No products in the cart.
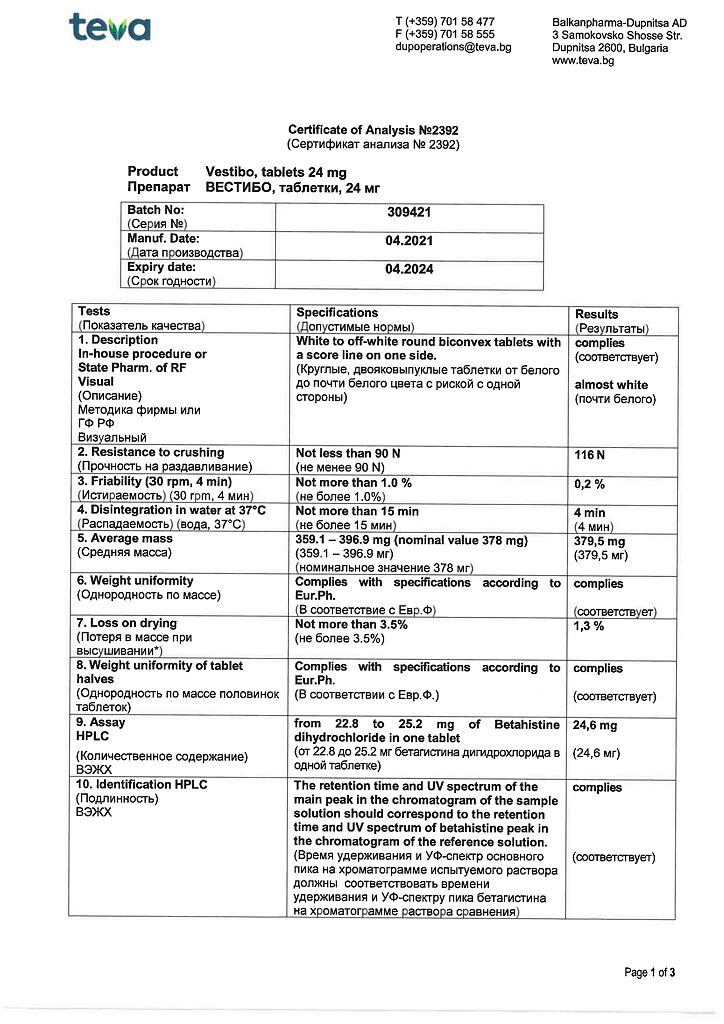
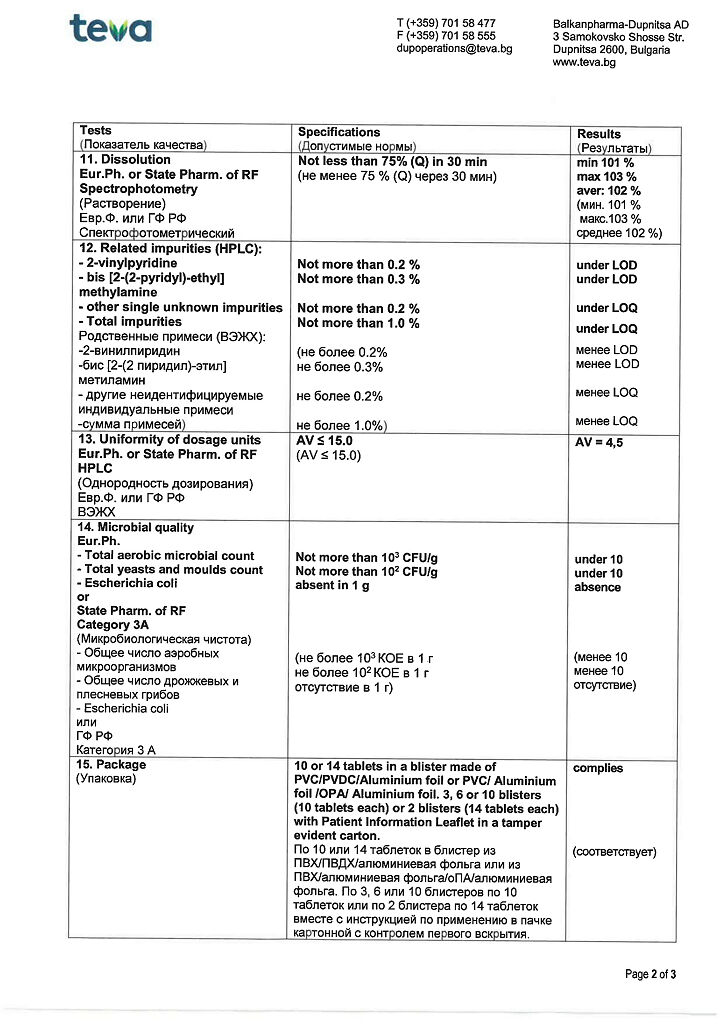
Vestibo, tablets 24 mg 30 pcs
€9.86 €8.63
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Histamine drug
ATX code: N07CA01
Pharmacological properties
.Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of betahistine is only partially known. There are several possible hypotheses supported by preclinical and clinical data:
Influence on the histaminergic system
Partial agonist of H1-histamine and antagonist of H3-histamine receptors of the vestibular nuclei of the central nervous system (CNS), with little activity against H2 receptors. Betahistine increases histamine metabolism and release by blocking presynaptic H3 receptors and decreasing H3 receptors.
