No products in the cart.
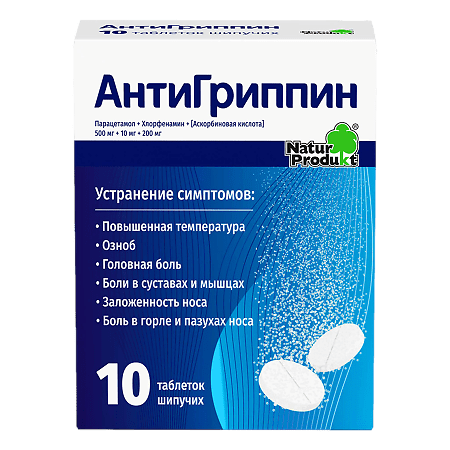
Antigrippin, 500 mg+10 mg+200 mg 10 pcs.
€10.71 €9.37
Description
Combination drug.
Paracetamol has analgesic and antipyretic effects.
Chlorphenamine (blocker of histamine H1-receptors) has anti-allergic effect, reduces mucosal edema of the upper respiratory tract.
Ascorbic acid normalizes capillary permeability, has an antioxidant effect and helps increase the body’s resistance.
Indications
Indications
Infectious and inflammatory diseases (ARVI, influenza), accompanied by fever, chills, headache, joint and muscle pain, nasal congestion and pain in the throat and sinuses.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Combined drug.
Paracetamol has an analgesic and antipyretic effect.
Chlorphenamine (histamine H1 receptor blocker) has an antiallergic effect, reduces swelling of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract.
Ascorbic acid normalizes capillary permeability, has an antioxidant effect, and helps increase the body’s resistance.
Special instructions
Special instructions
You should consult your doctor if you are taking metoclopramide, domperidone or cholestyramine.
Under the influence of paracetamol and ascorbic acid, laboratory test parameters (quantitative determination of glucose and uric acid in blood plasma, bilirubin, activity of “liver” transaminases, LDH) may be distorted.
With long-term use in doses significantly higher than recommended, the likelihood of impaired liver and kidney function increases; monitoring of the peripheral blood picture is necessary.
To avoid toxic liver damage, paracetamol should not be combined with alcoholic beverages, or taken by persons prone to chronic alcohol consumption. The risk of developing liver damage increases in patients with alcoholic hepatosis.
Prescribing ascorbic acid to patients with rapidly proliferating and intensively metastasizing tumors can aggravate the process. In patients with high iron levels in the body, ascorbic acid should be used in minimal doses.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Paracetamol, Chlorphenamine, [Ascorbic Acid]
Composition
Composition
1 effervescent tablet contains:
Active ingredients:
Paracetamol 500 mg.
Chlorphenamine maleate 10 mg.
Ascorbic acid 200 mg.
Excipients:
sodium bicarbonate;
citric acid;
sorbitol;
povidone;
sodium saccharinate;
sodium carbonate;
macrogol;
sodium lauryl sulfate;
lime flavor (aromatic fruit additive “Lime”).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of the drug during pregnancy and lactation is contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to paracetamol, ascorbic acid, chlorphenamine or any other component of the drug.
Erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (in the acute phase).
Severe renal and/or liver failure.
Alcoholism.
Angle-closure glaucoma.
Prostatic hyperplasia.
Children’s age (up to 15 years).
Pregnancy.
Lactation period.
With caution:
Renal and/or liver failure.
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Congenital hyperbilirubinemia:
Gilbert’s syndrome.
Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
Rotor syndrome.
Viral hepatitis.
Alcoholic hepatitis.
Old age.”
Side Effects
Side Effects
The drug is well tolerated in recommended doses.
In isolated cases there are:
From the side of the central nervous system: headache, feeling of fatigue.
From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, pain in the epigastric region.
From the endocrine system: hypoglycemia (up to the development of coma).
From the hematopoietic organs: anemia, hemolytic anemia (especially for patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency); extremely rarely – thrombocytopenia.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, urticaria, Quincke’s edema.
Other: hypervitaminosis, metabolic disorders, feeling of heat, dry mouth, accommodation paresis, urinary retention, drowsiness.
All side effects of the drug should be reported to your doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
Ethanol enhances the sedative effect of antihistamines. Antidepressants, antiparkinsonian drugs, antipsychotic drugs (phenothiazine derivatives) – increase the risk of side effects (urinary retention, dry mouth, constipation). Glucocorticosteroids – increase the risk of developing glaucoma.
When used simultaneously, it reduces the chronotropic effect of isoprenaline.
Reduces the therapeutic effect of antipsychotic drugs (neuroleptics) – phenothiazine derivatives, tubular resorption of amphetamine and tricyclic antidepressants.
Inducers of microsomal oxidation in the liver (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants) increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, which makes it possible to develop severe intoxications with small overdoses. Ethanol contributes to the development of acute pancreatitis.
Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation (including cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity. Simultaneous administration of the drug and diflunisal increases the plasma concentration of paracetamol by 50% and increases hepatotoxicity. Simultaneous use of barbiturates reduces the effectiveness of paracetamol and increases the excretion of ascorbic acid in the urine.
Paracetamol reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
Overdose
Overdose
An overdose of the drug is due to the substances included in its composition. The clinical picture of an acute overdose of paracetamol develops within 6-14 hours after administration.
Symptoms of chronic overdose: appear 2-4 days after increasing the dose of the drug.
Symptoms of acute overdose: include gastrointestinal disorders (diarrhea, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, abdominal discomfort and/or abdominal pain), increased sweating.
Symptoms of chlorphenamine overdose: depression, seizures and coma may occur.
Treatment: symptomatic.
Short product description
Short product description
Complex drug for symptomatic treatment of ARVI.
When there is no time to get sick – AntiGrippin – triple power against 8 symptoms of ARVI and colds.
1) 3 active components act on 8 symptoms of ARVI and colds
2) Does not contain phenylephrine and caffeine
3) AntiGrippin in the form of effervescent tablets does not contain sugar
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
Shelf life – 3 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Natur Product Pharma Sp. z o.o., Poland
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At 10-30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Natur Produkt Pharma, Poland |
| Medication form | effervescent tablets |
| Brand | Natur Produkt Pharma |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Antigrippin, 500 mg+10 mg+200 mg 10 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.