No products in the cart.
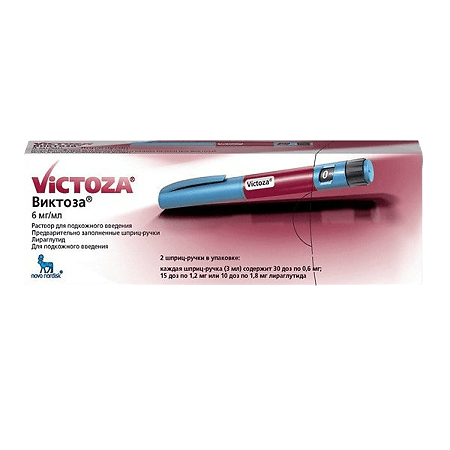
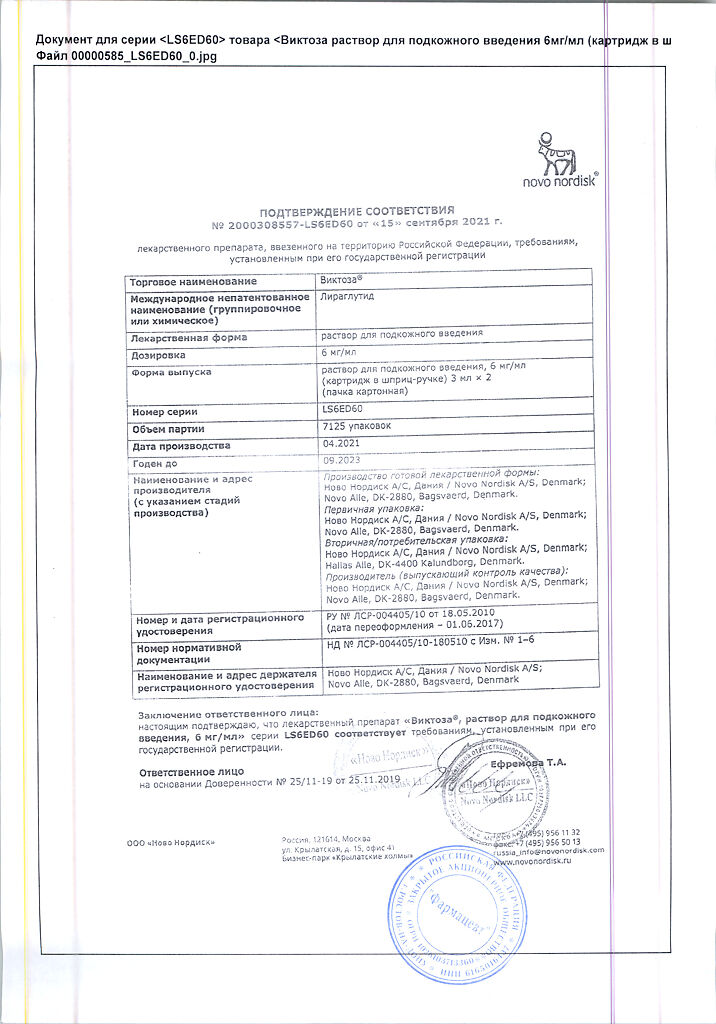
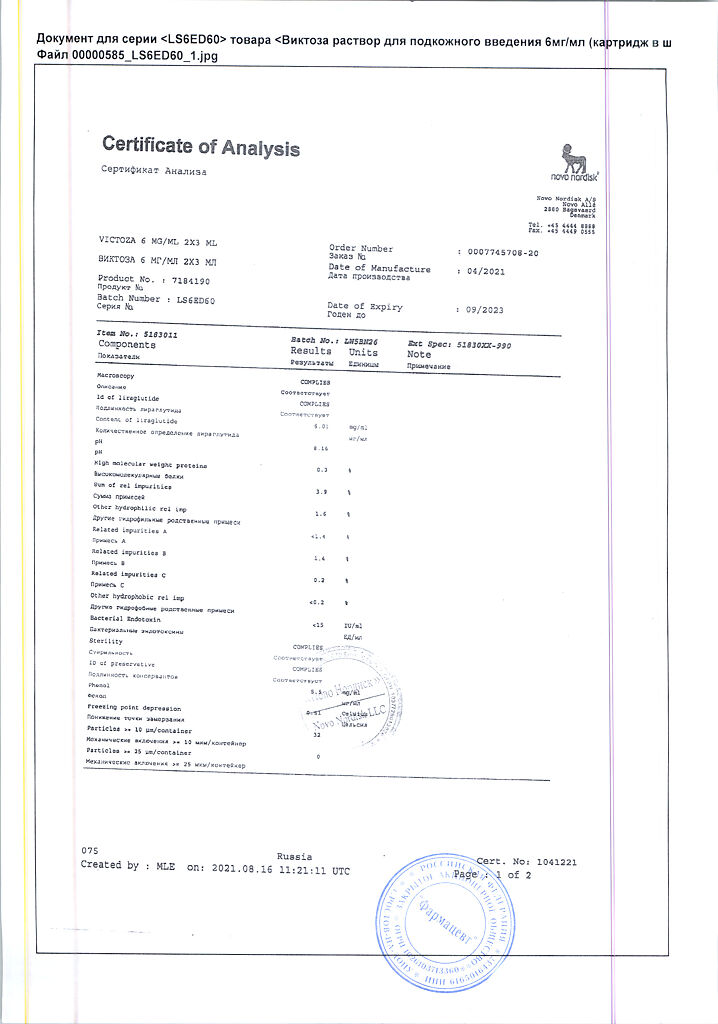
Victoza, 6 mg/ml 3 ml cartridges in syringe pens 2 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Hypoglycemic drug – glucagon-like receptor polypeptide agonist.
ATC code – A10BX07.
Indications
Indications
Victoza is indicated in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus along with diet and exercise to achieve glycemic control as:
Monotherapy
Combination therapy with one or more oral hypoglycemic drugs (metformin, sulfonylureas or thiazolidinediones) in patients who have not achieved adequate glycemic control on previous therapy.
Combination therapy with basal insulin in patients who have not achieved adequate glycemic control on therapy with Victoza® and metformin.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Hypoglycemic agent – glucagon-like polypeptide receptor agonist.
ATX code – A10BX07.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Victoza should not be used in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus or for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Victoza does not replace insulin. The administration of liraglutide to patients already receiving insulin has not been studied.
Experience with the use of Victosau in patients with heart failure of functional classes I–II in accordance with the NYHA functional classification of chronic heart failure is limited. There is no experience with the use of the drug Victoza in patients with heart failure of functional classes III–IV in accordance with the NYHA classification of chronic heart failure.
Experience with the use of the drug Victoza in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases and diabetic gastric paresis is limited, therefore the use of the drug Victoza in these groups of patients is contraindicated. The use of the drug Victoza is associated with the development of transient adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract, such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
