arthralgia.
Rarely: myalgia, arthritis, increased muscle tone, muscle cramps.
Very rare: muscular weakness, tendinitis, tendon rupture (mostly Achilles), exacerbation of myasthenia gravis symptoms.
Renal and urinary tract disorders
Infrequent: disorders of renal function.
Rarely: renal failure, hematuria, crystalluria, tubulointerstitial nephritis.
General disorders and disorders at the site of administration
Infrequent: Pain syndrome of nonspecific etiology, general malaise, fever.
Rarely: sedema, sweating (hyperhidrosis).
very rare: disordered gait.
Influence on the results of laboratory and instrumental studies
Infrequent: increased activity of alkaline phosphatase in the blood.
Rarely: changes in prothrombin, increased amylase activity.
Frequency unknown: increased INR (in patients receiving vitamin K antagonists).
*frequently in patients with a predisposition to develop QT interval prolongation.
The incidence of the following adverse reactions is higher with intravenous injection and with
Step therapy with ciprofloxacin (intravenous injection followed by oral administration) than with oral administration:
often – vomiting, increased “hepatic” transaminase activity, rash;
not infrequently – thrombocytopenia, thrombocythemia, confusion and disorientation,
hallucinations, paresthesias and dysesthesias, seizures, vertigo, visual disturbances, loss
hearing, tachycardia, vasodilation, decreased blood pressure, reversible liver function abnormalities, jaundice, renal failure, edema;
not infrequently – pancytopenia, bone marrow depression, anaphylactic shock, psychotic
reactions, migraine, sense of smell, hearing impairment, vasculitis, pancreatitis, liver tissue necrosis, petechiae, tendon rupture.
Children
The development of arthropathies has often been reported in children.
The incidence of arthropathy (arthralgia, arthritis) listed above is based on clinical studies in adult patients. In children, the incidence of arthropathy is estimated to be frequent.
Overdose
Overdose
Treatment: no specific antidote is known.
The patient’s condition should be monitored carefully, gastric lavage should be performed, the usual first aid measures should be carried out, and adequate fluid intake should be ensured.
Only a small (less than 10%) amount of the drug may be eliminated by hemo- or peritoneal dialysis.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
The use of ciprofloxacin is contraindicated in pregnancy and during breastfeeding. The safety of using ciprofloxacin in pregnant women has not been established.
But based on the results of animal studies, the potential for adverse effects on articular cartilage in newborns cannot be completely ruled out, and therefore ciprofloxacin should not be prescribed for pregnant women. No teratogenic effects (malformations) have been found in animal studies.
Ciprofloxacin is excreted in breast milk. Because of the potential risk of articular cartilage damage in newborns, ciprofloxacin should not be administered to breastfeeding women.
Application in children
The use of ciprofloxacin is contraindicated in children under 3 years of age (for this dosage form and dosage). Ciprofloxacin is not recommended for use in children
under 18 years of age for the treatment of other infectious diseases, except for the treatment of complications of pulmonary cystic fibrosis (in children from 5 to 17 years) caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and for the treatment and prevention of inhalational anthrax (after suspected or
proven infection with Bacillus anthracis). The use of ciprofloxacin in children should be initiated only after a benefit/risk assessment due to possible
adverse effects on the joints and periarticular tissues.
With caution
In diseases of the central nervous system: Epilepsy, decreased seizure threshold (or history of seizures), marked atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, impaired cerebral circulation, organic brain lesions or stroke; mental illness (depression, psychosis); marked renal and/or liver failure, tendon lesions with previous treatment with quinolones; increased risk of QT interval prolongation or pirouette arrhythmia (e.g., congenital QT interval prolongation syndrome, heart disease (heart failure, myocardial infarction, bradycardia), electrolyte imbalance (e.g., hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia)); simultaneous use of medications that prolong the QT interval (including, in the case of hypoglycaemia).Ñ. Antiarrhythmic drugs of classes IA and III, tricyclic antidepressants, macrolides, neuroleptics);
Concomitant use with inhibitors of CYP450 isoenzyme 1A2 (including theophylline, methylxanthine, caffeine, duloxetine, clozapine, ropinirole, olanzapine,
agomelatine); myasthenia gravis; glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency; use in elderly patients; patients with a family history of aortic aneurysm or patients with a diagnosed aortic aneurysm and/or aortic dissection or in the presence of the presence of other risk factors or conditions predisposing to the development of an aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection (e.g., Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Takayasu arteritis, gigantocellular arteritis, Behcet’s disease, arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis) (see
Particular indications
Particular indications
). See section “Special Indications”).
