No products in the cart.
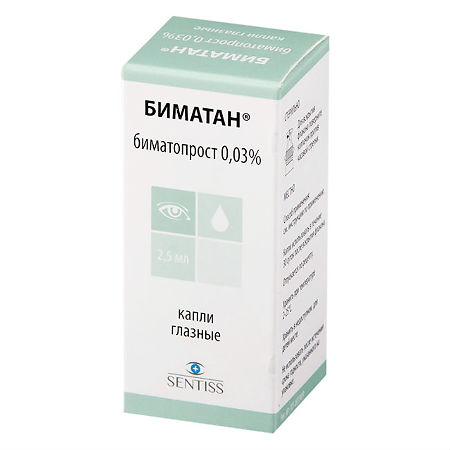
Bimatan, eye drops 0.03% 2.5ml
€19.54 €16.29
Description
Antiglaucoma agent. Bimatoprost is a synthetic prostamide structurally related to prostaglandin F2α, which does not act through known prostaglandin receptors. Bimatoprost selectively mimics the effects of recently discovered biosynthesized substances, prostamides. However, the structure of the prostaglandin receptors has not yet been identified.
Pharmacokinetics
Bimatoprost penetrates well into the human cornea and sclera in vitro. After instillation in adults, systemic exposure of bimatoprost is very low and no accumulation of the active substance has been noted.
After administration of one drop of the drug in both eyes once daily for 2 weeks, the blood concentration reached a maximum 10 min after administration of the dose, and within 1.5 h it was below the level of determination (0.025 ng/ml).
The mean Cmax and AUC0-24 h values were approximately the same on days 7 and 14, approximately 0.08 ng/mL and 0.09 ng×h/mL, respectively, indicating that the Css of bimatoprost was achieved within 1 week of instillation. Bimatoprost is moderately distributed in body tissues, and Vd at equilibrium is 0.67 L/kg. In human blood bimatoprost is mainly in plasma.
The binding of bimatoprost to plasma proteins is about 88%. Bimatoprost reaches the systemic bloodstream mainly in unchanged form. Then there is oxidation, N-deletylation and glucuronidation with the formation of a number of metabolites.
Bimatoprost is excreted mainly by the kidneys. Up to 67% of the dose administered by injection into healthy adult volunteers was excreted with the urine, 25% – in the feces. T1/2 after IV administration was approximately 45 min, total blood clearance was 1.5 l/h/kg.
Bimatoprost decreases intraocular pressure by increasing aqueous outflow through the trabecular meshwork and increasing uveoscleral outflow.
The decrease in intraocular pressure starts about 4 hours after the first injection, the maximum effect is achieved after about 8-12 hours. The effect lasts for at least 24 hours.
According to clinical studies, no significant effect of bimatoprost on HR and BP has been noted.
Indications
Indications
Open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension in adults (as monotherapy or in combination with beta-blockers).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Antiglaucoma agent. Bimatoprost is a synthetic prostamide, structurally related to prostaglandin F2α, which does not act through known prostaglandin receptors. Bimatoprost selectively mimics the effects of recently discovered biosynthesized substances, prostamides. However, the structure of the prostamide receptors has not yet been identified.
Pharmacokinetics
Bimatoprost penetrates well into the human cornea and sclera in vitro. After instillation by adults, the systemic exposure of bimatoprost is very small, no accumulation of the active substance was noted.
After administering one drop of the drug to both eyes 1 time/day for 2 weeks, the concentration in the blood reached a maximum 10 minutes after dosing, and within 1.5 hours this indicator was below the detection level (0.025 ng/ml).
The mean values of Cmax and AUC0-24 h were approximately the same on days 7 and 14 – approximately 0.08 ng/ml and 0.09 ng×h/ml, respectively, indicating that the Css of bimatoprost was achieved within 1 week of instillation. Bimatoprost is moderately distributed in body tissues, and Vd at steady state is 0.67 l/kg. In human blood, bimatoprost is found mainly in plasma.
The binding of bimatoprost to plasma proteins is about 88%. Bimatoprost reaches the systemic circulation mainly unchanged. Oxidation, N-deethylation and glucuronidation then occur to form a number of metabolites.
Bimatoprost is excreted mainly by the kidneys. Up to 67% of the dose administered intravenously to healthy adult volunteers was excreted from the body in urine, 25% in feces. T1/2 after IV administration was approximately 45 minutes, total blood clearance was 1.5 l/h/kg.
Pharmacodynamics
Bimatoprost reduces intraocular pressure by increasing the outflow of aqueous humor through the trabecular meshwork and increasing uveoscleral outflow.