The use of other GLP-1 agonists has been associated with a risk of pancreatitis. Several cases of acute pancreatitis have been reported. Patients should be informed about the characteristic symptoms of acute pancreatitis: persistent severe pain in the abdominal area. If pancreatitis is suspected, therapy with Victoza and other potentially dangerous drugs should be stopped immediately.
During clinical studies of Victoza in selected patients (particularly in patients with pre-existing thyroid disease), thyroid adverse events were reported, including increased serum calcitonin concentrations, goiter, and thyroid neoplasms.
During clinical studies, signs and symptoms of dehydration and renal failure were reported in patients taking Victoza. Patients receiving Victoza should be warned of the possible risk of dehydration due to gastrointestinal side effects and the need to take precautions to avoid the development of hypovolemia.
Patients receiving Victoza in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives have an increased risk of developing hypoglycemia. The risk of hypoglycemia can be reduced by reducing the dose of sulfonylurea derivatives.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. No studies have been conducted on the effect of the drug Victoza on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. It is unlikely that liraglutide may affect the ability to drive vehicles or use machines. Patients should be warned that they should take precautions to avoid the development of hypoglycemia while driving or operating machinery, especially when using Victoza in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives.
Instructions for use
Victoza should not be used if it appears other than a clear and colorless or almost colorless liquid.
Victoza cannot be used if it has been frozen.
The drug Victoza can be administered using needles up to 8 mm long and up to 32G thick. The syringe pen is intended for use in combination with NovoFine or NovoTwist disposable injection needles.
Injection needles are not included in the package.
