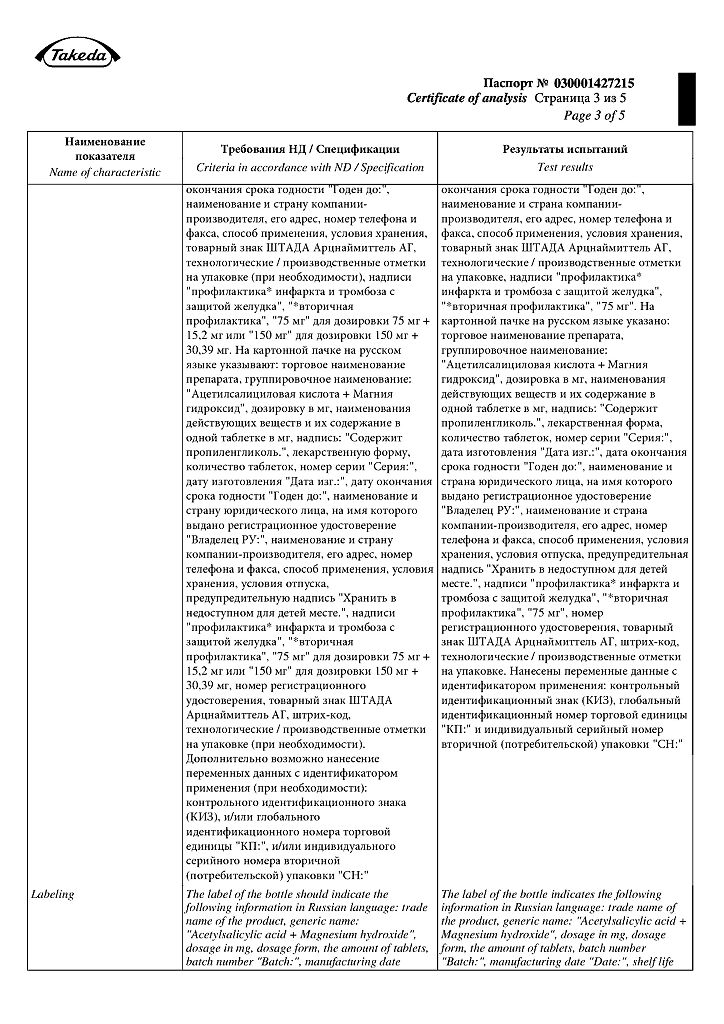
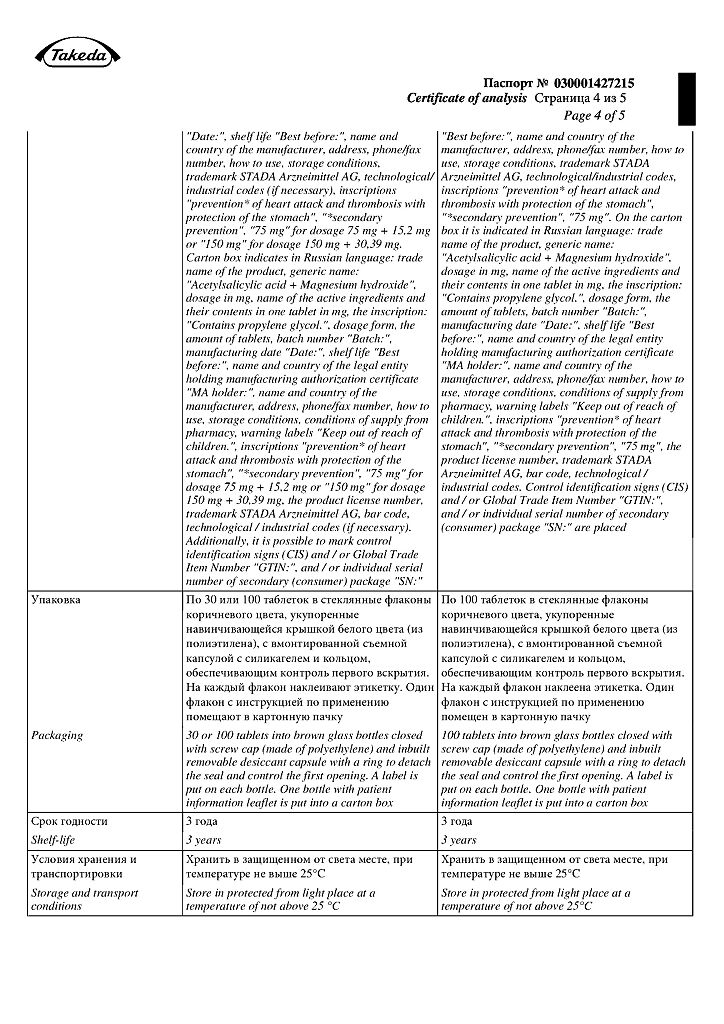
No products in the cart.
