No products in the cart.
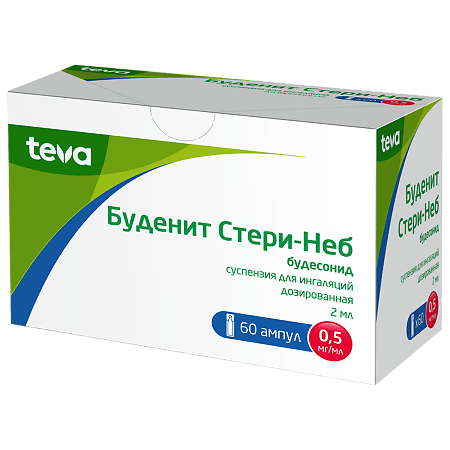
Budenit Steri-Neb, 0.5 mg/ml suspension 2 ml 60 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Glucocorticosteroid for topical use.
ATX code: R03BA02
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics. Glucocorticosteroid (GCS) with pronounced local anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects. Budesonide increases the production of lipocortin, which is an inhibitor of phospholipase A2, inhibits the release of arachidonic acid, inhibits the synthesis of leukotrienes and prostaglandins, reduces inflammatory exudation and cytokine production, inhibits macrophage migration, it reduces intensity of the processes of infiltration and granulation, formation of chemotaxis substance (which explains its effectiveness with delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions), inhibits release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells (immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions).
Budesonide restores the patient’s sensitivity to bronchodilators, allowing to reduce the frequency of their use, reduces bronchial mucosal edema, mucus production, sputum formation and reduces airway hyperresponsiveness. Increases mucociliary transport. It is well tolerated with long-term treatment and has no mineralocorticoid activity.
The time of onset of therapeutic effect after inhalation of a single dose of the drug is several hours. The maximum therapeutic effect is reached 1-2 weeks after treatment. Budesonide effectively prevents attacks of bronchial asthma of physical stress, but does not stop an acute attack of bronchospasm.
Pharmacokinetics. Budesonide is rapidly absorbed after inhalation. In adults, systemic bioavailability after inhalation of budesonide via nebulizer is approximately 15% of the total dose administered. The maximum concentration (Cmax) in plasma is 3.5 nmol/L and is reached 30 min after the start of inhalation.
The binding to plasma proteins is 85-90%. Volume of distribution is 3 l/kg.
Budesonide undergoes biotransformation with the participation of liver microsomal enzymes, primarily CYP3A4 isoenzyme. The main metabolites – 6-β-hydroxybudesonide and 16-α-hydroxyprednisolone have almost no biological activity (100 times less than budesonide).
It is excreted by the kidneys as metabolites – 70%, through the intestines – 10%. Systemic clearance of inhaled drug is 0.5 l/min. Systemic clearance of metabolites is 1.4 l/min. Period of half-life – 2-2.8 hours.
Indications
Indications
treatment of bronchial asthma (as a basic therapy; with insufficient effectiveness of beta2-adrenergic agonists; to reduce the dose of oral corticosteroids) in case of ineffectiveness or impossibility of using budesonide in an inhaler that pumps the drug into the respiratory tract, or an inhaler containing the drug in powder form;
treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
stenosing laryngotracheitis (false croup).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: glucocorticosteroid for local use.
ATX code: R03BA02
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics. Glucocorticosteroid (GCS) with a pronounced local anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effect. Budesonide increases the production of lipocortin, which is an inhibitor of phospholipase A2, inhibits the release of arachidonic acid, inhibits the synthesis of leukotrienes and prostaglandins, reduces inflammatory exudation and the production of cytokines, inhibits the migration of macrophages, reduces the severity of infiltration and granulation processes, the formation of a chemotaxis substance (which explains the effectiveness in delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions), inhibits release from mast cells inflammatory mediators (immediate hypersensitivity reaction).
Budesonide restores the patient’s sensitivity to bronchodilators, allowing them to reduce the frequency of their use, reduces swelling of the bronchial mucosa, mucus production, sputum formation and reduces airway hyperresponsiveness. Increases mucociliary transport. It is well tolerated during long-term treatment and does not have mineralocorticoid activity.
