No products in the cart.
Ascoril expectorant, syrup 100 ml
€12.00 €10.00
Description
Askoril expectorant – bronchodilator, mucolytic, expectorant.
Pharmacodynamics
A combined drug, has bronchodilator, expectorant and mucolytic action.
Salbutamol is a bronchodilator, stimulates beta2-adrenoreceptors of the bronchi, blood vessels and myometrium. It prevents or eliminates bronchial spasm, reduces resistance in the airways, increases the vital capacity of the lungs. Causes dilation of the coronary arteries, does not reduce BP.
Bromhexin is a mucolytic agent, has expectorant and anti-cough effect. It increases the serous component of bronchial secretion; it activates the cilia of the atrial epithelium, reduces the viscosity of sputum, increases its volume and improves discharge.
Guifenesin is a mucolytic agent; it reduces surface tension of bronchopulmonary apparatus structures; stimulates secretory cells of the bronchial mucosa producing neutral polysaccharides, depolymerizes acidic mucopolysaccharides, reduces sputum viscosity, activates the bronchial ciliary apparatus, facilitates sputum removal and promotes the transition of non-productive cough into productive one.
Pharmacokinetics
Salbutamol
If ingested, absorption is high. Food intake reduces the absorption rate but does not affect bioavailability. Binding with plasma proteins is 10%. It penetrates through the placenta. It is subjected to presystemic metabolism in liver and intestinal wall and is inactivated to 4-sulfate ester by phenolsulfotransferase. T1/2 is 3.8-6 h. It is excreted by the kidneys (69-90%), mainly as inactive phenolsulfate metabolite (60%) within 72 hours and with bile (4%). The bioavailability of orally administered salbutamol is about 50%.
Bromhexin
Bromhexin is almost completely (99%) absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract within 30 minutes when administered orally. Bioavailability is low (effect of primary passage through the liver). It penetrates through the placental barrier and the BBB. In the liver it undergoes demethylation and oxidation, metabolized to pharmacologically active ambroxol. T1/2 – 15 h (due to slow reverse diffusion from tissues). It is excreted by the kidneys. Excretion of metabolites is impaired in CKD. It may cumulate with repeated use.
Gvaifenesin
The absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is fast (25-30 min after oral administration). T1/2 – 1 h. It penetrates into tissues containing acidic mucopolysaccharides. Approximately 60% of the administered drug is metabolized in the liver. It is excreted with lungs (with sputum) and kidneys both unchanged and as inactive metabolites.
Indications
Indications
As part of combination therapy for acute and chronic bronchopulmonary diseases, accompanied by the formation of a difficult to separate viscous secretion:
bronchial asthma;
pneumoconiosis;
obstructive bronchitis;
tracheobronchitis;
pneumonia;
emphysema;
whooping cough;
pulmonary tuberculosis.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Ascoril expectorant – bronchodilator, mucolytic, expectorant.
Pharmacodynamics
The combined drug has a bronchodilator, expectorant and mucolytic effect.
Salbutamol is a bronchodilator that stimulates beta2-adrenergic receptors of the bronchi, blood vessels and myometrium. Prevents or eliminates bronchospasm, reduces resistance in the respiratory tract, increases the vital capacity of the lungs. Causes expansion of the coronary arteries, does not reduce blood pressure.
Bromhexine is a mucolytic agent that has an expectorant and antitussive effect. Increases the serous component of bronchial secretions; activates the cilia of the ciliated epithelium, reduces the viscosity of sputum, increases its volume and improves discharge.
Guaifenesin is a mucolytic agent that reduces the surface tension of the structures of the bronchopulmonary apparatus; stimulates secretory cells of the bronchial mucosa that produce neutral polysaccharides, depolymerizes acidic mucopolysaccharides, reduces the viscosity of sputum, activates the ciliary apparatus of the bronchi, facilitates the removal of sputum and promotes the transition of an unproductive cough to a productive one.
Pharmacokinetics
Salbutamol
When taken orally, absorption is high. Eating reduces the rate of absorption but does not affect bioavailability. Communication with plasma proteins – 10%. Penetrates through the placenta. Subjected to first-pass metabolism in the liver and intestinal wall, it is inactivated by phenol sulfotransferase to 4-o-sulfate ester. T1/2 – 3.8–6 hours. Excreted by the kidneys (69–90%), mainly in the form of an inactive phenol sulfate metabolite (60%) within 72 hours and with bile (4%). The bioavailability of orally administered salbutamol is about 50%.
Bromhexine
When taken orally, it is almost completely (99%) absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract within 30 minutes. Bioavailability is low (first pass effect through the liver). Penetrates through the placental barrier and BBB. In the liver it undergoes demethylation and oxidation, metabolized to the pharmacologically active ambroxol. T1/2 – 15 hours (due to slow reverse diffusion from tissues). Excreted by the kidneys. With chronic renal failure, the excretion of metabolites is impaired. May accumulate with repeated use.
