No products in the cart.
Description
Chloropyramine is a blocker of H1-histamine receptors. Its chemical structure is related to ethylenediamine derivatives. Chloropyramine selectively blocks H1-histamine receptors and reduces capillary permeability. It prevents the development and facilitates the course of allergic reactions. It has sedative, antihistamine, m-cholinoblocking and pronounced antipruritic effect. It has moderate antispasmodic and antiemetic activity.
Pharmacokinetics
It is evenly distributed in the body including the central nervous system. Penetrates through the blood-brain barrier. Binding of chloropyramine with blood plasma proteins is 7.9%. Peak binding is noted at pH 6.8-7.4. Therapeutic concentration is maintained for 4-6 hours. It is intensively metabolized in liver.
It is excreted mainly through kidneys with urine as metabolites. Excretion of chloropyramine in children may be faster than in adults.
Indications
Indications
Allergic diseases, including:
hives,
rhinitis,
conjunctivitis,
hay fever (hay fever),
angioedema,
serum sickness,
drug allergy,
skin diseases, including:
eczema,
contact dermatitis,
skin itching,
neurodermatitis,
toxicoderma.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamics
Chloropyramine is an H1-histamine receptor blocker. According to its chemical structure, it belongs to ethylenediamine derivatives. Chloropyramine selectively blocks H1-histamine receptors and reduces capillary permeability. Prevents the development and facilitates the course of allergic reactions. It has a sedative, antihistamine, m-anticholinergic and pronounced antipruritic effect. Has moderate antispasmodic activity and antiemetic effect.
Pharmacokinetics
Evenly distributed throughout the body, including the central nervous system. Penetrates the blood-brain barrier. The binding of chloropyramine to plasma proteins is 7.9%. Peak binding was observed at pH 6.8-7.4. The therapeutic concentration lasts 4-6 hours. It is intensively metabolized in the liver.
It is excreted primarily through the kidneys with urine in the form of metabolites. Elimination of chloropyramine may occur more rapidly in children than in adults.
Special instructions
Special instructions
During treatment, drinking alcoholic beverages is prohibited.
Taking the drug at night may increase the symptoms of reflux esophagitis.
If during long-term use of the drug there is an unreasonable increase in body temperature, laryngitis, pallor of the skin, jaundice, the formation of ulcers of the oral mucosa, the appearance of hematomas, unusual and difficult to stop bleeding, you should consult a doctor, since prolonged therapy with antihistamines can lead to hematopoietic disorders.
Antihistamines can distort the manifestation of the reaction when performing allergy skin tests, therefore, a few days before the planned test, the use of the drug should be discontinued.
When combined with ototoxic drugs, chloropyramine may mask early manifestations of ototoxicity.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Patients using chloropyramine are advised to refrain from driving vehicles, operating machinery, and other activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Chloropyramine
Composition
Composition
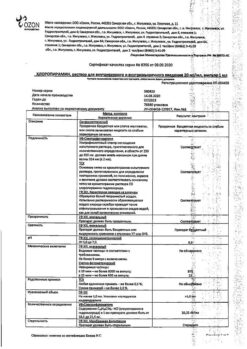
1 ml of solution for intramuscular and intravenous administration contains:
active ingredient:
chloropyramine hydrochloride 20 mg;
excipient: water for injection.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Individual hypersensitivity to the drug or its components;
acute attack of bronchial asthma;
simultaneous use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors;
newborn children (up to 1 month);
pregnancy and lactation;
gastric ulcer in the acute stage;
prostatic hyperplasia;
severe respiratory failure.
With caution
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the side of the central nervous system: lethargy, weakness, drowsiness, dizziness, headache, euphoria, feeling of fatigue, irritability, tremor, convulsions, impaired coordination of movements, blurred vision; in children, there may be some stimulating effect on WYC, manifested by anxiety, increased irritability, and insomnia.
From the digestive system: dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, gastralgia, diarrhea/constipation, loss or increase in appetite.
From the urinary system: difficulty urinating.
From the cardiovascular system: decreased blood pressure (more often in elderly patients), tachycardia, arrhythmia.
From the hematopoietic system: very rarely – leukopenia, agranulocytosis.
From the organs of vision: increased intraocular pressure.
Other: photosensitivity, muscle weakness.
Allergic reactions to the drug.
Interaction
Interaction
Enhances the effect of drugs for general anesthesia, sleeping pills, sedatives, tranquilizers, anticholinergic drugs, opioid analgesics, local anesthetics.
Tricyclic antidepressants and MAO inhibitors enhance the m-anticholinergic and inhibitory effect on the central nervous system.
Caffeine and phenamine reduce the inhibitory effect on the central nervous system.
Concomitant use with ethanol is not recommended (risk of severe CNS depression).
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: in children – agitation, anxiety, hallucinations, athetosis, ataxia, convulsions, mydriasis, pupillary immobility, facial skin flushing, hyperthermia; then – collapse, coma. In adults – depression (lethargy, depression) or excitation of the central nervous system (psychomotor agitation), very rarely – hallucinations, loss of coordination, dilated pupils and lack of reaction to light, dry mouth, hyperthermia and redness of the skin, convulsions, in severe cases – coma.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy (including the prescription of antiepileptic drugs, caffeine, phenamine), resuscitation measures, artificial ventilation – according to indications. There is no specific antidote.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
PharmFirma Sotex, Russia
Additional information
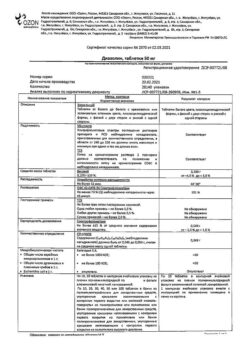
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | PharmFirm Sotex, Russia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | PharmFirm Sotex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Chloropyramine, 20 mg/ml 1 ml 5 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.