No products in the cart.
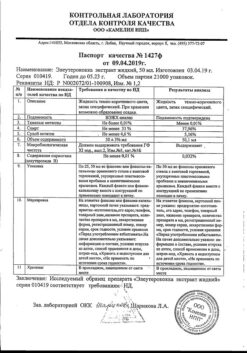
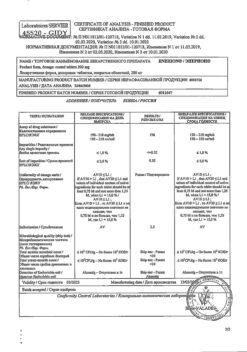
Calcium gluconate, 100 mg/ml 10 ml 10 pcs
€5.14 €4.57
Description
Pharmacological group: regulator of calcium-phosphorus metabolism.
Pharmacodynamics:
Calcium drug compensates the lack of calcium ions required for the transmission of nerve impulses, reduction of skeletal and smooth muscles, myocardial activity, bone formation, blood clotting.
Pharmacokinetics:
After parenteral administration with the bloodstream is evenly distributed in all tissues and organs. In blood plasma about 45% of calcium ions are in complex with proteins. It passes through the placental barrier and enters breast milk. It is eliminated from the body mainly by the kidneys.
Indications
Indications
– Diseases accompanied by hypocalcemia, increased permeability of cell membranes, disruption of the conduction of nerve impulses in muscle tissue.
– Hypoparathyroidism (latent tetany, osteoporosis), vitamin D metabolism disorders: rickets (spasmophilia, osteomalacia), hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic renal failure.
– Increased need for calcium ions (pregnancy, breastfeeding, period of increased growth of the body), insufficient content of calcium ions in food, disturbance of its metabolism (in the postmenopausal period).
– Enhanced excretion of calcium ions (prolonged bed rest, chronic diarrhea, secondary hypocalcemia due to long-term use of diuretics and antiepileptic drugs, glucocorticosteroids).
– Bleeding of various etiologies.
– Allergic diseases (serum sickness, urticaria, febrile syndrome, itching, pruritic dermatosis(s), reactions to medications and food intake, angioedema); bronchial asthma, dystrophic alimentary edema, pulmonary tuberculosis, rickets, osteomalacia, lead colic; eclampsia.
– Hyperkalemic form of paroxysmal myoplegia.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological group: regulator of calcium-phosphorus metabolism.
Pharmacodynamics:
The calcium supplement replenishes the deficiency of calcium ions, which is necessary for the transmission of nerve impulses, contraction of skeletal and smooth muscles, myocardial activity, bone tissue formation, and blood clotting.
Pharmacokinetics:
After parenteral administration through the bloodstream, it is evenly distributed in all tissues and organs. In blood plasma, about 45% of calcium ions are complexed with proteins. Passes through the placental barrier and enters breast milk. It is excreted from the body mainly by the kidneys.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug is heated to body temperature before administration.
With intravenous administration, a feeling of heat throughout the body is possible, which quickly passes.
During treatment, it is necessary to carefully monitor the concentration of calcium in the blood serum.
Due to the risk of local irritation, intramuscular injections should only be performed if intravenous injection is not possible. Intramuscular injections must be performed deep into the muscle, preferably in the gluteal region.
For obese patients, a longer needle should be selected to ensure safe insertion into muscle rather than fat tissue. If repeated injections are necessary, the injection site should be changed each time.
With intravenous administration of calcium gluconate, in exceptional cases, patients receiving cardiac glycosides require monitoring of cardiac activity and conditions should be provided for emergency treatment of cardiac complications, such as severe arrhythmias.
Calcium salts should be used with caution and only after carefully determining the indications in patients with nephrocalcinosis, heart disease, and elderly patients. Impaired renal function may be associated with hypercalcemia and secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Therefore, in patients with impaired renal function, parenteral calcium should be prescribed only after carefully determining the indications, and it is necessary to monitor the calcium-phosphate balance.
In patients with mild hypercalciuria, decreased glomerular filtration rate, or a history of nephrourolithiasis, treatment should be carried out under the control of the concentration of calcium ions in the urine.
To reduce the risk of developing nephrourolithiasis, drinking plenty of fluids is recommended.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
The drug does not affect the concentration of attention and the speed of psychomotor reactions when driving a car or engaging in potentially hazardous activities.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Calcium gluconate
Composition
Composition
Active substance:
Calcium gluconate – 100.0 mg
Excipients:
succinic acid – 5.0 mg,
sodium hydroxide solution 1 M – up to pH 6.0 – 7.5,
water for injection – up to 1.0 ml.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Possible use during pregnancy and breastfeeding according to indications and under strict control of serum calcium concentration, since hypercalcemia negatively affects the fetus and child.
When taking calcium supplements during breastfeeding, it may pass into breast milk.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Increased hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, hypercalcemia (calcium concentration should not exceed 12 mg% or 6 mEq/l), hypercalciuria, nephrolithiasis (calcium), sarcoidosis, simultaneous use of cardiac glycosides (risk of arrhythmias).
With caution: dehydration, electrolyte disturbances (risk of hypercalcemia), diarrhea, malabsorption syndrome, calcium nephrourolithiasis (history), moderate chronic renal failure, chronic heart failure, widespread atherosclerosis, hypercoagulation, for intramuscular administration – childhood (risk of necrosis).
Side Effects
Side Effects
With intramuscular and intravenous administration, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and bradycardia may occur. With intravenous administration, a burning sensation in the mouth, a feeling of heat may be observed, with rapid intravenous administration – a decrease in blood pressure, arrhythmia, fainting, cardiac arrest. When administered intramuscularly, necrosis may form at the injection site.
Interaction
Interaction
Pharmaceutically incompatible with ethanol, carbonates, salicylates, sulfates (forms insoluble or sparingly soluble calcium salts). Forms insoluble complexes with tetracycline antibiotics (reduces the antibacterial effect).
Reduces the effect of blockers of “slow” calcium channels (intravenous administration of calcium gluconate before or after verapamil reduces its hypotensive effect).
When used simultaneously with quinidine, intraventricular conduction may slow down and quinidine toxicity may increase.
During treatment with cardiac glycosides, parenteral use of calcium gluconate is not recommended (the cardiotoxic effect of cardiac glycosides may be enhanced).
When combined with thiazide diuretics, it may increase hypercalcemia.
Reduces the effect of calcitonin in hypercalcemia. Reduces the bioavailability of phenytoin.
Overdose
Overdose
Development of hypercalcemia (symptoms: drowsiness, weakness, anorexia, abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea, constipation, polydipsia, polyuria, increased fatigue, irritability, depression, dehydration, possible heart rhythm disturbances, myalgia, arthralgia, arterial hypertension). Severe hypercalcemia (calcium more than 3.4 mmol/l) is life-threatening and requires immediate fluid resuscitation.
Treatment: drug withdrawal; in severe cases – parenteral calcitonin at a dose of 5-10 IU/kg body weight per day (when diluted in 500 ml of sterile 0.9% physiological sodium chloride solution), intravenously drip over 6 hours.
Slow intravenous injection 2-4 times a day is possible.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature of 20 ° C to 30 ° C. Do not freeze.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ozon, Russia
Additional information
| Conditions of storage | In the dark place at the temperature from 20 ° C to 30 ° C. Do not freeze. Keep out of reach of children. |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Calcium gluconate, 100 mg/ml 10 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.