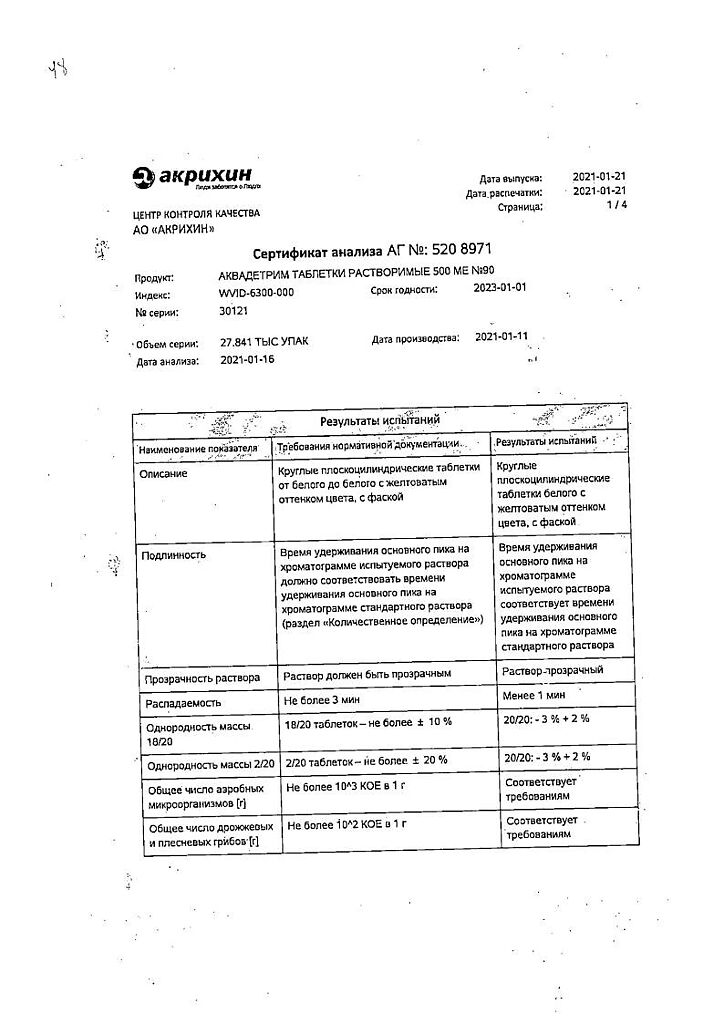
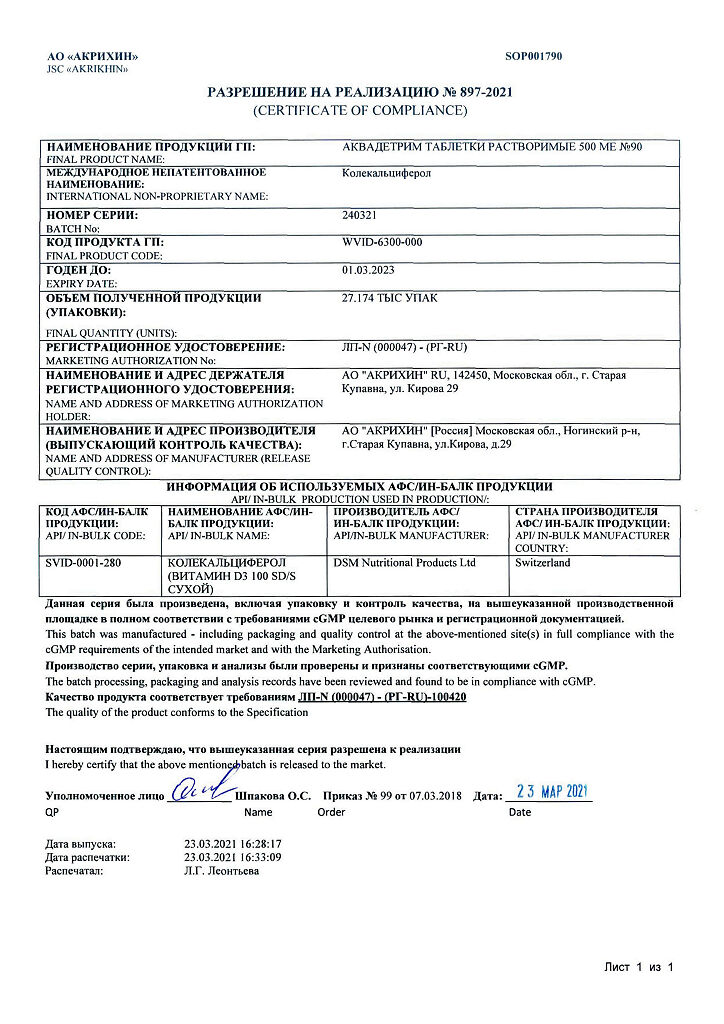
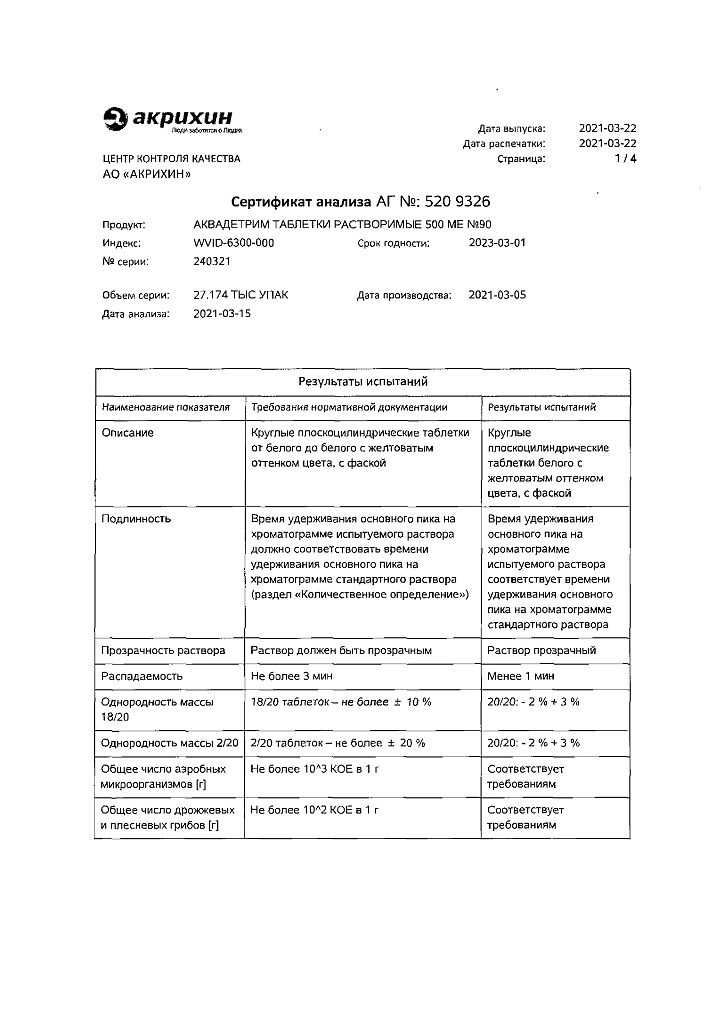
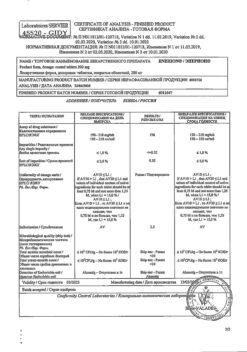
-
×


-
×


-
×

-
×


-
×


-
×


-
×


-
×


-
×


-
×


Subtotal: €165.50