The reduction in intraocular pressure begins approximately 4 hours after the first administration, the maximum effect is achieved after approximately 8-12 hours. The effect lasts for at least 24 hours.
According to clinical studies, there was no significant effect of bimatoprost on heart rate and blood pressure.
Special instructions
Special instructions
There is no experience with the use of bimatoprost in patients with concomitant respiratory dysfunction, which requires caution in such patients. In clinical studies in patients with impaired respiratory function, no significant adverse effects on the respiratory system were observed.
The effects of bimatoprost have not been studied in patients with second- and third-degree AV block or in patients with uncontrolled congestive heart failure.
Before starting treatment, patients should be informed of the possibility of eyelash growth, darkening of the eyelid skin, and increased pigmentation of the iris.
Some of these changes may be permanent and may result in differences in appearance between eyes when only one eye is treated. Changes in iris pigmentation occur slowly and may not be noticeable for months or years. Most often, the change in iris color is permanent.
Changes in iris color are more associated with an increase in melanin content in melanocytes than with an increase in the number of melanocytes. The long-term effects of increasing iris pigmentation are unknown.
In typical cases, brown pigment spreads from the area around the pupil to the root of the iris, resulting in the entire iris or parts of it becoming a browner color. The use of bimatoprost has no effect on nevi and lentigo of the iris. Periorbital tissue pigmentation is reversible in some patients.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Bimatoprost
Composition
Composition
1 ml:
Active ingredient:
bimatoprost 0.3 mg;
Excipients:
benzalkonium chloride – 0.05 mg,
sodium chloride – 8.3 mg,
citric acid monohydrate – 0.14 mg,
sodium hydrogen phosphate heptahydrate – 2.68 mg,
sodium hydroxide – up to pH 7.3,
hydrochloric acid – up to pH 7.3,
water for d/i – up to 1 ml.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Contraindicated in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
There are no data from clinical studies of the use of bimatoprost during pregnancy. The use of bimatoprost during pregnancy is not recommended, except in cases of strict indications.
According to preclinical studies in animals, reproductive toxicity is shown when bimaptoprost is used in high doses that are toxic to the mother’s body.
It is not known whether bimatoprost is excreted into breast milk in humans. Animal studies have shown that bimatoprost is excreted in breast milk. The decision to continue/discontinue breastfeeding or continue/discontinue treatment with bimatoprost should be made taking into account the benefits of breastfeeding for the child and the benefits of therapy for the mother.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to bimatoprost; age up to 18 years.
Caution is required when using bimatoprost preparations to treat patients with known risk factors for macular edema (for example, in patients with aphakia, in patients with pseudophakia and rupture of the posterior capsule of the lens); in patients with a history of severe eye infections (eg, those caused by herpes simplex virus) or iritis/uveitis.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Determination of the categories of frequency of adverse reactions: very often (&le1/10); often (&le1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (&le1/1000 to <1/100); rare (&le1/10,000 to <1/1000); very rare (< 1/10,000), frequency unknown (frequency cannot be estimated from available data).
From the nervous system: often – headache; infrequently – dizziness.
From the organ of vision: very often – conjunctival injection, itching in the eyes, eyelash growth; often – superficial punctate keratitis, corneal erosion, burning in the eyes, eye irritation, allergic conjunctivitis, blepharitis, decreased visual acuity, asthenopia, conjunctival edema, foreign body sensation in the eye, dry eye, eye pain, photophobia, lacrimation, discharge from the eyes, blurred vision, increased pigmentation of the iris, darkening of the eyelashes; infrequently – hemorrhagic disorders of the retina, uveitis, cystoid macular edema, iritis, blepharospasm, eyelid retraction, periorbital erythema; frequency unknown – enophthalmos. In very rare cases, corneal calcification has been reported when phosphate-containing eye drops were used in patients with concomitant significant corneal damage.
From the cardiovascular system: often – arterial hypertension.
From the hepatobiliary system: often – deviation from the norm of biochemical indicators of liver function.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: infrequently – hirsutism.
General reactions: infrequently – asthenia.
Interaction
Interaction
There was a decrease in the hypotensive effect of bimatoprost when it was used in combination with other prostaglandin analogues in the treatment of ocular hypertension or glaucoma.
Overdose
Overdose
There have been no cases of overdose with topical use. In case of overdose, treatment should be symptomatic and supportive.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Sentiss Pharma Pvt.Ltd, India
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Sentiss Pharma Pvt.Ltd, India |
|---|---|
| Medication form | eye drops |
| Brand | Sentiss Pharma Pvt.Ltd |
Related products
Buy Bimatan, eye drops 0.03% 2.5ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.