No products in the cart.
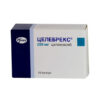
Celebrex, capsules 200 mg 10 pcs
€16.42 €14.23
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmgroup:
NSAIDs.
The celecoxib is an NSAID. Celecoxib has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects by blocking the formation of inflammatory prostaglandins (Pg) mainly by inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Induction of COX-2 occurs in response to inflammation and leads to the synthesis and accumulation of prostaglandins, especially prostaglandin E2, with increased manifestations of inflammation (swelling and pain).
In human therapeutic doses, celecoxib does not significantly inhibit cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and has no effect on prostaglandins synthesized by COX-1 activation, and does not affect normal physiological processes related to COX-1 and running in tissues, especially in stomach, intestine and platelet tissues.
The effect on renal function. Celecoxib reduces urinary excretion of PgE2 and 6-keto-PgF1 (a prostacyclin metabolite), but has no effect on serum thromboxane B2 and urinary excretion of 11-dehydro-thromboxane B2, a metabolite of thromboxane (both COX-1 products).
The celecoxib does not cause decreased glomerular filtration rate in elderly patients and those with chronic renal failure, transiently decreases sodium excretion. In patients with arthritis the observed incidence of peripheral edema, arterial hypertension and heart failure is comparable to that of non-selective COX inhibitors with inhibitory activity against COX-1 and COX-2.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption.
When taken on an empty stomach, celecoxib is well absorbed, reaching maximum concentration (Cmax) in plasma after about 2-3 hours. Cmax in plasma after administration of 200 mg is 705 ng/ml. Absolute bioavailability of the drug has not been studied. Cmax, and area under the pharmacokinetic curve “concentration-time” (AUC) are approximately proportional to the dose taken in the dose range up to 200 mg twice daily; when using the drug in higher doses the degree of increase in Cmax and AUC is less proportional.
The effect of ingestion. Administration of celecoxib with a fatty meal prolongs the time to reach Cmax by about 1 to 2 hours and increases total absorption by about 20%.
Distribution.
The binding to plasma proteins is independent of concentration and is about 97%, celecoxib does not bind to red blood cells. The drug penetrates through the blood-brain barrier.
Metabolism. celecoxib is metabolized in the liver by hydroxylation, oxidation and partially by glucuronidation. Metabolism mainly occurs with the participation of cytochrome P450 CYP2C9. (see “Interaction with other medicinal products”). Metabolites detected in blood are pharmacologically inactive against COX-1 and COX-2.
The activity of cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 is decreased in individuals with genetic polymorphisms, such as homozygous for CYP2C9*3 polymorphism, which leads to decreased enzyme activity.
Exhaustion.
The celecoxib is metabolized in the liver, excreted in the feces and urine as metabolites (57% and 27%, respectively), less than 3% of the dose taken is unchanged. When repeated use, the elimination half-life is 8-12 hours, and clearance is about 500 ml/min. With repeated use, equilibrium plasma concentrations are reached by day 5. The variability of the main pharmacokinetic parameters (AUC, Cmax, elimination half-life) is about 30%. Mean volume of distribution in the equilibrium state is about 400 l.
Particular groups
Elderly patients.
Patients older than 65 years of age show a 1.5-2-fold increase in the mean values of Cmax, AUC of celecoxib, which is caused more by changes in body weight than by age (elderly patients usually have lower mean body weight than younger patients, due to which they achieve higher celecoxib concentrations, other things being equal). For the same reason, older women usually have higher plasma concentrations than older men. These features of pharmacokinetics usually do not require dose adjustments. However, in elderly patients with body weight below 50 kg, treatment should be started with the lowest recommended dose.
Race. The representative Negro race has an AUC of celecoxib approximately 40% higher than that of Europeans. The reasons and clinical significance of this fact are not known, so it is recommended that their treatment be started with the lowest recommended dose.
Liver function impairment. Plasma concentrations of celecoxib in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A) are not significantly altered. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B) plasma concentrations of celecoxib may increase by almost 2-fold.
Kidney function impairment.
In patients with chronic renal insufficiency with glomerular filtration rate (GFR) > 65 ml/min/1.73 m2 and in patients with GFR equal to 35-60 ml/min/1.73 m2, celecoxib pharmacokinetics is not altered. No significant relationship is found between serum creatinine (or creatinine clearance) and celecoxib clearance. It is assumed that the presence of severe renal failure does not affect the clearance of celecoxib, since its main route of excretion is transformation in the liver into inactive metabolites.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 capsule:
– celecoxib 200 mg.
Excipients:
Lactose monohydrate,
Sodium lauryl sulfate,
povidone K30,
croscarmellose sodium and magnesium stearate;
coating:
titanium dioxide,
gelatin.
Capsule ink (SB-3002 yellow ink) contains:
shellac,
ethanol,
isopropanol,
butanol,
propylene glycol,
ammonia aqueous,
Iron oxide yellow dye (E172).
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
In adults with osteoarthritis, Celebrex is prescribed in a daily dose of 200 mg in 1 or 2 doses. Doses of up to 400 mg/day have been used in clinical trials.