The patient should be informed that the used needle should be thrown away after each injection and that the pen with the needle attached should not be stored. This measure will prevent contamination, infection and leakage of the drug from the syringe pen and guarantee dosing accuracy.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Liraglutide
Composition
Composition
1 ml of solution for subcutaneous administration contains:
active ingredient:
liraglutide 6 mg.
excipients:
sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate – 1.42 mg;
propylene glycol – 14 mg;
phenol – 5.5 mg;
hydrochloric acid/sodium hydroxide – q.s.;
water for injection – up to 1 ml.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
There are no adequate data on the use of Victoza in pregnant women. Animal studies have demonstrated reproductive toxicity of the drug. The potential risk to humans is unknown.
The drug Victosan cannot be used during pregnancy; instead, it is recommended to treat with insulin. If the patient is preparing for pregnancy or pregnancy has already occurred, therapy with Victoza must be stopped immediately.
It is not known whether liraglutide is excreted in women’s breast milk. Animal studies have shown that the penetration of liraglutide and closely related metabolites into breast milk is low. There is no experience with the use of Victosau in lactating women. The use of the drug during breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to the active substance or other components included in the drug;
pregnancy and breastfeeding;
diabetes mellitus type 1;
diabetic ketoacidosis;
severe renal dysfunction;
liver dysfunction;
heart failure of functional class III–IV (according to the NYHA classification);
inflammatory bowel diseases;
gastric paresis;
age under 18 years.
With caution: heart failure functional class I–II (according to the NYHA classification); moderate renal dysfunction; age 75 years and older Experience with the use of the drug in patients in these categories is limited.
Side Effects
Side Effects
During clinical trials, the most commonly reported gastrointestinal side effects were nausea and diarrhea (reported in >10% of patients); vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain and dyspeptic symptoms (reported in ≥1%, but ≤ 10% of patients).
At the beginning of therapy with Victoza, these gastrointestinal side effects may occur more frequently, but as treatment continues, the reactions usually decrease within a few days or weeks. Adverse reactions such as headache and upper respiratory tract infections were observed relatively frequently (1-10% of patients). In addition, the development of hypoglycemic conditions is possible, especially when using the drug Victoza in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives (registered in > 10% of patients). Severe hypoglycemia mainly develops against the background of combined use of the drug Victoza with sulfonylurea derivatives.
Serious side effects have been reported very rarely.
Table 1 provides information on side effects identified during long-term controlled phase III clinical trials of Victoza and spontaneous (post-marketing) reports. Adverse reactions identified during long-term phase III clinical trials with an incidence of >5% are presented, provided that their frequency was higher in the group of patients receiving Victoza compared to that in the group of patients receiving comparator drugs. Adverse reactions with an incidence of ≥1% were also included, provided that their incidence was 2 or more times higher than the incidence of adverse reactions in the groups of patients receiving therapy with comparator drugs.
The frequency of other spontaneous (post-marketing) reports was calculated based on their occurrence during phase III clinical trials.
All adverse reactions presented below, based on data obtained during clinical trials and in the post-marketing period, are divided into groups according to the frequency of development in accordance with MedDRA and organ systems. The incidence of adverse reactions is defined as: very often (≥ 1/10); often (≥ 1/100 to
Table 1 Adverse reactions identified in long-term placebo-controlled phase III clinical trials and spontaneous (post-marketing) reports
Organs and systems/adverse reactionsFrequency of development phase III studiesSpontaneous reportsMetabolic and nutritional disordersHypoglycemiaCommon AnorexiaCommon Decreased appetiteCommon Nervous system disordersHeadacheCommon Gastrointestinal disordersNauseaVery common DiarrheaVery common VomitingCommon DyspepsiaCommon Pain in the upper abdomenCommon Constipation Frequent Gastritis Frequent Flatulence Frequent Abdominal bloating Frequent Gastroesophageal reflux Frequent Belching Frequent Immune system disorders Anaphylactic reactions Rare Infections and infestations Upper respiratory tract infections Frequent General disorders and injection site reactions Malaise Uncommon Administration site reactions Frequent Renal and urinary tract disorders Acute kidney insufficiency* UncommonRenal dysfunction* UncommonMetabolic and nutritional disordersDehydration* UncommonSkin and subcutaneous tissue disordersHurticaria UncommonRash OftenItching Uncommon
N= 2501 patients receiving therapy with Victoza
Hypoglycemia
Most episodes of confirmed hypoglycemia recorded in clinical trials were mild.
