No products in the cart.
Description
Herpes, Itching and dryness in the genital area, Skin itching
Adults:
– Treatment of herpes zoster (Herpes zoster) (the drug helps relieve pain, reduces its duration and the percentage of patients with pain caused by shingles, including acute and post-herpetic neuralgia);
– Treatment of skin and mucous membrane infections caused by Herpes simplex virus type 1,2, including newly diagnosed and recurrent genital herpes (Herpes genitalis), and labial herpes (Herpes labialis);
– prevention (suppression) of recurrent infections of the skin and mucous membranes caused by Herpes simplex virus type 1,2, including genital herpes;
– Prevention of genital herpes virus transmission to a healthy partner when the drug is used as suppressive therapy in combination with safe sex;
Adults and children 12 years of age and older:
Prevention of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and acute transplant rejection reactions (in patients with kidney transplants), opportunistic infections and other herpesvirus infections (HPV, VZV) after organ transplants.
Indications
Indications
Adults:
– treatment of herpes zoster (the drug helps relieve pain, reduces its duration and the percentage of patients with pain caused by herpes zoster, including acute and postherpetic neuralgia);
– treatment of infections of the skin and mucous membranes caused by the Herpes simplex virus type 1.2, including newly diagnosed and recurrent genital herpes (Herpes genitalis), as well as labial herpes (Herpes labialis);
– prevention (suppression) of recurrent infections of the skin and mucous membranes caused by the Herpes simplex virus type 1.2, including genital herpes;
– prevention of transmission of the genital herpes virus to a healthy partner when using the drug as a suppressive therapy in combination with safe sex;
Adults and children aged 12 years and older:
– prevention of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection, as well as acute graft rejection (in patients with kidney transplants), opportunistic infections and other herpesvirus infections (HSV, VZV) after organ transplantation.
Special instructions
Special instructions
In patients at risk of dehydration, especially in elderly patients, adequate fluid replacement must be ensured during the treatment period.
Since acyclovir is excreted by the kidneys, the dose of Valcicon should be adjusted depending on the degree of renal impairment. Patients with renal failure are at increased risk of developing neurological complications and should be closely monitored. As a rule, these reactions are reversible and disappear after discontinuation of the drug.
In patients with chronic renal failure (CRF), it is recommended that creatinine clearance be determined frequently, especially during periods when renal function is rapidly changing (particularly immediately after transplantation or engraftment), and the dose of valacyclovir is adjusted according to creatinine clearance.
There are no data on the use of valacyclovir in high doses (4 g or more per day) in patients with liver disease, so high doses of Valcicon should be administered to them with caution.
Suppressive therapy with valacyclovir reduces the risk of transmission of genital herpes, but does not eliminate the risk of infection and does not lead to a complete cure. Therapy with Valcicon is recommended in combination with safe sex.
Taking the drug in high doses for a long time in conditions accompanied by severe immunodeficiency (bone marrow transplantation, clinical forms of HIV infection, kidney transplantation) led to the development of thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic-uremic syndrome, including death.
