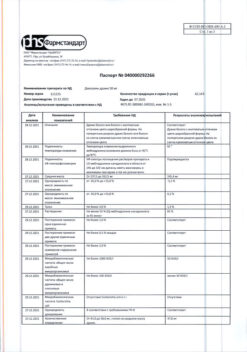
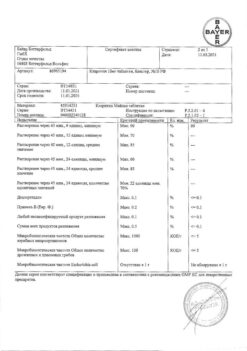
No products in the cart.
Description
Levocetirizine, the active ingredient in Xizal® , is the R-enantiomer of cetirizine, a powerful and selective histamine antagonist that blocks H1-histamine receptors.
Levocetirizine influences the histamine-dependent stage of allergic reactions and also reduces migration of eosinophils reduces vascular permeability and limits the release of inflammatory mediators.
Levocetirizine prevents and facilitates the development of allergic reactions has antiexudative antipruritic action with practically no anticholinergic and antiserotonin action. In therapeutic doses has practically no sedative effect.
Pharmacokinetics:
The pharmacokinetic parameters of levocetirizine change linearly.
Intake
After oral administration, the drug is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Food intake does not affect the completeness of absorption, although it reduces its rate. Maximal concentration (Cmax) in blood plasma is reached after 09 hours and equals 270 ng/ml Equilibrium concentration is reached after 2 days.
Distribution
Levocetirizine is 90% bound to plasma proteins. The volume of distribution (Vd) is 04 l/kg. Bioavailability reaches 100%.
Metabolism
In small amounts (< 14%) are metabolized in the body by N- and O-dealkylation (unlike other H1-histamine receptor antagonists which are metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome system) to form a pharmacologically inactive metabolite. Due to insignificant metabolism and lack of metabolic potential, interaction of levocetirizine with other drugs seems unlikely.
Elimination
The elimination half-life (T1/2) in adults is 79 ±19 hours.
The elimination half-life is shorter in young children. In adults, the total clearance is 063 ml/min/kg.
About 854% of the taken dose of the drug is excreted unchanged by the kidneys through glomerular filtration and tubular secretion; about 129% – through the intestine.
Patients with renal impairment
In patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance (CK) < 40 ml/min) the drug clearance is decreased. In patients on hemodialysis total clearance is reduced by 80%. Less than 10% of the drug is removed during a standard 4-hour hemodialysis procedure.
Patients with hepatic impairment
Pharmacokinetics of levocetirizine in patients with hepatic impairment has not been studied.
In patients with chronic liver disease (hepatocellular cholestatic and biliary cirrhosis) who received racemic cetirizine compound in dose of 10 or 20 mg once, a 50% increase in half-life and 40% decrease in clearance of the drug were observed compared to healthy subjects.
Children
The data from a study of the pharmacokinetics of the drug in 14 children aged 6 to 11 years with a body weight of 20 to 40 kg when 5 mg of levocetirizine was taken orally once showed that the Cmax and area under the curve (AUC) were approximately twice that of healthy adults in a cross-match control. The mean Cmax was 450 ng/mL and maximum concentration was reached after an average of 12 hours total body weight-adjusted clearance was 30% higher and the half-life was 24% shorter in children than in adults.
Special pharmacokinetic studies in children younger than 6 years have not been conducted. A retrospective pharmacokinetic analysis was performed in 323 patients (181 children aged 1 to 5 years 18 children aged 6 to 11 years and 124 adults aged 18 to 55 years) receiving one or more doses of levocetirizine from 125 mg to 30 mg.
The data obtained in the analysis showed that administration of the drug in a dose of 125 mg in children aged 6 months to 5 years resulted in plasma concentrations corresponding to those in adults when 5 mg of the drug was taken once daily.
Elderly patients
There are limited data on pharmacokinetics in elderly patients. When 30 mg of levocetirizine was repeatedly administered once daily for 6 days in 9 elderly patients (age 65 to 74 years), total clearance was approximately 33% lower than that of younger adults. The distribution of cetirizine racemate has been shown to be more dependent on renal function than on age. This may also apply to levocetirizine, as both levocetirizine and cetirizine are primarily excreted in the urine. Therefore, in elderly patients, the dose of levocetirizine should be adjusted depending on renal function.
