No products in the cart.
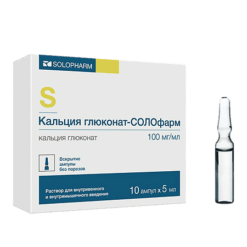
Calcium gluconate, 100 mg/ml 5 ml 10 pcs
€3.96 €3.52
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description Pharmacotherapeutic group: Calcium-phosphorus metabolism regulator Pharmacodynamics: Pharmacokinetics:
ATC:
A.12.A.A.03 Calcium gluconate
A.12.A.A Calcium preparations
The calcium preparation replenishes the deficiency of calcium ions necessary for nerve impulse transmission, skeletal and smooth muscle contraction, myocardial activity, bone formation, and blood clotting.
After parenteral administration with the bloodstream, it is distributed evenly in all tissues and organs. In blood plasma about 45% of calcium ions are in complex with proteins. It passes through the placental barrier and enters breast milk. Excreted from the body mainly by the kidneys.
.
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use the drug with an expired shelf life. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In the dark place at 20 ° C to 30 ° C. Do not freeze. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Calcium gluconate, 100 mg/ml 5 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.