Augment blood flow to the cochlear region as well as the entire brain
According to preclinical studies, betahistine improves blood flow in the inner ear vasculature by relaxing the precapillary sphincters of the inner ear vessels. Betahistine has also been shown to increase cerebral blood flow in humans.
Easing central vestibular compensation
Betahistine accelerates the recovery of vestibular function in animals after unilateral vestibular neurectomy by accelerating and facilitating central vestibular compensation through antagonism with H3-histamine receptors.
The recovery time after vestibular neurectomy in humans is also reduced with treatment with betahistine.
Anxiety of neurons in the vestibular nuclei
Dose-dependently reduces the generation of action potentials in neurons of the lateral and medial vestibular nuclei.
Pharmacodynamic properties found in animals provide a positive therapeutic effect of betahistine in the vestibular system.
The efficacy of betahistine has been demonstrated in patients with vestibular vertigo and Meniere’s syndrome, as evidenced by a reduction in the severity and frequency of dizziness.
Pharmacokinetics
absorption
. When taken orally, betahistine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. After absorption, betahistine is rapidly and almost completely metabolized to form the metabolite 2-pyridylacetic acid. The plasma concentration of betahistine is very low. Thus, pharmacokinetic assays are based on measuring the concentration of the metabolite 2-pyridylacetic acid in plasma and urine.
When the drug is taken with food, the maximum concentration (Cmax) of betahistine in the blood is lower than when taken on an empty stomach. However, the total absorption of betahistine is the same in both cases, indicating that food intake only slows the absorption of betahistine.
Distribution
The binding of betahistine to plasma proteins is less than 5%.
Biotransformation
After absorption, betahistine is rapidly and almost completely metabolized to form the metabolite 2-pyridylacetic acid (which has no pharmacological activity). The maximum concentration (Cmax) of 2-pyridylacetic acid in blood plasma (or urine) is reached one hour after taking the drug. The elimination half-life (T1/2) is approximately 3.5 h.
Elimation
2-pyridylacetic acid is rapidly excreted in the urine. When the drug is taken at a dose of 8 to 48 mg, about 85% of the initial dose is detected in the urine. Excretion of betahistine by the kidneys or through the intestine is insignificant.
Linearity
The rate of excretion remains constant with oral administration of 8 – 48 mg of the drug, indicating linearity in the pharmacokinetics of betahistine, and suggesting that the metabolic pathway involved remains unsaturated.
Indications
Indications
Meniere’s syndrome, characterized by the following main symptoms:
– dizziness (accompanied by nausea/vomiting);
– hearing loss (hearing loss);
– tinnitus;
Symptomatic treatment of vestibular dizziness (vertigo).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: histamine preparation
ATX code: N07CA01
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of betahistine is only partially known. There are several possible hypotheses supported by preclinical and clinical data:
Effect on the histaminergic system
Partial agonist of H1-histamine and antagonist of H3-histamine receptors of the vestibular nuclei of the central nervous system (CNS), has little activity against H2 receptors. Betahistine increases histamine metabolism and release by blocking presynaptic H3 receptors and reducing the number of H3 receptors.
Increased blood flow to the cochlear region, as well as the entire brain
According to preclinical studies, betahistine improves blood circulation in the stria vascularis of the inner ear by relaxing the precapillary sphincters of the vessels of the inner ear. Betahistine has also been shown to increase cerebral blood flow in humans.
Facilitating the process of central vestibular compensation
Betahistine accelerates the recovery of vestibular function in animals after unilateral vestibular neurectomy by accelerating and facilitating central vestibular compensation through antagonism of histamine H3 receptors.
Recovery time after vestibular neurectomy in humans is also reduced when treated with betahistine.
Excitation of neurons in the vestibular nuclei
Dose-dependently reduces the generation of action potentials in neurons of the lateral and medial vestibular nuclei.
Pharmacodynamic properties identified in animals provide a positive therapeutic effect of betahistine in the vestibular system.
The effectiveness of betahistine has been demonstrated in patients with vestibular vertigo and Meniere’s syndrome, which was manifested by a decrease in the severity and frequency of dizziness.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
When taken orally, betahistine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). After absorption, betahistine is rapidly and almost completely metabolized to form the metabolite 2-pyridylacetic acid. The concentration of betahistine in blood plasma is very low. Thus, pharmacokinetic assays are based on measuring the concentration of the metabolite 2-pyridylacetic acid in plasma and urine.