Guaifenesin
Absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is rapid (25–30 minutes after oral administration). T1/2 – 1 hour. Penetrates tissues containing acidic mucopolysaccharides. Approximately 60% of the administered drug is metabolized in the liver. It is excreted by the lungs (with sputum) and the kidneys both unchanged and in the form of inactive metabolites.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Bromhexine, Guaifenesin, Salbutamol
Composition
Composition
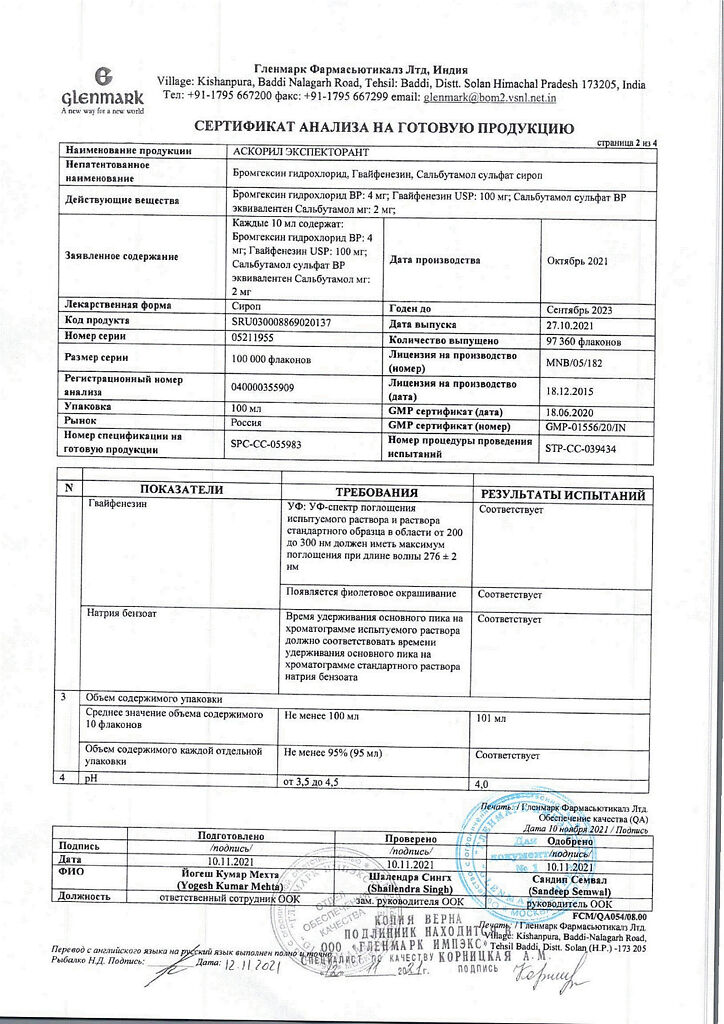
10 ml of syrup contains:
Active substances:
salbutamol (in the form of sulfate) 2 mg,
bromhexine hydrochloride 4 mg,
guaifenesin 100 mg,
menthol 1 mg;
Excipients:
flavoring additives,
sucrose,
sodium benzoate,
sorbitol,
glycerol,
propylene glycol,
sunset yellow dye,
purified water.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Contraindicated during pregnancy and children under three years of age
Contraindications
Contraindications
tachyarrhythmia;
myocarditis;
heart defects;
decompensated diabetes mellitus;
thyrotoxicosis;
glaucoma;
liver or kidney failure;
peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute stage;
pregnancy;
lactation period;
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Prescribe with caution to patients with diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, gastric and duodenal ulcers in remission.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Rarely when used in high doses:
headache,
dizziness,
increased nervous excitability,
sleep disorder,
drowsiness,
tremor,
convulsions,
nausea,
vomit,
diarrhea,
exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers,
rapid heartbeat,
urine may turn pink,
allergic reactions (rash, urticaria),
collapse,
bronchospasm.
Interaction
Interaction
Other beta2-adrenergic agonists and theophylline enhance the effect of salbutamol and increase the likelihood of side effects.
Ascoril is not prescribed simultaneously with drugs containing codeine and other antitussives, because this makes it difficult to clear liquefied sputum.
Bromhexine, which is part of the drug Ascoril, promotes the penetration of antibiotics (erythromycin, cephalexin, oxytetracycline) into the lung tissue.
It is not recommended to use Ascoril simultaneously with non-selective beta-adrenergic blockers, such as propranolol.
The drug Ascoril salbutamol, which is part of the drug, is not recommended for patients receiving MAO inhibitors.
Diuretics and corticosteroids enhance the hypokalemic effect of salbutamol.
It is not recommended to take alkaline drinks at the same time as Ascoril.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: increased side effects.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd, India
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd, India |
| Medication form | syrup |
| Brand | Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Ascoril expectorant, syrup 100 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.