No products in the cart.
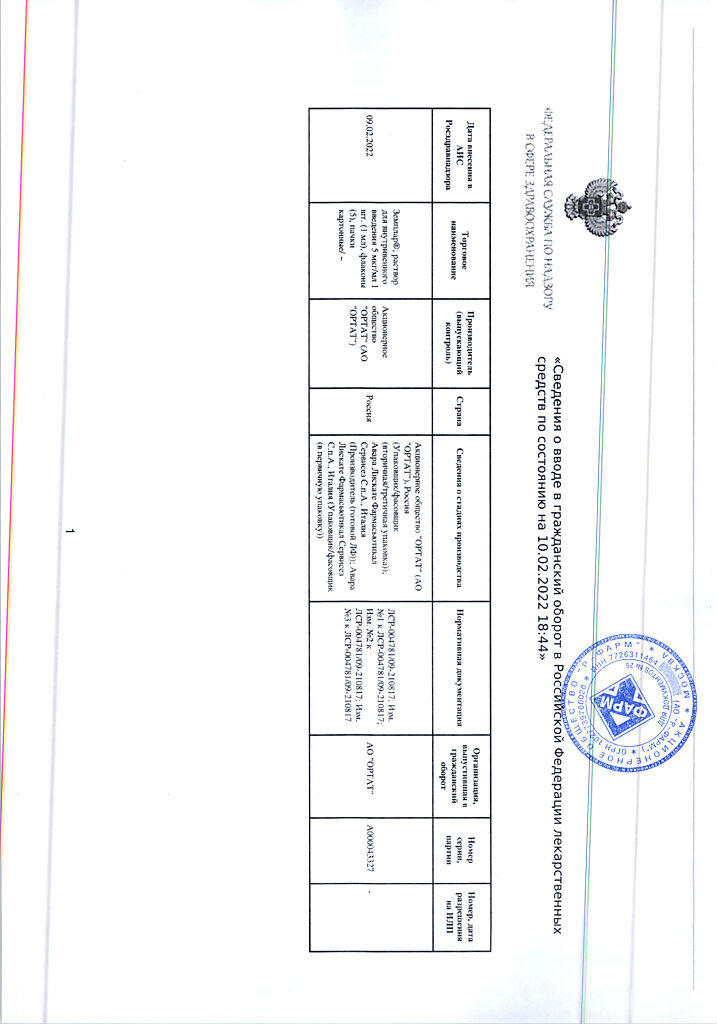
Zemplar, 5 µg/ml 1 ml 5 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacodynamics
The drug regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism. Paricalcitol is a synthetic analogue of the biologically active vitamin D (calcitriol). Paricalcitol has a biological effect by interacting with vitamin D receptors, resulting in selective activation of the response mediated by this vitamin. Vitamin D and paricalcitol reduce parathyroid hormone levels by inhibiting its synthesis and secretion. In the early stages of chronic kidney disease there is a decrease in calcitriol levels.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism is characterized by increased levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH), which is associated with inadequate levels of active vitamin D. This vitamin is synthesized in the skin and is ingested with food. Vitamin D is sequentially hydroxylated in the liver and kidneys into the active form, which interacts with vitamin D receptors.
Calcitriol [1,25(OH)2 D3] is an endogenous hormone that activates vitamin D receptors in the parathyroid glands, intestines, kidneys and bones (thus supporting parathyroid function and calcium and phosphorus homeostasis) and in many other tissues, including the prostate, endothelium and immune cells. Receptor activation is necessary for normal bone formation. Kidney disease suppresses vitamin D activation, resulting in increased PTH levels, development of secondary hyperparathyroidism and impaired calcium and phosphorus homeostasis. Decreased calcitriol levels and increased PTH activity, which often precede changes in plasma levels of calcium and phosphorus, cause changes in the rate of bone metabolism and can lead to the development of renal osteodystrophy. In patients with chronic kidney disease, reducing PTH levels has a beneficial effect on bone ALP activity, bone metabolism, and bone fibrosis. Therapy with active vitamin D not only reduces PTH level and improves metabolic processes in bone tissue, but also allows to prevent or eliminate other consequences of insufficiency of vitamin D.
Pharmacokinetics
For two hours after an IV bolus injection of paricalcitol at doses of 0.04 µg/kg to 0.24 µg/kg, the drug concentration rapidly decreases; however, thereafter, the drug concentration decreases linearly, with a mean T1/2 of approximately 15 h. There is no evidence of cumulation when paricalcitol is used repeatedly.
Distribution
Paricalcitol is actively bound to plasma proteins (more than 99%). In healthy individuals, the Vd in equilibrium is about 23.8 liters. In patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease treated with hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, the Vd of paricalcitol at a dose of 0.24 µg/kg averages 31-35 L. The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol were studied in patients with chronic renal failure treated with hemodialysis.