When taking the drug with food, the maximum concentration (Cmax) of betahistine in the blood is lower than when taken on an empty stomach. However, the total absorption of betahistine is the same in both cases, indicating that food intake only slows down the absorption of betahistine.
Distribution
The binding of betahistine to plasma proteins is less than 5%.
Biotransformation
After absorption, betahistine is rapidly and almost completely metabolized to form the metabolite 2-pyridylacetic acid (which has no pharmacological activity). The maximum concentration (Cmax) of 2-pyridylacetic acid in the blood plasma (or urine) is reached one hour after taking the drug. The half-life (T1/2) is approximately 3.5 hours.
Removal
2-pyridylacetic acid is rapidly excreted in the urine. When taking the drug at a dose of 8–48 mg, about 85% of the initial dose is found in the urine. Excretion of betahistine by the kidneys or through the intestines is negligible.
Linearity
The rate of elimination remains constant with oral doses of 8–48 mg of the drug, indicating linear pharmacokinetics of betahistine and suggesting that the metabolic pathway involved remains unsaturated.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The score on the tablet is intended to break the tablet to make it easier to swallow and is not intended to be divided into two equal doses.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
Betahistine does not affect or only slightly affects the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery; in clinical studies, no adverse reactions that could affect such ability were identified.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Betahistine
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
active ingredient: betahistine dihydrochloride 24.0 mg;
excipients: povidone K90 6.0 mg, microcrystalline cellulose (Vivapur 101) 99.0 mg, lactose monohydrate 210.0 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide 7.5 mg, crospovidone 18.0 mg, stearic acid 13.5 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
There is insufficient data available on the use of betahistine in pregnant women. Animal studies have shown no direct or indirect reproductive toxicity. Betahistine should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly needed.
Breastfeeding
It is not known whether betahistine is excreted into breast milk in humans. Betahistine is excreted in breast milk in rats. Animal studies have been limited to very high doses of the drug. The question of prescribing a drug to the mother should be made only after comparing the benefits of breastfeeding with the potential risk to the infant.
Fertility
Animal studies (rats) showed no effect on fertility.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– hypersensitivity to any of the components of the drug;
– pheochromocytoma;
Betahistine is not recommended for use in children under 18 years of age due to insufficient data on efficacy and safety.
The drug contains an excipient – lactose. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency (Lapp type) or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not use it.
With caution
Patients with bronchial asthma, gastric and/or duodenal ulcers require careful monitoring during treatment.
Side Effects
Side Effects
In accordance with the classification of the World Health Organization (WHO), all reactions are distributed according to organ systems and frequency of development: very frequent (> 1/10); frequent (> 1/100, 1/1000, 1/10000, < 1/1000); very rare (< 1/10000); frequency unknown (cannot be determined from available data).
Nervous system disorders:
common: headache.
Gastrointestinal (GIT) disorders:
common: nausea and dyspepsia.
In addition to the above undesirable effects identified during clinical trials, the following undesirable effects have been reported during post-marketing use and in the scientific literature. The available data are insufficient to estimate their frequency.
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic reactions.
Gastrointestinal (GIT) disorders: moderate disorders such as vomiting, gastrointestinal pain, bloating. These effects usually disappear after taking the drug with food or after reducing the dose.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues:
hypersensitivity reactions, especially angioedema, urticaria, itching and rash.
If you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, or if any side effect becomes serious, please notify your doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
If you have currently or in the recent past taken other medications, including those without a doctor’s prescription, please inform your doctor.
In vivo studies aimed at studying interactions with other drugs have not been conducted. Based on in vitro data, it can be assumed that there is no inhibition of the activity of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes in vivo.
In vitro data have shown inhibition of betahistine metabolism by drugs that inhibit MAO, including MAO subtype B (eg, selegiline). Caution should be exercised when prescribing betahistine and MAO inhibitors (including MAO subtype B).
Betahistine is a histamine analogue, and the interaction of betahistine with histamine H1 receptor blockers could theoretically affect the effectiveness of one of these drugs.
Overdose
Overdose
There are several known cases of drug overdose. Some patients experienced mild to moderate symptoms (nausea, drowsiness, abdominal pain) after taking the drug in doses up to 640 mg. More serious complications (convulsions, cardiopulmonary complications) have been observed with deliberate use of increased doses of betahistine, especially in combination with overdose of other drugs.
Symptomatic treatment is recommended.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not higher than 25°C. Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Catalent Germani Schorndorf GmbH, Germany
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At the temperature not more than 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children! |
| Manufacturer | Catalent Germani Schorndorf GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Catalent Germani Schorndorf GmbH |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Vestibo, tablets 24 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.