Indications
Indications
For adults and children over 6 years of age: treatment of symptoms of year-round and seasonal allergic rhinitis and allergic conjunctivitis, such as conjunctival hyperemia, itching, sneezing, lacrimation; hay fever (hay fever); urticaria, including chronic idiopathic urticaria, Quincke’s edema; other allergic dermatoses accompanied by itching and rashes.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Levocetirizine – the active substance of the drug Xyzal® – is the R-enantiomer of cetirizine, a powerful and selective histamine antagonist that blocks H1-histamine receptors.
Levocetirizine has an effect on the histamine-dependent stage of allergic reactions and also reduces the migration of eosinophils, reduces vascular permeability and limits the release of inflammatory mediators.
Levocetirizine prevents the development and facilitates the course of allergic reactions, has an antiexudative antipruritic effect, and has virtually no anticholinergic and antiserotonin effects. In therapeutic doses it has virtually no sedative effect.
Pharmacokinetics:
The pharmacokinetic parameters of levocetirizine change linearly.
Suction
After oral administration, the drug is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Eating does not affect the completeness of absorption, although it reduces its speed. The maximum concentration (Cmax) in the blood plasma is reached after 09 hours and is 270 ng/ml; the equilibrium concentration is achieved after 2 days.
Distribution
Levocetirizine is 90% bound to plasma proteins. The volume of distribution (Vd) is 04 l/kg. Bioavailability reaches 100%.
Metabolism
In small quantities (<14%) it is metabolized in the body by N- and O-dealkylation (unlike other H1-histamine receptor antagonists which are metabolized in the liver using the cytochrome system) to form a pharmacologically inactive metabolite. Due to negligible metabolism and lack of metabolic potential, interaction of levocetirizine with other drugs is unlikely.
Removal
The half-life (T1/2) in adults is 79 ± 19 hours.
In young children, the half-life is shorter. In adults, the total clearance is 063 ml/min/kg.
About 854% of the administered dose of the drug is excreted unchanged by the kidneys through glomerular filtration and tubular secretion; about 129% – through the intestines.
Selected patient groups
Patients with renal failure
In patients with renal failure (creatinine clearance (CC) < 40 ml/min), drug clearance is reduced. In patients on hemodialysis, total clearance is reduced by 80%. Less than 10% of the drug is removed during a standard 4-hour hemodialysis procedure.
Patients with liver failure
The pharmacokinetics of levocetirizine in patients with hepatic impairment have not been studied.
In patients with chronic liver diseases (hepatocellular cholestatic and biliary cirrhosis) receiving the racemic compound cetirizine at a single dose of 10 or 20 mg, an increase in half-life by 50% and a decrease in clearance of the drug by 40% were observed compared with healthy people.
Children
Data from a study of the pharmacokinetics of the drug in 14 children aged 6 to 11 years with a body weight of 20 to 40 kg after oral administration of a single dose of 5 mg of levocetirizine showed that Cmax and area under the curve (AUC) were approximately twice as high as those in healthy adults during cross-control. The average Cmax was 450 ng/ml, the maximum concentration was reached on average after 12 hours, the total clearance taking into account body weight was 30% higher and the half-life was 24% shorter in children than the corresponding values in adults.
Specific pharmacokinetic studies have not been conducted in children under 6 years of age. A retrospective pharmacokinetic analysis was conducted in 323 patients (181 children aged 1 to 5 years, 18 children aged 6 to 11 years, and 124 adults aged 18 to 55 years) who received one or more doses of levocetirizine from 125 mg to 30 mg.
The data obtained during the analysis showed that taking the drug at a dose of 125 mg in children aged 6 months to 5 years leads to plasma concentrations corresponding to those in adults when taking 5 mg of the drug once a day.
Elderly patients
Pharmacokinetic data in elderly patients is limited. When repeated dosing of levocetirizine 30 mg once daily for 6 days in 9 elderly patients (age 65 to 74 years) total clearance was approximately 33% lower than that in younger adults. The distribution of cetirizine racemate has been shown to be more dependent on renal function than on age. This statement may also apply to levocetirizine since both drugs, levocetirizine and cetirizine, are excreted primarily in the urine. Therefore, in elderly patients, the dose of levocetirizine should be adjusted depending on renal function.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The intervals between doses should be individualized depending on renal function.
Caution is recommended when consuming concomitantly with alcohol.
If patients have predisposing factors for urinary retention (eg spinal cord injury, prostatic hyperplasia), caution should be exercised as levocetirizine may increase the risk of urinary retention.