Cardiomagnil, 75 mg+15, 2 mg 100 pcs
€7.53 €6.59
Description
Cardiomagnesin is an antiaggregative.
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is based on irreversible inhibition of COX-1, resulting in blocking the synthesis of thromboxane A2 and suppressing platelet aggregation. It is believed that ASA has other mechanisms to inhibit platelet aggregation, which expands the field of its use in various vascular diseases. ASA also has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects.
Magnesium hydroxide, a component of Cardiomagnil®, protects the gastrointestinal mucosa from the effects of ASA.
Pharmacokinetics
ASK is almost completely absorbed from the GI tract. T1/2 of ASK is about 15 minutes, because with the participation of enzymes ASK is rapidly hydrolyzed into salicylic acid (SA) in the intestine, liver and blood plasma. T1/2SC is about 3 hours, but it can be significantly increased with simultaneous administration of large doses of ASA (more than 3 g) as a result of enzyme system saturation.
The bioavailability of ASK is about 70%, but this value varies considerably because ASK undergoes presystemic hydrolysis (gastrointestinal mucosa, liver) into SC under the action of enzymes. The bioavailability of SC is 80-100%.
The doses of magnesium hydroxide used do not affect the bioavailability of acetylsalicylic acid.
Indications
Indications
prevention of recurrent myocardial infarction and blood vessel thrombosis;
Primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases such as thrombosis and acute heart failure in the presence of risk factors (for example, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, obesity, smoking, old age);
unstable angina;
prevention of thromboembolism after vascular surgery (coronary artery bypass grafting, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Cardiomagnyl – antiaggregation.
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is based on the irreversible inhibition of COX-1, as a result of which the synthesis of thromboxane A2 is blocked and platelet aggregation is suppressed. It is believed that ASA has other mechanisms for suppressing platelet aggregation, which expands the scope of its use in various vascular diseases. ASA also has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects.
Magnesium hydroxide, which is part of Cardiomagnyl®, protects the gastrointestinal mucosa from the effects of ASA.
Pharmacokinetics
ASA is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract almost completely. T1/2 ASA is about 15 minutes, because with the participation of ASA enzymes, it is quickly hydrolyzed into salicylic acid (SA) in the intestines, liver and blood plasma. T1/2SA is about 3 hours, but it can increase significantly with the simultaneous administration of large doses of ASA (more than 3 g) as a result of saturation of enzyme systems.
The bioavailability of ASA is about 70%, but this value fluctuates significantly, since ASA undergoes presystemic hydrolysis (gastrointestinal mucosa, liver) into SA under the action of enzymes. The bioavailability of SA is 80–100%.
The doses of magnesium hydroxide used do not affect the bioavailability of acetylsalicylic acid.
Special instructions
Special instructions
You should take the drug Cardiomagnyl after a doctor’s prescription.
Acetylsalicylic acid can provoke bronchospasm, as well as cause attacks of bronchial asthma and other hypersensitivity reactions. Risk factors include a history of bronchial asthma, hay fever, nasal polyposis, chronic respiratory diseases, and allergic reactions (for example, skin reactions, itching, urticaria) to other drugs.
Acetylsalicylic acid can cause bleeding of varying severity during and after surgery.
Several days before planned surgery, the risk of bleeding should be assessed compared with the risk of ischemic complications in patients taking low doses of acetylsalicylic acid. If the risk of bleeding is significant, acetylsalicylic acid should be temporarily discontinued.
The combination of acetylsalicylic acid with anticoagulants, thrombolytics and antiplatelet drugs is accompanied by an increased risk of bleeding.
Taking acetylsalicylic acid in low doses can trigger the development of gout in predisposed individuals (those with reduced excretion of uric acid).
The combination of acetylsalicylic acid with methotrexate is accompanied by an increased incidence of side effects from the hematopoietic organs.
Taking acetylsalicylic acid in high doses has a hypoglycemic effect, which must be kept in mind when prescribing it to patients with diabetes mellitus receiving oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin.
When using systemic corticosteroids and salicylates in combination, it should be remembered that during treatment the concentration of salicylates in the blood is reduced, and after discontinuation of systemic corticosteroids, an overdose of salicylates is possible.
The combination of acetylsalicylic acid with ibuprofen is not recommended in patients with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases: when used simultaneously with ibuprofen, a decrease in the antiplatelet effect of acetylsalicylic acid in doses of up to 300 mg is observed, which leads to a decrease in the cardioprotective effects of acetylsalicylic acid.
