No products in the cart.
Ceftriaxone, 1 g 50 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
A third-generation broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic for parenteral administration. Bactericidal activity is caused by inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. It is characterized by resistance to action of most beta-lactamases of gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms.
It is active against the following microorganisms: Gram-positive aerobes – Staphylococcus aureus (including strains producing penicillinase), Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus spp. viridans group;
Gram-negative aerobes: Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Borrelia burgdorferi, Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae (including strains producing penicillinase), Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Klebsiella spp. Klebsiella pneumoniae), Moraxella catarrhalis, (including penicillin-producing strains), Morganella morganii, Neisseria gonorrhoeae (including penicillinase-producing strains), Neisseria meningitidis, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Serratia spp. (including Serratia marcescens); some strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa are also sensitive; anaerobes: Bacteroides fragilis), Clostridium spp. (except Clostridium difficile), Peptostreptococcus spp.
Has in vitro activity against most strains of the following microorganisms, although the clinical significance of this is unknown: Citrobacter diversus, Citrobacter freundii, Providencia spp. (including Providencia rettgeri), Salmonella spp, including Salmonella typhi, Shigella spp.; Streptococcus agalactiae, Bacteroides bivius, Bacteroides melaninogenicus.
Methicillin-resistant staphylococci are also resistant to cephalosporins, including ceftriaxone.Many strains of group D streptococci and enterococci, including Enterococcus faecalis, are also resistant to ceftriaxone.
Indications
Indications
Bacterial infections caused by susceptible microorganisms: Abdominal organ infections (peritonitis, inflammatory diseases of the GI tract, biliary tract, incl.Ñ. Cholangitis, gallbladder empyema), infections of the pelvic organs, infections of the lower respiratory tract (including pneumonia, lung abscess, pleural empyema), acute otitis media, infections of bones and joints, skin and soft tissue (including Infections of the urinary tract (complicated and uncomplicated), uncomplicated gonorrhea, bacterial meningitis, bacterial septicemia, Lyme disease.
Prophylaxis of post-surgical infections.
Infectious diseases in immunocompromised people.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Intravenously, intramuscularly.
In adults the initial daily dose, depending on the type and degree of infection severity is 1-2 g 1 time per day or divided into 2 doses (every 12 hours), the total daily dose should not exceed 4 g.
Lyme disease: to adults and children – 50 mg/kg (but not more than 2 g) 1 time per day during 14 days.
In uncomplicated gonorrhea – 250 mg in /m once.
To prevent postoperative complications – once 1 g 30-60 minutes before surgery. For colorectal and rectal surgeries an additional preparation from 5-nitroimidazole group is recommended.
The daily dose for infants is 20-50 mg/kg/day.
For treatment of skin and soft tissue infections in children the recommended daily dose is 50-75 mg/kg divided into two doses (every 12 hours). The total daily dose in children should not exceed 2 g.
In case of bacterial meningitis in children the initial dose is 100 mg/kg (but not more than 4 g) once a day and further 100 mg/kg/day (but not more than 4 g) once a day or divided into 2 doses (every 12 hours). The course of treatment is 7-14 days.
In treatment of acute otitis media in children a single injection in a dosage of 50 mg/kg/day (but not more than 1 g) is recommended.
In treatment of other infections in children the recommended daily dose in children is 50-75 mg/kg divided into 2 doses (every 12 hours). The total daily dose in children should not exceed 2 g.
In children with body weight of 50 kg and more we use doses for adults.
Doses over 50 mg/kg of body weight should be administered as an intravenous infusion during 30 min.
In patients with CKD (CKD less than 10 ml/min) the daily dose should not exceed 2 g; patients on hemodialysis do not require an additional dose after hemodialysis session, however, it is necessary to monitor ceftriaxone concentration in plasma as its excretion in such patients may be delayed (dose adjustment may be required).
Treatment with ceftriaxone should be continued for at least 2 days after symptoms and signs of infection have disappeared. The course of treatment is usually 4-14 days; for complicated infections a longer administration may be required. The course of treatment in infections caused by Streptococcus pyogenes should be at least 10 days.
