No products in the cart.
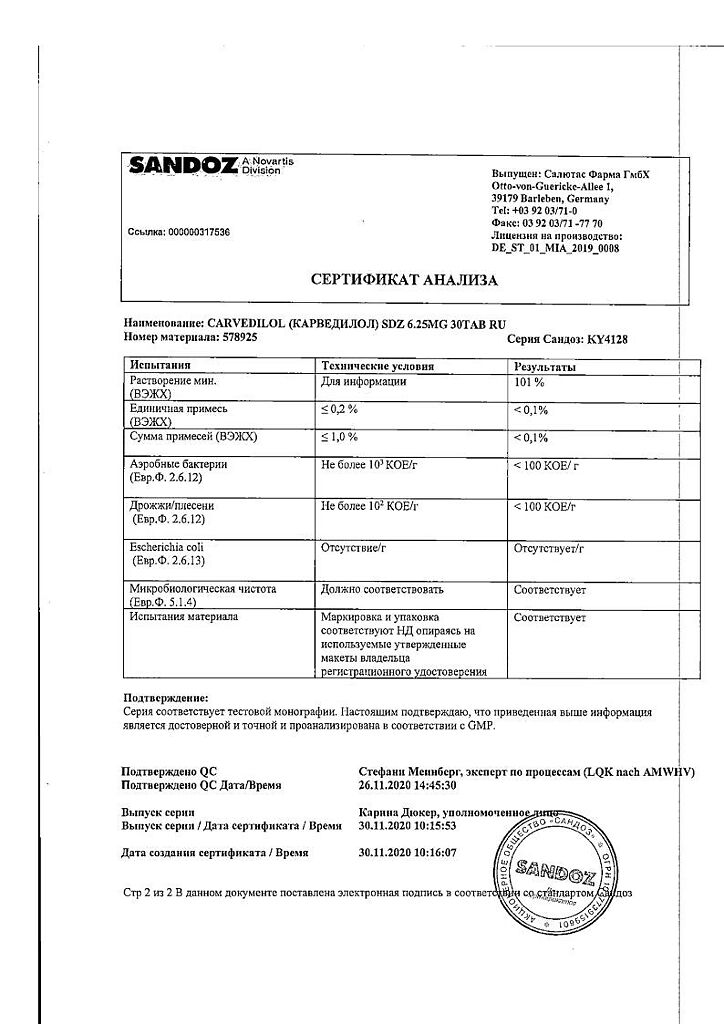
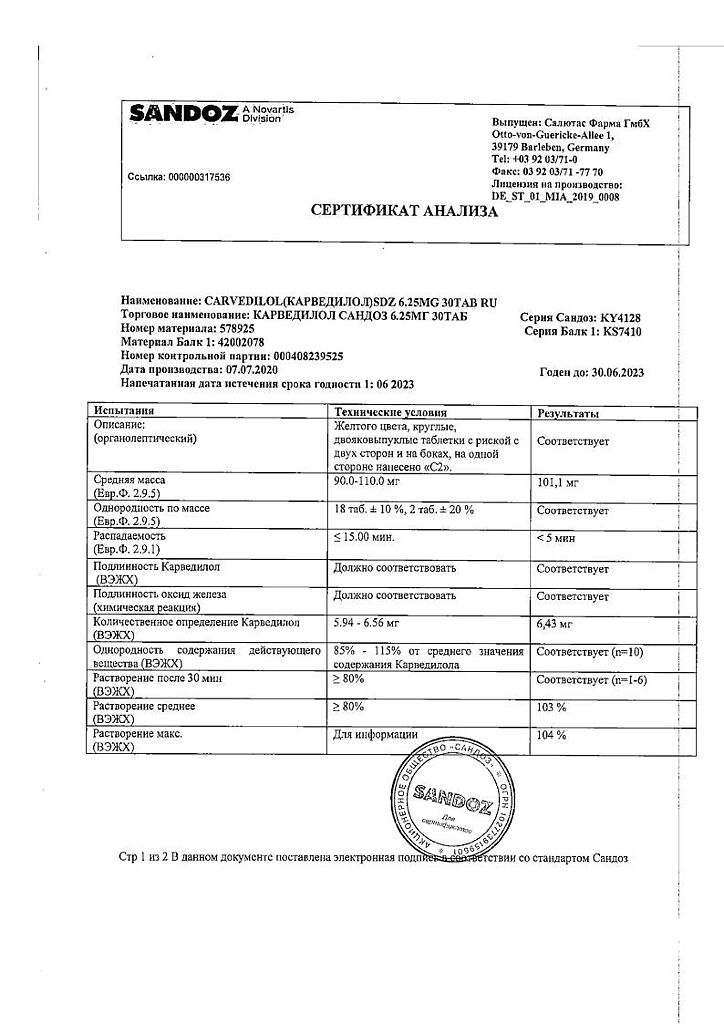
Carvedilol Sandoz, tablets 6,25mg 30 pcs
€6.25 €5.56
Description
Carvedilol has vasodilatory, antianginal, antiarrhythmic effects.
Blocks alpha1-, beta1- and beta2-adrenoreceptors.
Does not have sympathomimetic activity of its own, has membrane-stabilizing properties.
Carvedilol has an antioxidant effect, eliminating free oxygen radicals.
Indications
Indications
Arterial hypertension (monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs), stable angina.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Carvedilol has vasodilating, antianginal, and antiarrhythmic effects.
Blocks alpha1-, beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors.
It does not have its own sympathomimetic activity, but has membrane-stabilizing properties.
Carvedilol has an antioxidant effect by eliminating free oxygen radicals.