Exceeding the dose of acetylsalicylic acid beyond the recommended therapeutic doses is associated with the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
With long-term use of acetylsalicylic acid in low doses as antiplatelet therapy, caution is required in elderly patients due to the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
When taking acetylsalicylic acid with ethanol at the same time, there is an increased risk of damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa and prolongation of bleeding time.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During treatment with acetylsalicylic acid, patients should be careful when driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Acetylsalicylic acid, [Magnesium hydroxide]
Composition
Composition
1 tablet acetylsalicylic acid 75 mg
magnesium hydroxide15.2 mg
Excipients:
corn starch – 9.5 mg,
microcrystalline cellulose – 12.5 mg,
magnesium stearate – 150 mcg,
potato starch – 2.0 mg.
Shell composition:
hypromellose (methylhydroxypropylcellulose 15) – 460 mcg,
propylene glycol – 90 mcg,
talc – 280 mcg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
bleeding in the brain;
tendency to bleeding (vitamin K deficiency, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhagic diathesis);
bronchial asthma induced by taking salicylates and NSAIDs;
erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (in the acute phase);
gastrointestinal bleeding;
severe renal failure (creatinine clearance < 10 ml/min);
deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
simultaneous use with methotrexate (>15 mg per week);
I and III trimesters of pregnancy;
lactation period (breastfeeding);
children and adolescents up to 18 years of age;
hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, excipients of the drug and other NSAIDs.
The drug should be prescribed with caution in case of gout, hyperuricemia, a history of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract or bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, renal and/or liver failure, bronchial asthma, hay fever, nasal polyposis, allergic conditions, in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The frequency of the adverse reactions listed below was determined according to the following: very often (≥1/10); often (> 1/100.1/1000.1/10,000,
Allergic reactions: often – urticaria, Quincke’s edema; sometimes – anaphylactic reactions.
From the digestive system: very often – heartburn; often – nausea, vomiting; sometimes – pain in the abdomen, ulcers of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum, gastrointestinal bleeding; rarely – perforation of a stomach or duodenal ulcer, increased activity of liver enzymes; very rarely – stomatitis, esophagitis, erosive lesions of the upper gastrointestinal tract, strictures, colitis, irritable bowel syndrome.
From the respiratory system: often – bronchospasm.
From the hematopoietic system: very often – increased bleeding; rarely – anemia; very rarely – hypoprothrombinemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, aplastic anemia, eosinophilia, agranulocytosis.
From the side of the central nervous system: sometimes – dizziness, drowsiness; often – headache, insomnia; rarely – tinnitus, intracerebral hemorrhage.
Interaction
Interaction
When used simultaneously, ASA enhances the effect of the following drugs:
methotrexate – by reducing renal clearance and displacing it from protein binding;
heparin and indirect anticoagulants – due to disruption of platelet function and displacement of indirect anticoagulants from binding with proteins;
thrombolytic and antiplatelet drugs (ticlopidine);
digoxin – due to a decrease in its renal excretion;
hypoglycemic agents (insulin and sulfonylurea derivatives) – due to the hypoglycemic properties of ASA itself in high doses and displacing sulfonylurea derivatives from binding with proteins;
valproic acid – by displacing it from its connection with proteins.
An additive effect is observed when taking ASA simultaneously with ethanol (alcohol).
ASA weakens the effect of uricosuric drugs (benzbromarone) due to competitive tubular elimination of uric acid.
By enhancing the elimination of salicylates, systemic corticosteroids weaken their effect.
Antacids and cholestyramine reduce the absorption of the drug.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms of moderate overdose: nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness, confusion.
Treatment: rinse the stomach, prescribe activated charcoal, and carry out symptomatic therapy.
Symptoms of severe overdose: fever, hyperventilation, ketoacidosis, respiratory alkalosis, coma, cardiovascular and respiratory failure, severe hypoglycemia.
Treatment: immediate hospitalization in specialized departments for emergency treatment – gastric lavage, determination of acid-base balance, alkaline and forced alkaline diuresis, hemodialysis, administration of saline solutions, activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy.
When carrying out alkaline diuresis, it is necessary to achieve pH values between 7.5 and 8. Forced alkaline diuresis should be carried out when the concentration of salicylates in plasma is more than 500 mg/l (3.6 mmol/l) in adults and 300 mg/l (2.2 mmol/l) in children.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored in a dry place, protected from light and out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Takeda Pharmaceuticals LLC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | The drug should be stored in a dry place, protected from light and out of reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C |
| Manufacturer | Takeda Pharmaceuticals LLC, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Takeda Pharmaceuticals LLC |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Cardiomagnil, 75 mg+15, 2 mg 100 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.