In children with skin and soft tissue infections, a daily dose of 50-75 mg/kg once daily or 25-37.5 mg/kg every 12 hours, not more than 2 g/day. In case of severe infections with other localizations – 25-37.5 mg/kg once in 12 hours, not more than 2 g/day.
In otitis media – once in a month, 50 mg/kg, not more than 1 g.
In patients with CKD a dose adjustment is required only if CK is less than 10 ml/min. In this case the daily dose should not exceed 2 g.
In patients with renal-hepatic insufficiency the daily dose should not exceed 2 g without determining the drug concentration in plasma. For intravenous administration 0.25 or 0.5 g of the drug is dissolved in 2 ml, and 1 g in 3.5 ml of 1% lidocaine solution. It is recommended to inject not more than 1 g to one buttock.
For intravenous injection 0.25 or 0.5 g should be dissolved in 5 ml and 1 g in 10 ml of water for injection. It is administered slowly (2-4 min).
For intravenous infusion 2 g is dissolved in 40 ml of Ca2+-free solution (0.9% NaCl solution, 5-10% dextrose solution, 5% levulose solution). Doses of 50 mg/kg or more should be administered by IV drip, within 30 minutes.
Interaction
Interaction
Bacteriostatic antibiotics reduce the bactericidal effect of ceftriaxone.
Antagonism with chloramphenicol in vitro.
Pharmaceutically incompatible with solutions containing Ca2+ (including Hartmann’s and Ringer’s solutions.
Pharmaceutically incompatible with solutions containing Ca2+ (including Hartmann’s and Ringer’s solutions), as well as with amsacrine, vancomycin, fluconazole and aminoglycosides.
Contains no N-methylthiotetrazole group, therefore upon interaction with ethanol it does not lead to disulfiram-like reactions typical for some cephalosporins.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
In combined severe renal and hepatic insufficiency, as well as in patients on hemodialysis, the drug concentration in plasma should be determined regularly.
During long-term treatment it is necessary to monitor regularly peripheral blood count, liver and renal function indexes.
In rare cases at biliary bladder ultrasound there may be obscuration (precipitates of calcium salt of ceftriaxone) that disappear after discontinuation of therapy. In case of development of symptoms or signs indicating possible gallbladder disease or in presence of ultrasound signs of “sludge phenomenon” it is recommended to stop the drug administration.
Rare cases of pancreatitis developed probably due to biliary tract obstruction have been described while using the drug. Most patients had risk factors of biliary tract stasis (previous therapy with the drug, severe concomitant diseases, complete parenteral nutrition); herewith it is impossible to exclude a trigger role of precipitate formation in the biliary tract under the influence of ceftriaxone.
Ceftriaxone does not contain N-methylthiotetrazole group, which causes disulfiram-like effects with simultaneous use of ethanol and bleeding, which are inherent to some cephalosporins.
In pregnancy, use only if the estimated benefit to the mother is greater than the risk to the fetus. If it is necessary to prescribe the drug during lactation, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Rare cases of changes in prothrombin time have been described during the use of the drug. Patients with vitamin K deficiency (synthesis disorders, eating disorders) may require control of prothrombin time and administration of vitamin K (10 mg/week) if prothrombin time increases before or during therapy.
There have been described cases of fatal reactions due to deposits of ceftriaxone-Ca2+ precipitates in lungs and kidneys of neonates. Theoretically there is a possibility of interaction of ceftriaxone with Ca2+-containing solutions for IV administration and in other age groups of patients, therefore ceftriaxone should not be mixed with Ca2+-containing solutions (including for parenteral nutrition), and also administered simultaneously, including through separate accesses for infusion at different sites. Theoretically, based on the calculation of 5 T1/2 ceftriaxone, the interval between the administration of ceftriaxone and Ca2+-containing solutions should be at least 48 hours. There are no data on possible interaction of ceftriaxone with oral Ca2+-containing drugs, as well as ceftriaxone for I / M administration with Ca2+-containing drugs (IV and oral).
During treatment with ceftriaxone false positive results of Coombs test, galactosemia test, in determining glucose in urine may be observed (glucosuria is recommended to determine only by enzymatic method).
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to other cephalosporins, penicillins, carbapenems), hyperbilirubinemia in newborns, newborns who are shown by IV administration of solutions containing Ca2+.
