No products in the cart.
Ascorbic acid, 100 mg/ml 2 ml 10 pcs
€1.92 €1.75
Description
Ascorbic acid has pronounced reducing properties, is involved in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, redox processes, blood coagulation, normalization of capillary permeability, tissue regeneration, synthesis of steroid hormones, collagen, procollagen.
Pharmacokinetics
Binding with plasma proteins – 25%. The concentration of ascorbic acid in plasma is normally about 10 – 20 µg/ml. It penetrates easily into leukocytes, platelets and then into all tissues; the highest concentration is in glandular organs, leukocytes, liver and eye lens; penetrates through placenta.
The concentration of ascorbic acid in leukocytes and platelets is higher than in erythrocytes and plasma. In deficiency states, the concentration in leukocytes decreases later and more slowly and is considered a better criterion for assessing deficiency than the concentration in plasma.
It is metabolized primarily in the liver to deoxyascorbic acid and then to oxalic acid and ascorbate-2-sulfate.
.
Form of release
Form of release
Solution for injection.
Additional information
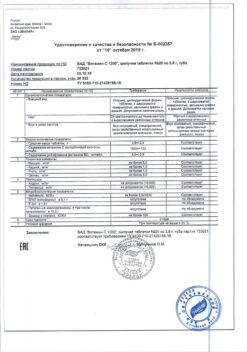
| Shelf life | 1 year. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 15 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Biosintez, Russia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Biosintez |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Ascorbic acid, 100 mg/ml 2 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.