Caution should be exercised in patients with epilepsy and increased convulsive readiness since levocetirizine may cause exacerbation of seizures.
The reaction to skin allergy tests is suppressed by antihistamines and you must refrain from taking the drug for 3 days before testing.
Itching may occur after stopping taking levocetirizine, even if such symptoms were not present at the beginning of treatment. Symptoms may go away on their own. In some cases, symptoms may be severe and may require resumption of treatment. Once treatment is resumed, these symptoms should subside.
Children
Levocetirizine film-coated tablets are contraindicated in children under 6 years of age since this dosage form does not allow the use of an appropriate dosage for this age group. It is recommended to use the pediatric dosage form (oral drops).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and fur.:
Levocetirizine may cause increased drowsiness; therefore, Xyzal® may affect the ability to drive a car or operate machinery. During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Levocetirizine
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Core:
active substance: levocetirizine dihydrochloride 5.0 mg;
excipients: lactose monohydrate 63.50 mg, microcrystalline cellulose 30.00 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide 0.50 mg, magnesium stearate 1.00 mg.
Shell: opadry Y-1-7000 3.00 mg (contains hypromellose 62.5%, titanium dioxide (E171) 31.25%, macrogol 400 6.25%).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Data on the use of levocetirizine during pregnancy are virtually absent or limited (less than 300 pregnancy outcomes). However, the use of cetirizine racemate levocetirizine during pregnancy (more than 1000 pregnancy outcomes) was not accompanied by malformations and intrauterine and neonatal toxic effects. Animal studies have not revealed any direct or indirect adverse effects on the course of pregnancy, embryonic and fetal development, childbirth and postnatal development.
During pregnancy, the use of levocetirizine may be considered if necessary.
Breastfeeding period
Cetirizine racemate of levocetirizine is excreted in breast milk. Therefore, it is also likely that levocetirizine is excreted in breast milk. Breastfed children may experience adverse reactions to levocetirizine. Therefore, caution must be exercised when prescribing levocetirizine during breastfeeding.
Fertility
There are no clinical data on levocetirizine.
Before using the drug, if you are pregnant or think you might be pregnant or are planning a pregnancy, you should consult your doctor.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance cetirizine hydroxyzine, any piperazine derivative or to any other excipient of the drug.
Lactase deficiency, lactose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption.
End-stage renal failure (creatinine clearance <10 ml/min).
Children’s age up to 6 years.
With caution:
In case of chronic renal failure (correction of the dosage regimen is necessary).
In elderly patients (with an age-related decrease in glomerular filtration).
In patients with spinal cord injury, prostatic hyperplasia, or in the presence of other factors predisposing to urinary retention, since levocetirizine may increase the risk of urinary retention.
When used simultaneously with alcohol (see Interactions with other drugs).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
Caution should be exercised in patients with epilepsy and increased convulsive readiness since levocetirizine may cause exacerbation of seizures.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Headache, fatigue, drowsiness, dry mouth.
Rarely – migraine, dizziness, dyspeptic disorders, allergic reactions (angioedema, rash, urticaria, itching).
Interaction
Interaction
The interaction of levocetirizine with other drugs has not been studied.
When studying the drug interactions of cetirizine racemate with antipyrine azithromycin cimetidine diazepam erythromycin glipizide ketoconazole and pseudoephedrine, no clinically significant adverse interactions were identified.
When used simultaneously with theophylline (400 mg/day), the total clearance of cetirizine is reduced by 16% (theophylline kinetics does not change).
A study with simultaneous administration of ritanovir (600 mg 2 times a day) and cetirizine (10 mg per day) showed that the exposure of cetirizine increased by 40% and the exposure of ritanovir changed slightly (-11%).
In sensitive patients, the simultaneous use of levocetirizine and alcohol or drugs that have a suppressive effect on the central nervous system (CNS) can cause lethargy and deterioration in performance.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: may be accompanied by signs of intoxication in the form of drowsiness; in children, an overdose of the drug may be accompanied by anxiety and increased irritability.
Treatment: if symptoms of overdose appear (especially in children), the drug should be stopped, gastric lavage, activated charcoal, and symptomatic therapy are necessary. There is no specific antidote.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
4 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
YUSB Farshim S.A., Switzerland
Additional information
| Shelf life | 4 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | SSB Farshim S.A., Switzerland |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | SSB Farshim S.A. |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Xizal, 5 mg 14 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.