The time for the onset of the therapeutic effect after inhalation of one dose of the drug is several hours. The maximum therapeutic effect is achieved 1-2 weeks after treatment. Budesonide effectively prevents attacks of bronchial asthma of physical exertion, but does not stop an acute attack of bronchospasm.
Pharmacokinetics. After inhalation, budesonide is rapidly absorbed. In adults, systemic bioavailability after inhalation of budesonide via nebulizer is approximately 15% of the total prescribed dose. The maximum concentration (Cmax) in blood plasma is 3.5 nmol/l and is achieved 30 minutes after the start of inhalation.
Plasma protein binding – 85-90%. Volume of distribution – 3 l/kg.
Budesonide undergoes biotransformation with the participation of microsomal liver enzymes, primarily the CYP3A4 isoenzyme. The main metabolites – 6-β-hydroxybudesonide and 16-α-hydroxyprednisolone are practically devoid of biological activity (100 times less than budesonide).
Excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites – 70%, through the intestines – 10%. Systemic clearance of the drug administered by inhalation is 0.5 l/min. Systemic clearance of metabolites – 1.4 l/min. The half-life is 2-2.8 hours.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug Budenit Steri-Neb is not intended for rapid relief of attacks of bronchial asthma; to relieve acute bronchospasm, it is recommended to use short-acting inhaled bronchodilators.
Patients not receiving GCS
Usually the therapeutic effect occurs within 10 days. In patients with excessive mucus secretion in the bronchi, a short (about 2 weeks) additional treatment with oral corticosteroids may initially be given. After a course of oral therapy, in many cases it is possible to completely stop taking GCS orally.
Patients on GCS therapy
Before transferring a patient from treatment with oral corticosteroids to treatment with Budenit Steri-Nab, the patient’s condition should be relatively stable. After which the drug Budenit Steri-Neb is used in combination with the previously used dose of GCS for oral administration for about 10 days. Subsequently, the dose of oral corticosteroids should be gradually reduced (for example, by 2.5 mg of prednisolone or its equivalent every month) as far as possible to the lowest level. In most cases, oral GCS can be completely replaced with Budenit Steri-Neb.
Sometimes, during a transfer from treatment with oral corticosteroids to treatment with Budenit Steri-Neb, symptoms that were previously relieved by systemic drugs are observed: for example, rhinitis, eczema and muscle and joint pain. The occurrence of symptoms such as fatigue, headache, nausea and vomiting may indicate the development of systemic insufficiency of GCS. In such cases, it may even be necessary to temporarily increase the dose of oral corticosteroids.
Systemic side effects of inhaled corticosteroids can occur primarily when high doses are administered over a long period of time. The likelihood of this effect occurring is significantly less than with treatment with oral corticosteroids. Possible systemic effects include adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, decreased bone mineral density, cataracts, and glaucoma. Therefore, it is very important to titrate the dose of inhaled corticosteroids to the lowest dose that maintains effective disease control. It is recommended to regularly monitor growth in children receiving inhaled corticosteroids for an extended period of time. In case of growth retardation, treatment should be adjusted to reduce the dose of GCS for inhalation to the lowest dose at which effective control of bronchial asthma is maintained.
Oral administration of ketoconazole and itraconazole or other inhibitors of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme increases the systemic exposure of budesonide. Therefore, if combined use is necessary, they should be taken at maximum intervals. A dose reduction of budesonide should also be considered.
To minimize the risk of fungal stomatitis, the patient and/or the child’s parents should be informed about the need to rinse the mouth with water after each inhalation of the drug.
Impact on the ability to drive a vehicle and operate equipment
The drug Budenit Steri-Neb does not have a negative effect on the ability to drive a vehicle or operate machinery. In case of rare adverse reactions from the nervous system, activities that require rapid psychomotor reactions should be avoided.
Technique of use
Ultrasonic nebulizers are not suitable for use with Budenit Steri-Neb. The dose required by the patient may vary depending on the nebulizer used. Inhalation time and dose of the drug depend on the air flow speed, the volume of the nebulizer chamber and the filling volume. Therefore, to inhale the drug Budenit Steri-Neb, it is necessary to use an appropriate nebulizer, as well as a mouthpiece and a special face mask. The nebulizer must be connected to an air compressor to create adequate air flow.
Before using the drug, you must read the instructions from the nebulizer manufacturer.
Prepare the nebulizer according to its manufacturer’s instructions.
