No products in the cart.
Vinpocetine, tablets 5 mg 30 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
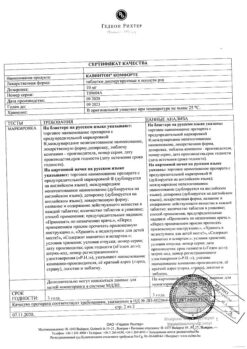
The mechanism of action of vinpocetine consists of several elements: it improves cerebral blood flow and metabolism, has a favorable effect on the rheological properties of the blood.
Neuroprotective effect is realized by reducing the adverse cytotoxic effects of excitatory amino acids. It blocks Na+- and Ca2+-channels and NMDA- and AMRA-receptors. Selectively inhibits Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent HMF-phosphodiesterase. Increases serotonin and noradrenaline metabolism in the brain, stimulates noradrenergic neurotransmitter system and has antioxidant effect.
It improves microcirculation in the brain by inhibiting platelet aggregation, decreasing pathologically elevated blood viscosity, increasing erythrocyte deformability and inhibiting adenosine reuptake.
Selectively increases cerebral blood flow by reducing cerebral vascular resistance without a significant effect on systemic parameters of blood circulation (blood pressure (BP), cardiac output, heart rate, total peripheral vascular resistance); does not cause the effect of “stealing”.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Interaction
Interaction
An interaction is not observed with beta-adrenoblockers (pindolol), clopamide, glibenclamide, digoxin, acenocoumarol and hydrochlorothiazide.
Methyldopa may increase the hyponensive effect of vinpocetine; therefore, systematic BP control is required with their concomitant use.
While there is no data to support the possibility of interactions, caution is recommended when concomitant use with central, antiarrhythmic, and anticoagulant drugs.
Directions for use
Directions for use
Ingestion, after meals.
The course of treatment and the dose are determined by the attending physician.
The usual daily dose is 15-30 mg (5-10 mg 3 times a day).
The starting daily dose is 15 mg. The maximum daily dose
30 mg.
No dose adjustment is required for the elderly, for hepatic or renal dysfunction.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
In the presence of prolonged QT interval syndrome or concomitant use of drugs that cause prolongation of the QT interval, periodic ECG control is required. In patients with severe cardiac rhythm disturbances, increased intracranial pressure, taking antiarrhythmic drugs, prolonged QT syndrome or concomitant use of drugs causing prolongation of the QT interval, the drug should be used with caution.
Effects on ability to concentrate: During treatment, caution should be exercised when driving motor vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities requiring increased concentration and rapid psychomotor reactions.
Synopsis
Synopsis
Features
Features
absorption
After oral administration, it is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Time of reaching maximum concentration (TSmax) in blood plasma is 1 hour. Absorption occurs mainly in the proximal parts of the gastrointestinal tract. During passage through the intestinal wall it is not metabolized.
Distribution
In oral administration of radioactively labeled vinpocetine to rats, the highest concentration was found in the liver and gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration in tissues was observed 2-4 hours after administration. The radioactivity in the brain did not exceed the values detected in the blood.
In humans the binding to plasma proteins is 66%, bioavailability when administered orally is 7%. The volume of distribution is 246.7-88.5 L, which indicates high tissue binding. Total clearance (66.7 l/h) exceeds hepatic blood flow rate (50 l/h), indicating extrahepatic metabolism.
Metabolism
The major metabolite is apovincaminate (AVA), which is
25-30% of the parent compound. The area under the curve “concentration – time” of ABA after oral administration is twice as large as that of intravenous administration of vinpocetine. Thus, vinpocetine is subject to a pronounced “primary passage” effect through the liver. Other metabolites include: hydroxyvinpocetine, hydroxy-AVA, ABA-dioxyglycinate and their conjugates (sulfates and9 or) glucuronides). Dosage adjustment is not required if liver or renal function is impaired because vinpocetine does not cumulate.
Elimation
Elimation of unchanged vinpocetine is low (several percent). When administered multiple times at doses of 5 mg and 10 mg, the kinetics are linear, with equilibrium plasma concentrations of 1.2±0.27 and 2.1±0.33 ng/mL, respectively. The elimination half-life in humans
4.8±1.29 h. It is excreted by the kidneys and through the intestine at a ratio of 60:40. In rats and dogs high radioactivity when administered radioactively labeled vinpocetine is found in bile, but significant enterohepatic recirculation is noted.
Special patient groups
Because vinpocetine is primarily intended to treat the elderly, the decreased absorption and distribution as well as excretion in this age group must be considered, especially with prolonged use. However, according to the results of clinical studies, it was found that the kinetics of vinpocetine in the elderly is not significantly different from the young, and there is no cumulation. No cumulation is noted in liver and kidney function disorders, which allows for long-term therapy. Vinpocetine penetrates through the placenta and is excreted in breast milk.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to vinpocetine or any of the ingredients of the drug.
Pregnancy, lactation.
Children under 18 years of age (due to insufficient data).
Side effects
Side effects
Overdose
Overdose
There have been no recorded cases of overdose. According to the literature, the use of 60 mg of vinpocetine per day is safe. Single oral administration of 360 mg vinpocetine does not cause clinically significant cardiovascular and other reactions.
The treatment is symptomatic.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
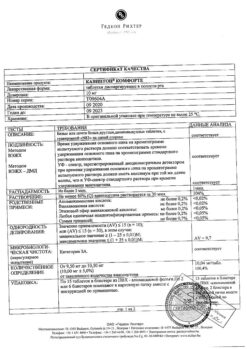
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In the dark place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °С. Store out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Izvarino Pharma, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Izvarino Pharma |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Vinpocetine, tablets 5 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.