No products in the cart.
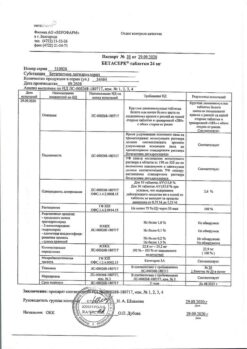
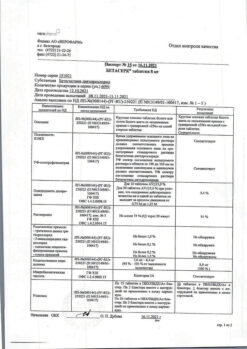
Betaserk, tablets 24 mg 60 pcs
€36.11 €30.09
Description
Pharmgroup:
The drug improving microcirculation of the labyrinth, used for pathology of the vestibular system.
Pharmic action:
Betaserk is a synthetic analog of histamine. It is an agonist of histamine H1 receptors of the inner ear vessels and an antagonist of histamine H3 receptors of the vestibular nuclei of the CNS. According to preclinical studies through relaxation of precapillary sphincters of the vessels of the inner ear improves blood flow in the vascular shelf of the inner ear.
Dose-dependently reduces the generation of action potentials in the neurons of the lateral and medial vestibular nuclei. It accelerates recovery of vestibular function after unilateral vestibular neurectomy, accelerating and facilitating central vestibular compensation (due to antagonism with histamine H3-receptors). Relieves symptoms in Meniere’s syndrome and vertigo.
Pharmacokinetics:
Betahistine is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract when ingested. After absorption, the drug is rapidly and almost completely metabolized to form the inactive metabolite 2-pyridylacetic acid.
If the drug is taken at a dose of 8-48 mg, about 85% of the initial dose is detected in the urine as 2-pyridylacetic acid. Excretion of betahistine by the kidneys or through the intestine is insignificant. The excretion rate remains constant with oral administration of 8-48 mg of the drug, indicating linearity in the pharmacokinetics of betahistine, and suggesting that the metabolic pathway involved remains unsaturated.
When the drug is taken with food, the maximum blood concentration of the drug is lower than when taken on an empty stomach. However, the total absorption of betahistine is the same in both cases, indicating that food intake only slows the absorption of betahistine.
Indications
Indications
Meniere’s syndrome, characterized by the following main symptoms: dizziness (accompanied by nausea/vomiting); hearing loss (hearing loss); tinnitus.
symptomatic treatment of vestibular dizziness (vertigo).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmaceutical group:
A drug that improves microcirculation of the labyrinth, used for pathology of the vestibular apparatus.
Pharmaceutical action:
Betaserc is a synthetic analogue of histamine. An agonist of histamine H1 receptors in the vessels of the inner ear and an antagonist of histamine H3 receptors in the vestibular nuclei of the central nervous system. According to preclinical studies, by relaxing the precapillary sphincters of the vessels of the inner ear, it improves blood circulation in the vascular shelf of the inner ear.
Dose-dependently reduces the generation of action potentials in neurons of the lateral and medial vestibular nuclei. Accelerates the recovery of vestibular function after unilateral vestibular neurectomy, accelerating and facilitating central vestibular compensation (due to antagonism with histamine H3 receptors). Relieves symptoms of Meniere’s syndrome and vertigo.
Pharmacokinetics:
When taken orally, betahistine is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After absorption, the drug is quickly and almost completely metabolized to form the inactive metabolite 2-pyridylacetic acid.
When taking the drug at a dose of 8-48 mg, about 85% of the initial dose is found in the urine in the form of 2-pyridylacetic acid. Excretion of betahistine by the kidneys or through the intestines is negligible. The rate of elimination remains constant with oral dosing of 8-48 mg of the drug, indicating linear pharmacokinetics of betahistine and suggesting that the metabolic pathway involved remains unsaturated.
When taking the drug with food, the maximum concentration of the drug in the blood is lower than when taken on an empty stomach. However, the total absorption of betahistine is the same in both cases, indicating that food intake only slows down the absorption of betahistine.
Special instructions
Special instructions
It should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastric or duodenal ulcers, in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, as well as in children.
It must be taken into account that the desired clinical effect is achieved after several months of treatment.
For dyspeptic symptoms, betahistine is recommended to be taken during or after meals.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Betahistine
Composition
Composition
1 tab.:
– betahistine dihydrochloride 24 mg
Excipients:
microcrystalline cellulose,
mannitol (E421),
citric acid monohydrate,
colloidal silicon dioxide,
talc.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy.
There is insufficient data available on the use of betahistine in pregnant women. Animal studies have shown no direct or indirect reproductive toxicity. Betahistine should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly needed.
Breast-feeding.
It is unknown whether betahistine is excreted in human breast milk. Betahistine is excreted in breast milk in rats. Animal studies have been limited to very high doses of the drug. The question of prescribing a drug to the mother should be made only after comparing the benefits of breastfeeding with the potential risk to the infant.
Fertility.
Animal studies (rats) have not shown any effect on fertility.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Pheochromocytoma;
hypersensitivity to any of the components of the drug.
Betaserc® is not recommended for use in children under 18 years of age due to insufficient data on efficacy and safety.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Common: nausea and dyspepsia; headache;
Not known: hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic reaction, vomiting, gastrointestinal pain, bloating, angioedema, urticaria, itching, rash
Interaction
Interaction
In vivo studies aimed at studying interactions with other drugs have not been conducted.
Based on in vitro data, it can be assumed that there is no inhibition of the activity of isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system in vivo.
In vitro data have shown inhibition of betahistine metabolism by drugs that inhibit MAO, including MAO subtype B (eg, selegiline). Caution should be exercised when prescribing betahistine and MAO inhibitors (including MAO-B) simultaneously.
Betahistine is a histamine analogue, and the interaction of betahistine with histamine H1 receptor blockers could theoretically affect the effectiveness of one of these drugs.
The patient should tell the doctor if they are currently or recently taking any medications.
Overdose
Overdose
There are several known cases of overdose of Betaserc.
Symptoms: mild to moderate nausea, drowsiness, abdominal pain were observed in some patients after taking the drug in doses up to 640 mg.
More serious complications (convulsions, cardiopulmonary complications) have been observed with deliberate use of betahistine in increased doses, especially in combination with overdose of other drugs.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
1 year
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Veropharm LLC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 1 year |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Veropharm AO, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Veropharm AO |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Betaserk, tablets 24 mg 60 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.