Special instructions
Special instructions
If the heart rate decreases to 55 beats/min, the drug should be discontinued. In individuals with allergies or undergoing desensitization, taking carvedilol may increase allergy sensitivity. Contact lens wearers should be warned that the drug reduces tear production.
When completing a course of treatment with Carvedilol Sandoz, simultaneously with clonidine, first gradually reduce the dosage of clonidine and then first discontinue clonidine and then carvedilol. If it is necessary to use Carvedilol Sandoz during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to avoid alcohol consumption. If circulatory failure progresses during treatment, it is recommended to increase the dose of diuretics; in case of renal failure, adjust the dose taking into account indicators of the functional state of the kidneys.
If surgery using general anesthesia is necessary, the anesthesiologist should be warned about previous therapy with carvedilol. It should be borne in mind that the drug can mask the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis and hypoglycemia, therefore it is recommended to regularly monitor blood glucose levels and, if necessary, adjust doses.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Carvedilol
Composition
Composition
1 table contains carvedilol 6.25 mg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, severe liver failure, severe bradycardia, sick sinus syndrome, AV block II and III degrees (except for patients with a pacemaker), decompensated heart failure, pulmonary hypertension or cardiogenic shock, arterial hypotension, pregnancy, breastfeeding, age under 18 years (safety and effectiveness in persons under 18 years of age have not been established).
Side Effects
Side Effects
At recommended doses, Carvedilol is well tolerated, but side effects are possible in some cases.
From the digestive system: nausea, dry mouth, abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation, vomiting, increased activity of liver transaminases.
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, feeling of fatigue, loss of consciousness, muscle weakness (usually at the beginning of treatment), sleep disturbance, depression, paresthesia.
From the senses: decreased tear production.
From the genitourinary system: impaired renal function, edema, impaired urination.
From the hematopoietic organs: leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Allergic reactions: urticaria, itching, rashes, appearance and/or exacerbation of psoriasis, sneezing, nasal congestion, bronchospasm, shortness of breath (in predisposed patients), very rarely – anaphylactoid reaction.
From the cardiovascular system: bradycardia, orthostatic hypotension, angina pectoris, AV block, progression of circulatory failure (cold extremities), progression of heart failure, exacerbation of intermittent claudication syndrome, Raynaud’s syndrome.
Endocrine disorders: weight gain.
Other: pain in the limbs, flu-like symptoms.
As with the use of other drugs that block alpha-adrenergic receptors, latent diabetes mellitus may appear or its symptoms may intensify.
Interaction
Interaction
Catecholamine depleting agents (reserpine, MAO inhibitors) can cause severe bradycardia and hypotension. Concomitant administration of ACE inhibitors, thiazide diuretics, and vasodilators prescribed simultaneously with carvedilol can lead to a sharp drop in blood pressure.
Enhances the effect of insulin and sulfonylurea derivatives (while masking or weakening the severity of symptoms of hypoglycemia, reducing the breakdown of liver glycogen to glucose).
When coadministered with insulin or oral hypoglycemic drugs, blood glucose levels should be monitored. Inhibitors of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme (quinidine, fluoxetine, propafenone) may increase the concentration of the R(+)-enantiomer of carvedilol.
Combined use with antiarrhythmic drugs (especially class I) and BMCC (verapamil, diltiazem) can provoke severe arterial hypotension and heart failure. Intravenous administration of these drugs together with carvedilol is contraindicated.
Increases the concentration of digoxin, which requires monitoring its concentration, because simultaneous administration with cardiac glycosides can lead to AV blockade.
General anesthetics enhance negative inotropic and hypotensive effects. Phenobarbital and rifampicin accelerate metabolism and reduce plasma concentrations of carvedilol. Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation (cimetidine), diuretics and ACE inhibitors increase the concentration and enhance the hypotensive effect of carvedilol. Carvedilol delays the metabolism of cyclosporine.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: pronounced decrease in blood pressure (sBP 80 mmHg and below), severe bradycardia (less than 50 beats/min), impaired respiratory function (bronchospasm, etc.), chronic circulatory failure, cardiogenic shock, cardiac arrest.
Treatment: during the first two hours, induce vomiting and rinse the stomach. An overdose requires intensive treatment, monitoring of vital functions is necessary. The patient should be in a position with his legs elevated, i.e. in the Trendelenburg position. Beta-blocking antidotes include orciprenaline or isoprenaline 0.5–1 mg IV and/or glucagon 1–5 mg (maximum dose 10 mg).
Severe hypotension is treated with parenteral fluids and repeated administration of epinephrine 5–10 mg (or IV infusion at a rate of 5 mcg/min). For excessive bradycardia, atropine is prescribed intravenously at a dose of 0.5–2 mg. To maintain cardiac activity: glucagon is administered intravenously quickly (within 30 seconds), followed by a continuous infusion at a rate of 2–5 mg/hour. If the peripheral vasodilatory effect predominates (warm extremities, in addition to significant arterial hypotension), it is necessary to prescribe norepinephrine 5-10 mcg as an intravenous infusion – 5 mcg/min.
To relieve bronchospasm, beta-agonists (in the form of an aerosol or IV) or aminophylline IV are prescribed. If convulsions develop, slow administration of diazepam or clonazepam is recommended.
In severe cases of intoxication, when symptoms of shock dominate, treatment should continue until the patient’s condition stabilizes, taking into account the T1/2 of carvedilol, which is 6–10 hours.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Salutas Pharma GmbH, Germany
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Salutas Pharma GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Salutas Pharma GmbH |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Carvedilol Sandoz, tablets 6,25mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.