No products in the cart.
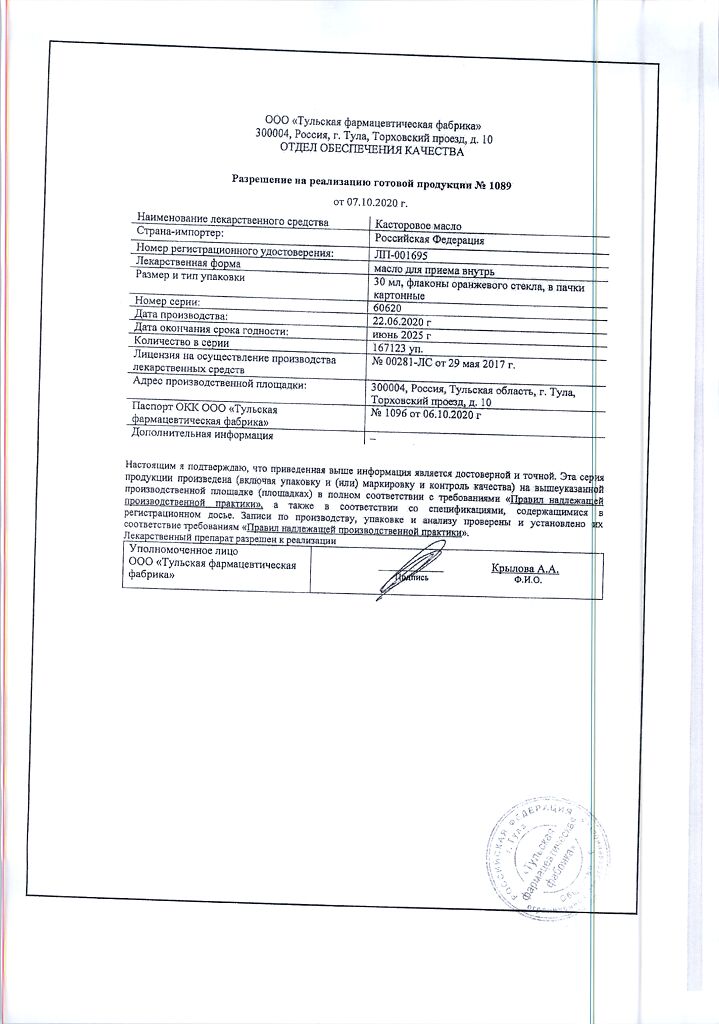
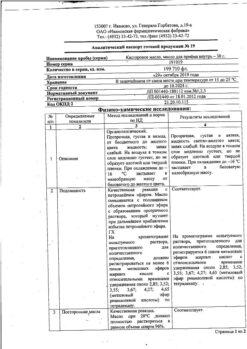
Castor oil for oral administration 30 ml
€4.30 €3.58
Description
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration in the alkaline environment of the duodenum in the presence of bile, ricinoleic acid is formed from the oil under the influence of lipase. Absorption of ricinoleic acid is inversely proportional to the amount of dose taken.
When the oil is administered in a dose of 4 g, the absorption of ricinolic acid is about 100%; when administered in a dose of 50 g, only 36% is absorbed (the rest of the acid is excreted in the faeces within 24 hours); when administered in a dose of 60 g, the percentage of absorbed acid is only 10%. The absorption rate of ricinoleic acid is half the absorption rate of oleic acid. At least 10 g of oil should be taken to develop a loosening effect.
The absorbed portion of ricinolic acid undergoes β-oxidation in the liver and skeletal muscles and is included in metabolic processes.
Pharmacodynamics
Castor oil is a laxative of vegetable origin.
The mechanism of action of castor oil is related to the ricinolic acid released from it in the duodenal lumen. At concentrations of 0.5 mmol/L, ricinolic acid irritates receptors throughout the intestine and inhibits Na+/K+/2Cl–transporters, resulting in loss of electrolyte absorption and a secondary delay in water absorption. In concentrations greater than 2 mmol/L ricinoleic acid increases water secretion into the intestinal lumen.