Separate the STERI-NEB (ampoule with a sterile solution) from the block by turning and pulling it (Fig. 1).
Holding the ampoule vertically with the cap up, break off the cap (Fig. 2).
Squeeze the solution into the nebulizer reservoir (Fig. 3).
Use the nebulizer according to its manufacturer’s instructions.
You should rinse your mouth after finishing inhalation. If you used a mask, you must rinse your face.
Any solution remaining unused in the nebulizer chamber should be discarded.
Wash the nebulizer thoroughly.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Budesonide
Composition
Composition
1 ml contains:
Active ingredient: budesonide 0.25 mg and 0.50 mg.
Excipients:
polysorbate-80 0.20 mg, sodium chloride 8.50 mg, sodium citrate dihydrate 0.50 mg, citric acid monohydrate 0.31 mg, disodium edetate 0.10 mg, water for injection up to 1.0 ml.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of budesonide during pregnancy is only possible if the benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus. If use is necessary, the drug is used in the minimum effective dose.
There are no data on the excretion of budesonide in breast milk. Prescribing the drug during lactation is possible only under the supervision of a physician in cases where the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the child.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to budesonide or any other component of the drug; age up to 6 months.
With caution
Pulmonary tuberculosis, fungal, bacterial, parasitic and viral respiratory infections, liver cirrhosis, pregnancy, lactation.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Often (≥1/100, <1/10): irritation and dryness of the pharyngeal mucosa, candidal stomatitis, hoarseness, cough, dry oral mucosa, unpleasant taste.
Rarely (≥1/10000, <1/1000): nervousness, excitability, depression, behavioral disturbances, immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions (including rash, contact dermatitis, urticaria, angioedema and bronchospasm), skin bruising or thinning of the skin, headache, nausea, esophageal candidiasis.
When inhaled treatment of GCS, systemic effects may occur, especially with long-term treatment with high doses. The likelihood of such effects occurring is significantly less than with the treatment of oral corticosteroids. Possible systemic effects include adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, decreased bone mineral density, cataracts, and glaucoma.
The drug Budenit Steri-Neb contains 0.1 mg/ml disodium edetate, which can cause bronchospasm at concentrations above 1.2 mg/ml.
As with other inhaled therapies, paradoxical bronchospasm may occur with rapid worsening of dyspnea after dosing. If a severe reaction occurs, alternative therapy should be prescribed.
In some cases, facial skin irritation occurs when using a nebulizer with a mask. To prevent irritation, after using the mask, the facial skin should be rinsed with water.
Interaction
Interaction
Pharmaceutical: Budenit Steri-Neb can be mixed with 0.9% sodium chloride solution and with other solutions intended for use with nebulizers, for example, with terbutaline, salbutamol, fenoterol, acetylcysteine, sodium cromoglycate or ipratropium bromide.
Pharmacological: the metabolism of budesonide is mainly carried out with the participation of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme. Taking 100 mg of ketoconazole 2 times a day increases the plasma concentration of orally taken budesonide at a dose of 10 mg once on average by 7-8 times. There is no information on such interactions with inhaled dosage forms of budesonide, but a marked increase in plasma concentrations of the drug should be expected; therefore, inhibitors of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme such as ketoconazole and itraconazole may increase the systemic exposure of budesonide. Other strong CYP3A4 inhibitors are also likely to markedly increase budesonide plasma concentrations.
Pre-inhalation of beta-agonists dilates the bronchi, improves the entry of budesonide into the respiratory tract and enhances its therapeutic effect.
Phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampicin reduce effectiveness (induction of microsomal liver enzymes).
Methandienone and estrogens enhance the effect of budesonide.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of acute overdose of budesonide, clinical manifestations usually do not occur. Treatment is drug withdrawal, inhalation of short-acting bronchodilators.
With prolonged use in doses exceeding the recommended ones, a systemic glucocorticosteroid effect may develop in the form of hypercortisolism and suppression of adrenal function.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not higher than 25°C.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN!
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Norton Healthcare Limited, UK
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25C. KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN! |
| Manufacturer | Norton Healthcare Limited, United Kingdom |
| Medication form | inhalation suspension |
| Brand | Norton Healthcare Limited |
Related products
Buy Budenit Steri-Neb, 0.5 mg/ml suspension 2 ml 60 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.