During clinical studies, no cases of severe hypoglycemia were observed when using the drug Victoza as monotherapy. Severe hypoglycemia may occur infrequently and is mainly observed when using the drug Victoza in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives (0.02 cases/patient per year). When Victoza was used in combination with other oral hypoglycemic drugs (not sulfonylureas), the development of hypoglycemia was observed very rarely (0.001 cases/patient per year).
During therapy with liraglutide at a dose of 1.8 mg in combination with insulin detemir and metformin, no cases of severe hypoglycemia were observed. The incidence of mild hypoglycemia was 0.228 cases/patient per year. In the groups of patients treated with liraglutide 1.8 mg and metformin, the incidence of mild hypoglycemia was 0.034 and 0.115 cases/patient per year, respectively.
Adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract
In most cases, nausea was mild or moderate in nature, was transient and rarely led to discontinuation of therapy.
20.7% of patients receiving Victoza in combination with metformin experienced at least one episode of nausea, and 12.6% experienced at least one episode of diarrhea. When taking Victoza in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives, 9.1% of patients experienced at least one episode of nausea, and 7.9% experienced at least one episode of diarrhea.
In long-term controlled clinical studies (26 weeks or more), the rate of discontinuation of patients from the study due to side effects was 7.8% in the group of patients receiving Victoza and 3.4% in the group of patients receiving comparators. The most common adverse reactions that led to discontinuation of Victoza were nausea (2.8% of patients) and vomiting (1.5%).
In patients over the age of 70 years, the incidence of adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract when using the drug Victoza may be higher.
When using the drug Victoza in patients with mild renal failure (creatinine clearance ≤ 60-90 ml/min), the frequency of adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract may be higher.
Immunogenicity
Considering the possibility of immunogenic effects of protein and peptide drugs, the use of Victoza in patients may lead to the formation of antibodies to liraglutide. Antibody formation is observed in an average of 8.6% of patients. The formation of antibodies does not reduce the effectiveness of the drug Victoza.
Reactions at the injection site
In long-term (26 weeks or more) controlled studies, approximately 2% of patients receiving Victoza experienced injection site reactions. These reactions were usually mild.
Pancreatitis
Several cases of acute pancreatitis have been reported (
Adverse reactions from the thyroid gland
The overall incidence of thyroid adverse reactions in all intermediate and long-term clinical studies with liraglutide, placebo and comparators was 33.5; 30.0 and 21.7 cases per 1000 patient-years of cumulative exposure, respectively; and the incidence of serious adverse reactions is 5.4, respectively; 2.1 and 1.2 cases.
The most common thyroid side effects were thyroid neoplasms, increased serum calcitonin concentrations, and goiter. The incidence of these events per 1000 patient-years of exposure was 6.8; 10.9 and 5.4 cases, respectively, in patients treated with liraglutide, compared with 6.4; 10.7 and 2.1 cases – in patients receiving placebo, and 2.4; 6.0 and 1.8 cases – in patients receiving comparator drugs.
Allergic reactions
In the post-marketing period, allergic reactions such as urticaria, rash and itching have been reported.
In the post-registration period, several cases of anaphylactic reactions accompanied by symptoms such as arterial hypotension, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and edema have been described with the use of the drug Victoza.
Interaction
Interaction
Assessment of drug interactions in vitro. Liraglutide showed a very low ability for pharmacokinetic interaction with drugs, due to metabolism in the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system, as well as binding to plasma proteins.
Assessment of drug interactions in vivo. A slight delay in gastric emptying when using liraglutide may affect the absorption of concomitant oral medications. Drug interaction studies have not shown any clinically significant inhibition of absorption of these drugs. Several patients treated with Victoza experienced at least one episode of acute diarrhea. Diarrhea may affect the absorption of oral medications that are used concomitantly with Victoza.
Paracetamol. A single use of paracetamol at a dose of 1000 mg while using liraglutide does not cause a change in systemic exposure. Cmax of paracetamol in plasma decreased by 31%, and the average Tmax in plasma increased by 15 minutes. When taking liraglutide and paracetamol simultaneously, no dose adjustment of the latter is required.
Atorvastatin. A single use of atorvastatin at a dose of 40 mg while using liraglutide does not cause a change in systemic exposure. Thus, while taking the drug Victoza, no dose adjustment of atorvastatin is required. Cmax of atorvastatin in plasma decreased by 38%, and the average Tmax in plasma while taking liraglutide increased from 1 to 3 hours.