The volume of intestinal contents increases under the influence of castor oil, increases intestinal motility and accelerates its emptying. The oil remaining in the intestine facilitates the movement of feces through the large intestine. The laxative effect develops 2-6 hours after taking the oil and weakens after emptying the bowels.
When irritating the intestinal receptors, castor oil reflexively stimulates the centers of the spinal cord which coordinate the contractile activity of the myometrium. As a result, castor oil increases uterine contractions during pregnancy.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
Castor oil
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
As a laxative administered to adults 15 – 30 g once a day. When cleansing bowels before diagnostic procedures it is taken 2 to 6 hours before the study. Children at the age of 12-14 years old are prescribed 5 – 15 g once a day.
In case of weakness of labor strength and in order to stimulate labor activity the castor oil is administered in dose of 40-50 g once against the background of using medicines stimulating uterine contractile activity.
In dermatological practice to soften the skin and remove scales from excessive keratinization it is used topically in the form of boltushka in ethyl alcohol in 1:10 ratio with 2% salicylic acid added (10 g of castor oil, 2 g of salicylic acid, ethyl alcohol up to 100 ml). Boltushka shall be rubbed into the lesion once a day for 4 – 7 days, after which mechanical cleaning of the lesion shall be carried out and treatment shall be continued.
In the treatment of burns, skin wounds it is prescribed topically in the form of boltushkas and emulsions in distilled water 1 – 2 times a day under a bandage.
For strengthening hair growth a solution consisting of 10 g of castor oil and 100 ml of 96% ethyl alcohol is prepared and rubbed into the scalp.
Interaction
Interaction
In concomitant use reduces absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D and K. In doses up to 4 g / day increases absorption of fat-soluble drugs – male fern extract, mebendazole, griseofulvin, probucol.
In concomitant use with saline laxatives a sharp increase in the laxative effect is possible.
M-cholinoblocking agents (atropine sulfate, platifiline, pirenzepine), antispasmodics (papaverine, drotaverine) weaken the effect of castor oil.
The anticholinesterase agents (neostigmine, pyridostigmine, rivastigmine) and glycerol increase the laxative effect of castor oil.
It enhances the effect of agents that stimulate myometrial contractile activity (methylergometrine, ergometrine, oxytocin, prostaglandins) up to the threat of uterine rupture in labor.
When used topically, it increases the transcutaneous absorption of drugs applied together with it on the skin.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Impact on driving and operating machinery. During administration of castor oil it is not recommended to drive a motor vehicle, you should refrain from other operator’s activities due to possible impairment of concentration during the onset of the effect.
Caution when using. Castor oil as a laxative for more than 3 days is not recommended because it may interfere with digestion and absorption of vitamins A and D, with the development of associated hypovitaminosis.
The use of castor oil in the treatment with medicines derived from the male fern is contraindicated because systemic absorption and development of neurotoxic action are possible.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
Overdose
Overdose
It occurs when ingestion of castor oil in doses greater than 7 g/kg body weight. Diarrhea, abdominal cramps, impaired renal function, dizziness, hallucinations, loss of consciousness are characteristic.
The specific antidotes are atropine sulfate and loperamide. Treatment measures include drug withdrawal, fluid and electrolyte replacement (combined oral and intravenous administration is preferable), and supportive and symptomatic therapy to correct the abnormalities that have occurred.
If neurotoxic effects develop, diazepam 5 – 10 mg intravenously is administered.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.072 kg |
|---|---|
| Shelf life | 5 years |
| Conditions of storage | In the dark place at a temperature not exceeding 25 ºC. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Tula Pharmaceutical Factory, Russia |
| Medication form | oil for oral administration |
| Brand | Tula Pharmaceutical Factory |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Castor oil for oral administration 30 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.