Metabolism
In urine and feces several metabolites of the drug are determined. Unchanged paricalcitol was not detected in the urine. Paricalcitol is metabolized by hepatic and nonhepatic enzymes, including mitochondrial CYP24 as well as CYP3A4 and UGT1A4. Identified metabolites include products of 24(R)-hydroxylation (found in low concentrations in plasma) as well as 24,26- and 24,28-dihydroxylation and direct glucuronidation. Paricalcitol has no inhibitory effect on CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 or CYP3A at concentrations below 50 nM (21 ng/mL). CYP2B6, CYP2C9, and CYP3A4 activity is increased less than 2-fold at similar concentrations of paricalcitol.
Paricalcitol is excreted by excretion with bile. In healthy subjects, approximately 63% of the drug is excreted through the intestine and 19% by the kidneys. T1/2 paricalcitol at doses of 0.04 to 0.16 mcg/kg in healthy volunteers averages 5-7 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in Special Clinical Cases
Pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol in persons older than 65 years has not been studied.
Pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol in children and adolescents less than 18 years of age have not been studied. The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol are independent of gender.
The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol (0.24 µg/kg) were compared in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh classification) and healthy subjects.
The pharmacokinetics of unbound paricalcitol were similar in these patient groups. No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol in patients with severe hepatic impairment have not been studied.
The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol have been studied in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5 treated with hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis had no significant effect on paricalcitol excretion. However, patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5 showed decreased clearance and increased T1/2 compared with healthy subjects.
Indications
Indications
Prevention and treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism developing in chronic renal failure (stage 5 chronic kidney disease).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamics
A drug that regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus. Paricalcitol is a synthetic analogue of biologically active vitamin D (calcitriol). Paricalcitol exerts its biological effects by interacting with vitamin D receptors, resulting in selective activation of the vitamin D-mediated response. Vitamin D and paricalcitol reduce parathyroid hormone levels by inhibiting its synthesis and secretion. In the early stages of chronic kidney disease, there is a decrease in calcitriol levels.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism is characterized by an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH), which is associated with inadequate levels of active vitamin D. This vitamin is synthesized in the skin and enters the body with food. Vitamin D is sequentially hydroxylated in the liver and kidneys and converted to its active form, which interacts with vitamin D receptors.
Calcitriol [1,25(OH)2 D3] is an endogenous hormone that activates vitamin D receptors in the parathyroid glands, intestines, kidneys and bone (thereby supporting parathyroid function and calcium and phosphorus homeostasis), as well as in many other tissues, including the prostate, endothelium and immune cells. Activation of the receptors is necessary for normal bone formation. In kidney disease, the activation of vitamin D is suppressed, which leads to an increase in PTH levels, the development of secondary hyperparathyroidism and disruption of calcium and phosphorus homeostasis. Decreased calcitriol levels and increased PTH activity, which often precede changes in plasma calcium and phosphorus levels, cause changes in bone turnover and may lead to the development of renal osteodystrophy. In patients with chronic kidney disease, a decrease in PTH levels has a beneficial effect on bone alkaline phosphatase activity, metabolic processes in bone tissue, and bone fibrosis. Therapy with active vitamin D not only reduces PTH levels and improves metabolic processes in bone tissue, but also helps prevent or eliminate other consequences of vitamin D deficiency.
Pharmacokinetics
Within two hours after an intravenous bolus administration of paricalcitol in doses from 0.04 mcg/kg to 0.24 mcg/kg, the drug concentration decreases rapidly; however, subsequently the concentration of the drug decreases linearly, with an average T1/2 of about 15 hours. With repeated use of paricalcitol, no signs of cumulation are observed.
Distribution
Paricalcitol actively binds to plasma proteins (more than 99%). In healthy people, Vd at steady state is about 23.8 l. In patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease treated with hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, the Vd of paricalcitol at a dose of 0.24 mcg/kg averages 31-35 l. The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol was studied in patients with chronic renal failure treated with hemodialysis.
Metabolism
Several metabolites of the drug are detected in urine and feces. Unchanged paricalcitol was not detected in urine. Paricalcitol is metabolized by hepatic and non-hepatic enzymes, including mitochondrial CYP24, as well as CYP3A4 and UGT1A4. Identified metabolites include products of 24(R)-hydroxylation (found in low concentrations in plasma), as well as 24,26- and 24,28-dihydroxylation and direct glucuronidation. Paricalcitol does not have an inhibitory effect on CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 or CYP3A at concentrations up to 50 nM (21 ng/ml). At similar concentrations of paricalcitol, the activity of CYP2B6, CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 increases by less than 2 times.
Removal
Paricalcitol is eliminated by excretion in bile. In healthy people, approximately 63% of the drug is excreted through the intestines and 19% by the kidneys. T1/2 of paricalcitol when used in doses from 0.04 to 0.16 mcg/kg in healthy volunteers averages 5-7 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol in people over 65 years of age have not been studied.
The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol in children and adolescents under 18 years of age have not been studied. The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol does not depend on gender.
The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol (0.24 mcg/kg) were compared in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh classification) and healthy subjects.
The pharmacokinetics of unbound paricalcitol were similar in these patient groups. No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild or moderate liver dysfunction. The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol in patients with severe hepatic impairment has not been studied.