Griseofulvin. A single dose of griseofulvin at a dose of 500 mg during the use of liraglutide does not cause a change in systemic exposure. The Cmax of griseofulvin increased by 37%, while the mean Tmax in plasma did not change. Dose adjustment of griseofulvin and other drugs with low solubility and high permeability is not required.
Digoxin. With simultaneous single administration of digoxin at a dose of 1 mg and liraglutide, a decrease in digoxin AUC by 16% was observed; Digoxin Cmax decreased by 31%. The average Tmax of digoxin in plasma increased from 1 to 1.5 hours. Based on the results obtained, no dose adjustment of digoxin is required while taking liraglutide.
Lisinopril. A single dose of lisinopril 20 mg with liraglutide resulted in a 15% decrease in lisinopril AUC; Cmax of lisinopril decreased by 27%. The average Tmax of lisinopril in plasma while taking liraglutide increased from 6 to 8 hours. Based on the results obtained, dose adjustment of lisinopril while taking liraglutide is not required.
Oral contraceptives. Cmax of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel after their single use during therapy with liraglutide decreased by 12 and 13%, respectively. The use of both drugs together with liraglutide was accompanied by an increase in Tmax of these drugs by 1.5 hours. Liraglutide does not have a clinically significant effect on the systemic exposure of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel in the body. Thus, the expected contraceptive effect of both drugs does not change during liraglutide therapy.
Warfarin and other coumarin derivatives. No interaction studies have been conducted. At the beginning of treatment with Victoza in patients receiving warfarin or other coumarin derivatives, it is recommended to monitor MHO more frequently.
Insulin. No pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic interaction of liraglutide with insulin detemir was detected when a single dose of insulin detemir was administered at a dose of 0.5 U/kg with liraglutide at a dose of 1.8 mg in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Incompatibility. Substances added to Victoza may cause degradation of liraglutide. The drug Victoza cannot be mixed with other drugs, incl. with infusion solutions.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: During clinical trials and in the post-marketing period, cases of use of the drug Victoza in doses up to 40 times higher than the average recommended (72 mg) were reported, which was accompanied by the development of severe nausea and vomiting. There were no cases of severe hypoglycemia. All patients recovered completely without complications.
Treatment: appropriate symptomatic therapy is recommended.
Recommendations for use
Recommendations for use
Patient instructions
Before using the Victoza® syringe pen, you should carefully study these instructions.
The Victoza® syringe pen contains 18 mg of liraglutide. The patient can choose any of three possible dosages: 0.6; 1.2 and 1.8 mg. The Victoza® syringe pen is intended for use with NovoFine® or NovoTwist® disposable needles up to 8 mm long and up to 32G thick (0.25/0.23 mm).
Syringe pen Victoza®
Needle (example)
Preparing a syringe pen for injection
Check the name and color code on the pen label to make sure it contains liraglutide. Using the wrong drug can be harmful to the patient’s health.
A. Remove the cap from the syringe pen.
B. Remove the paper sticker from the disposable needle. Carefully and tightly screw the needle onto the syringe pen.
C. Remove the outer needle cap and set it aside without throwing it away.
D. Remove the inner needle cap and discard it.
Important information. Always use a new needle with each injection. This measure will prevent contamination, infection, leakage of the drug from the syringe pen, clogging of needles and guarantee dosing accuracy. Be careful when handling the needle to avoid bending or damaging the needle before using it.
Important information. Never put the inner cap back on the needle. This will prevent the risk of accidental needle sticks.
Syringe pen care
– do not try to repair the syringe pen yourself or disassemble it into parts;
– protect the syringe pen from dust, dirt and all types of liquids;
– the pen can be cleaned with a cloth dampened in a mild detergent. Do not immerse the syringe pen in liquid, do not wash or lubricate it, because this may damage the mechanism.
Important information
The syringe pen is intended for individual use – it should not be shared with others. Keep the syringe pen out of the reach of everyone, and especially children.
Checking the operation of a new syringe pen
Important information
Always check the operation of the pen as shown below before using a new injection pen.
If the patient is already using a pen, he should proceed to step H, “Setting the dose.”
E. Turn the dose selector until the operation check symbol in the indicator window is aligned with the dose indicator.
F. Holding the pen needle up, tap the cartridge several times with your finger to force air bubbles to the top of the cartridge.