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
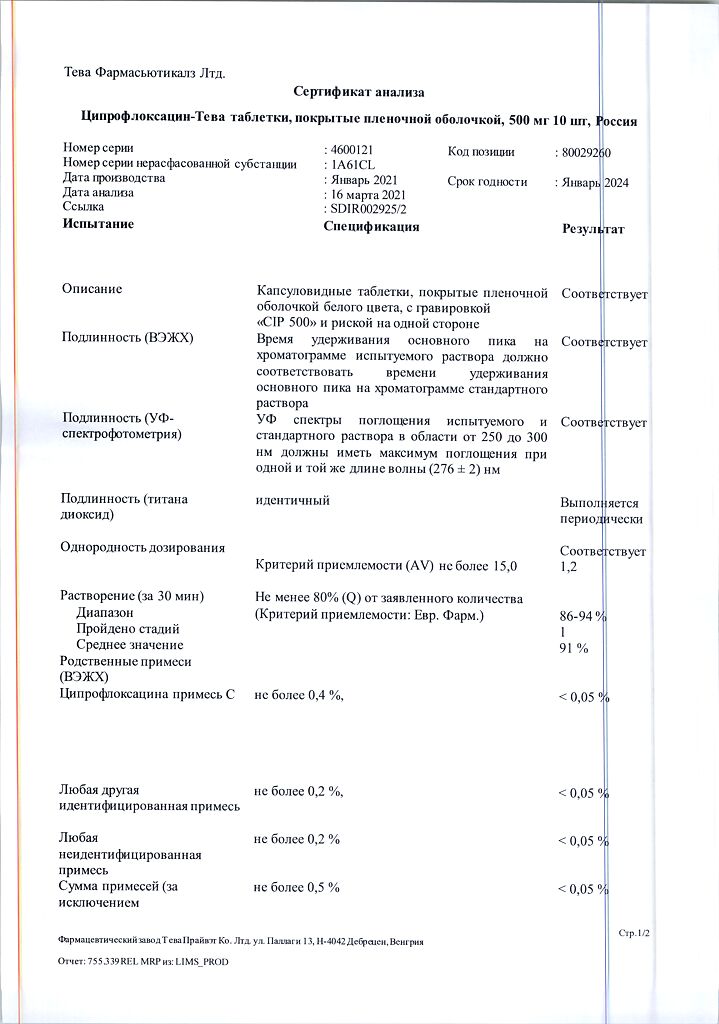
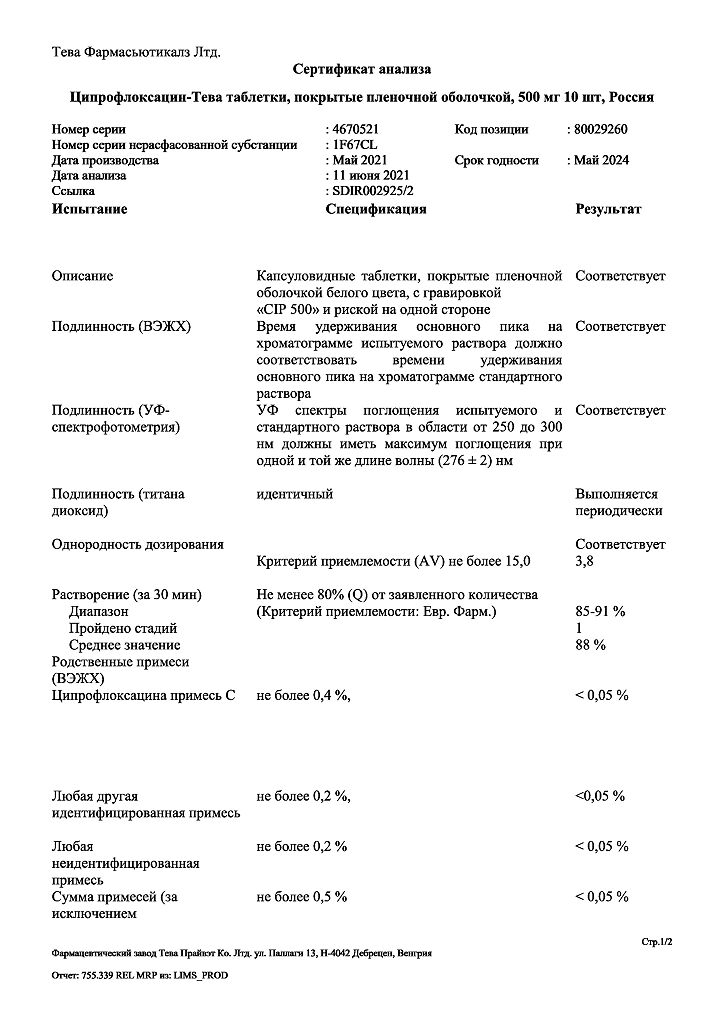
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Teva Pharmaceutical Works Production Limited Company, Hungary |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Teva Pharmaceutical Works Production Limited Company |
Related products
Buy Ciprofloxacin-Teva, 500 mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.