With caution. Premature infants, renal and/or hepatic insufficiency, ulcerative colitis, enteritis or colitis associated with the use of antibacterial drugs, pregnancy, lactation.
Side effects
Side effects
Allergic reactions: rash, itching, fever or chills.
Nervous system: headache, dizziness.
Digestive system: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, taste disorders, pseudomembranous colitis.
Blood organs: anemia (including hemolytic.
Blood organs: anemia (including hemolytic), leukopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis, eosinophilia.
Genitourinary system: vaginal candidiasis, vaginitis.
Local reactions: when administered intravenously – phlebitis, pain, thickening along the vein, intravenous – pain, warmth, tautness or thickening at the injection site.
Laboratory parameters: increased (decreased) prothrombin time, increased activity of “liver” transaminases and ALP, hyperbilirubinemia, hypercreatininemia, increased concentration of urea, presence of sediment in urine.
Other: increased sweating, “tides” of blood.
Adverse reactions with a frequency less than 0.1%: abdominal pain, agranulocytosis, allergic pneumonitis, anaphylaxis, basophilia, cholelithiasis, bronchospasm, colitis, dyspepsia, nasal bleeding, abdominal bloating, gallbladder “sludge phenomenon”, glucosuria, hematuria, jaundice, leukocytosis, lymphocytosis, monocytosis, nephrolithiasis, palpitation, seizures, serum disease.
Postmarketing experience: stomatitis, glossitis, oliguria, rash, allergic dermatitis, urticaria, edema, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell syndrome.
Overdose
Overdose
Treatment: symptomatic. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are not effective.
Additional information
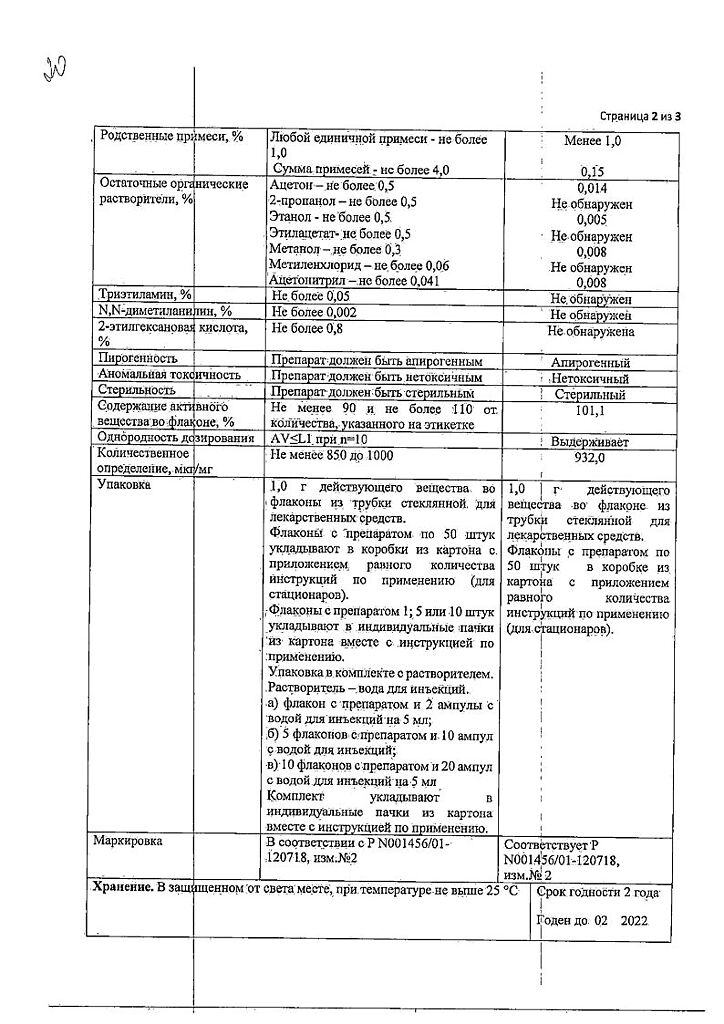
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry, light-protected place at 15-25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Biokhimik JSC, Russia |
| Medication form | Powder for preparation of solution |
| Brand | Biokhimik JSC |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Ceftriaxone, 1 g 50 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.