G. Hold the pen with the needle up and press the start button until 0 mg appears in the indicator window opposite the dose indicator. A drop of the drug should appear at the end of the needle. If a drop does not appear, repeat steps E–G until a drop of liraglutide appears at the end of the needle. If after 4 repetitions of these operations a drop of the drug does not appear at the end of the needle, change the needle for a new one and repeat operations E–G again. If a drop of the drug does not appear at the end of the needle, this means that the syringe pen is faulty and the patient should use a new syringe pen.
Important information. If the patient has dropped the syringe pen on a hard surface or has doubts about its full serviceability, before starting to administer the drug, it is necessary to attach a new disposable needle and check the operation of the syringe pen.
Setting the dose
First of all, you need to make sure that in the indicator window “0 mg” is opposite the dose indicator.
H. Turn the dose selector until the dose required by the patient (0.6, 1.2 or 1.8 mg) in the indicator window is aligned with the dose indicator (mg means mg). You can correct an erroneously set dose by rotating the dose selector forward or backward until the numbers of the desired dose in the indicator window line up with the dose indicator. When turning the dose selector back, be careful not to accidentally press the start button to avoid releasing the dose of liraglutide. If the dose selector stops before the dose required by the patient appears in the indicator window opposite the dose indicator, this means that the liraglutide remaining in the syringe pen is not enough to administer the full dose. In this case, you should do one of the two steps below.
Administer the required dose in two doses
Rotate the dose selector in any direction until the dose of 0.6 or 1.2 mg is opposite the dose indicator. Give an injection. Prepare a new pen for the second injection and inject the remainder of the dose (in milligrams) to complete the full dose. You can divide the dose of the drug between a used and a new syringe pen only if the patient has been trained to do so or the doctor has recommended it. A calculator should be used to plan doses. If the patient does not split the dose correctly, they may receive too little or too much liraglutide.
Inject the full dose of the drug using a new syringe pen
If the dose selector stopped before the numbers 0.6 mg appeared in the indicator window opposite the dose indicator, prepare a new syringe pen for injection and administer the full dose of the drug using a new syringe pen.
Important information. Do not try to choose doses other than doses 0.6; 1.2 or 1.8 mg. The numbers in the indicator window should be exactly opposite the dose indicator – this position ensures that the patient receives the correct dose of the drug.
The dose selector makes a clicking sound when rotated. Do not use these clicks to measure the dose of liraglutide a patient needs to inject.
Do not use the cartridge scale to measure the dose of liraglutide for injection – it does not show accurate enough values.
Administration of the drug
Insert the needle under the skin using the injection technique recommended by your doctor or nurse. Then follow the instructions given below:
I. Press the start button all the way until “0 mg” appears in the indicator window opposite the dose indicator. Be careful not to touch the indicator window with your fingers or press the dose selector – this may cause the pen mechanism to lock. Keep the start button pressed all the way and the needle under the skin for at least 6 s. This will ensure that the full dose of the drug is administered.
J. Remove the needle from under the skin. The patient may see a drop of liraglutide at the end of the needle. This is a normal phenomenon and does not in any way affect the dose of the drug that was just administered.
K. Insert the end of the needle inside the outer needle cap without touching the needle and outer cap.
L. With the needle in the cap, gently push the outer needle cap forward until the needle is fully seated. Then unscrew the needle. Discard the needle, observing safety precautions, and close the syringe pen with the cap. If the syringe pen is empty, unscrew the needle and throw away the empty syringe pen without a needle. Follow local regulations for disposal of used medical supplies.
Important information. Remove the used needle after each injection and do not store the pen with the needle attached. This will help prevent contamination, infection, and leakage of liraglutide from the pen and blockage of the needles. In addition, this will ensure dosing accuracy.
Important information. Caregivers should handle used needles with extreme care to avoid accidental sticks and cross-contamination.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At 2–8 °C (do not freeze)
Shelf life
Shelf life
30 months
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Novo Nordisk A/S, Denmark
Additional information
| Shelf life | 30 months |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At 2-8 °C (do not freeze) |
| Manufacturer | Novo Nordisk A/S, Denmark |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Novo Nordisk A/S |
Related products
Buy Victoza, 6 mg/ml 3 ml cartridges in syringe pens 2 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.