In rheumatoid arthritis the drug is prescribed in a daily dose of 200-400 mg divided into 2 doses. Doses of up to 800 mg/day have been used in clinical trials.
In pain syndrome, the recommended single dose is 100-200 mg. If necessary, subsequent use of the drug in the same dose with an interval between doses of at least 4-6 hours until the maximum daily dose of 400 mg is reached.
In acute pain and algodysmenorrhea, the recommended starting dose is 400 mg, followed by another 200 mg dose if necessary; the maximum dose on the first day of treatment is 600 mg/day; on subsequent days the daily dose of the drug may vary from 200 mg to 400 mg.
The use of Celebrex in patients under 18 years of age has not been studied.
Interaction
Interaction
Concomitant use of celebrex with the CYP2C9 inhibitor fluconazole may increase the plasma concentration of celecoxib (celecoxib should be used at the lowest recommended dose).
It has been established in vitro that celecoxib is an inhibitor of CYP2D6, therefore there is a possibility of drug interaction with other drugs that are biotransformed with participation of this isoenzyme.
The antacids (aluminum and magnesium) decrease the degree of absorption of celecoxib by 10%, which does not cause clinically significant effects.
When studying the effect of celebrex on pharmacokinetics and/or pharmacodynamics of CYP2C9 substrates gliburide, glibenclamide, tolbutamide in vivo no clinically significant interaction was found.
In in vitro studies it was found that CYP2C19 isoenzyme may participate in the metabolism of celecoxib only to a small extent. In an in vivo study, multiple doses of celecoxib (200 mg 2 times daily for 7 days) did not affect the clearance of a single dose of the CYP2C19 substrate phenytoin. The risk of clinically significant inhibition of CYP2C19 substrate metabolism by celecoxib is considered to be insignificant.
When co-administration of Celecoxib with warfarin and similar medicinal agents may increase prothrombin time and development of serious bleeding (coagulation parameters should be monitored and precautions should be taken).
No clinically significant interaction of celecoxib with ketoconazole, lithium preparations, methotrexate was found.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Caution should be exercised when using Celebrex in gastric or duodenal ulcer disease, ulcerative colitis, heart failure, edema syndrome, arterial hypertension.
Celebrex can be used with low doses of acetylsalicylic acid. Due to the lack of action on platelets, Celebrex is not a substitute for acetylsalicylic acid in the prophylactic treatment of cardiovascular disorders.
Cerebrex should be prescribed with caution if CYP2C9 activity is decreased, as plasma levels of celecoxib may be excessively elevated.
Control of laboratory parameters
Peripheral blood counts and laboratory parameters of liver and kidney function should be monitored while using the drug.
If 17-ketosteroid determination is necessary, the drug should be stopped 48 hours before testing.
Pediatric use
There are no clinical data on the efficacy and safety of Celebrex in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Impact on ability to drive and operate machinery
The possibility of engaging in potentially hazardous activities requiring increased attention and quick psychomotor reactions should only be decided after assessing the patient’s individual response to the drug.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– history of allergic reactions (urticaria, bronchospasm) associated with taking acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs;
– marked renal dysfunction;
– marked liver dysfunction;
– III trimester of pregnancy;
– lactation (breastfeeding);
– known hypersensitivity to sulfonamides;
– hypersensitivity to the components of the preparation.
Side effects
Side effects
The digestive system: often – abdominal pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia; rarely – nausea, vomiting, heartburn, anorexia; with prolonged use in high doses – gastrointestinal mucosal ulceration, bleeding, NSAID gastropathy, constipation, flatulence, increased AST and ALT activity.
CNS and peripheral nervous system disorders: rarely – headache, dizziness, somnolence or insomnia, blurred vision, depression, agitation, confusion, anxiety, hallucinations, decreased hearing, tinnitus.
Respiratory system: rarely – sore throat, cough, shortness of breath, bronchospasm.
Urinary system disorders: rarely – renal failure, edema syndrome.
Hematopoietic system: rarely – agranulocytosis, anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Cardiovascular system disorders: rare – arterial hypertension, arrhythmia, hot flashes, palpitations, congestive heart failure, tachycardia.
Allergic reactions: bullous skin rash, angioedema, bronchospasm, anaphylaxis, vasculitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Others: alopecia, increased sweating, nasal bleeding. There are separate reports of acute pancreatitis.
Overdose
Overdose
There is no clinical experience with overdose. Healthy volunteers have taken single dose up to 1200 mg and multiple dose up to 1200 mg 2 times/day without clinically significant adverse effects.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy is carried out. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
The use of Celebrex during pregnancy (especially in III trimester) is possible only when the estimated benefit to the mother exceeds the potential risk to the fetus.
If it is necessary to use Celebrex during lactation, discontinuation of breastfeeding should be considered.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place, at 15-30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Pfizer, Puerto Rico |
| Medication form | capsules |
| Brand | Pfizer |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Celebrex, capsules 200 mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.