The pharmacokinetics of paricalcitol was studied in patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease treated with hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis did not have a significant effect on the excretion of paricalcitol. However, in patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease, a decrease in clearance and an increase in T1/2 was detected compared to healthy people.
Special instructions
Special instructions
When titrating the dose of paricalcitol, more frequent laboratory tests may be required. Once the dose is adjusted, serum calcium and phosphorus levels should be measured at least once a month. Serum or plasma PTH levels are recommended to be monitored every 3 months. For reliable analysis of biologically active PTH in patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease, it is recommended to use a second or subsequent generation method.
There were no differences in the effectiveness or safety of the drug in patients under 65 years of age and over 65 years of age.
Use in pediatrics
Experience with the use of paricalcitol injection in children and adolescents under 18 years of age is limited.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Paricalcitol
Composition
Composition
1 ml of solution contains:
Active ingredients:
paricalcitol 5 mcg.
Excipients:
ethanol 95%,
propylene glycol,
water d/i.
The ampoule contains 5 ml of solution.
There are 5 ampoules in a cardboard package.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypervitaminosis D;
combined use with phosphates or vitamin D derivatives;
hypercalcemia;
children under 18 years of age (clinical studies have not been conducted);
breastfeeding period;
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
With caution: the drug should be prescribed simultaneously with cardiac glycosides.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Frequency of adverse events recorded in phase 2 and 3 clinical studies.
The table lists adverse events of any origin, the frequency of which in the paricalcitol group was 2% or more (patients in whom the same reaction was recorded repeatedly were counted once).
Incidence of adverse events in all placebo-controlled studies
Adverse events
Paricalcitol (n=62)
Placebo (n=51)
General
Chills
5%
2%
Malaise
3%
0
Fever
5%
2%
Flu
5%
4%
Sepsis
5%
2%
From the cardiovascular system
Rapid heartbeat
3%
0
From the digestive system
Dry mouth
3%
2%
Gastrointestinal bleeding
5%
2%
Nausea
13%
8%
Vomit
8%
6%
From the side of the central nervous system
Dizziness
5%
2%
From the respiratory system
Pneumonia
5%
0
Others
Edema
7%
0
Changes in mean levels of calcium, phosphorus, and Ca × P product in an open-label 13-month study confirm the safety of long-term paricalcitol therapy in this group of patients.
Adverse events in phase 4 clinical trials
In one phase 4 study, headache (2%) and dysgeusia (2%) were frequently reported.
Adverse reactions recorded during post-marketing surveillance
In clinical practice, the following adverse reactions have rarely been reported when using injectable paricalcitol:
Allergic reactions: urticaria, Quincke’s edema, laryngeal edema.
From the peripheral nervous system: taste perversion (metallic taste).
Dermatological reactions: rash, itching.
Interaction
Interaction
Based on in vitro studies, paricalcitol should not inhibit the clearance of drugs metabolized by CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 or CYP3A, or induce the clearance of substances biotransformed by CYP2B6, CYP2C9 or CYP3A.
The interaction of paricalcitol injection with other drugs has not been specifically studied.
When studying the interaction of ketoconazole and paricalcitol in capsules, it was shown that ketoconazole causes an approximately 2-fold increase in the AUC of paricalcitol. Paricalcitol is partially metabolized by the CYP3A isoenzyme, and ketoconazole is a potent inhibitor of this isoenzyme, so caution should be exercised when combining paricalcitol with ketoconazole and other potent inhibitors of the CYP3A isoenzyme.
Hypercalcemia of any origin increases intoxication with cardiac glycosides, so caution must be exercised when using them in combination with paricalcitol.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: An overdose of paricalcitol can lead to the development of hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, hyperphosphatemia and suppression of PTH secretion.
Acute overdose of paricalcitol can lead to the development of hypercalcemia and requires emergency care. During dose selection, serum calcium and phosphorus levels should be regularly monitored. Long-term therapy with paricalcitol may be complicated by hypercalcemia, an increase in the Ca × P product and calcification of soft tissues (metastatic calcification).
Treatment: in case of clinically significant hypercalcemia, the dose of paricalcitol should be immediately reduced or treatment should be interrupted. Recommended measures include a hypocalcium diet, discontinuation of calcium supplements, monitoring of fluid and electrolyte balance, assessment of ECG changes (critical for patients receiving cardiac glycosides) and hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis using a calcium-free dialysate. Serum calcium levels should be monitored regularly until they return to normal. When PTH levels are suppressed below normal, adynamic bone disease, a pathological condition with low bone turnover, may develop.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At 15–25 °C (do not freeze)
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Avara Liscate Pharmaceutical Services S.p.A., Italy
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At 15-25 °C (do not freeze) |
| Manufacturer | Avara Liscate Pharmaceutical Services S.p.A., Italy |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Avara Liscate Pharmaceutical Services S.p.A. |
Related products
Buy Zemplar, 5 µg/ml 1 ml 5 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.