If side effects from the central nervous system occur (including agitation, hallucinations, confusion, delirium, convulsions and encephalopathy), the drug is discontinued.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Valaciclovir
Composition
Composition
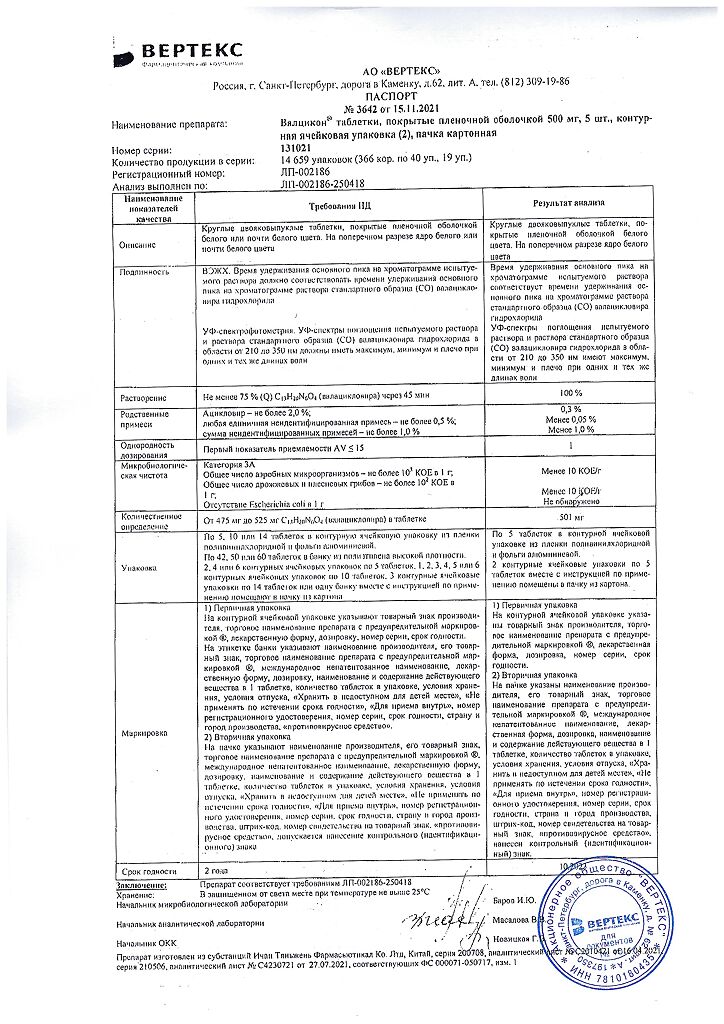
1 tablet contains:
Active substance:
valacyclovir hydrochloride – 556.00 mg (in terms of valacyclovir 500.00 mg).
Excipients:
microcrystalline cellulose – 95.00 mg,
hyprolose (hydroxypropylcellulose) – 14.00 mg,
crospovidone – 28.00 mg,
magnesium stearate – 7.00 mg.
Film casing:
[hypromellose – 10.50 mg, hyprolose (hydroxypropyl cellulose) – 4.07 mg, talc – 4.12 mg, titanium dioxide – 2.31 mg] or [dry mixture for film coating – white, containing hypromellose (50%), hydroxypropyl cellulose (19.4%), talc (19.6%), titanium dioxide (11%)] – 21.00 mg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to valacyclovir, acyclovir and any other component included in the drug; HIV infection with a CD4+ lymphocyte count of less than 100 in 1 μl; children’s age (up to 12 years for the prevention of cytomegalovirus infection after transplantation, up to 18 years for other indications).
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the central nervous system: headache, dizziness, psychotic symptoms, agitation, decreased mental capacity, ataxia, coma, confusion or depression of consciousness, dysarthria, encephalopathy, mania, hallucinations, convulsions, tremor. These reactions are reversible and are usually observed in patients with impaired renal function or against the background of other predisposing conditions. In patients with a transplanted organ receiving valacyclovir in high doses (8 g/day) for the prevention of cytomegalovirus infection, neurological reactions develop more often than when taken in lower doses.
From the respiratory system: dyspnea.
From the digestive system: nausea, abdominal discomfort, vomiting, diarrhea, reversible disturbances in liver function tests (increased activity of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase), which are sometimes regarded as manifestations of hepatitis.
From the hematopoietic system: leukopenia (mainly observed in patients with reduced immunity), thrombocytopenia, anemia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
From the skin: erythema multiforme, rashes, photosensitivity, alopecia.
Allergic reactions: itching, urticaria, angioedema, anaphylaxis.
From the urinary system: pain in the projection of the kidneys, renal dysfunction, incl. acute renal failure, renal colic. Renal colic may be associated with impaired renal function.
From the senses: visual impairment.
Laboratory indicators: decreased hemoglobin content, hypercreatininemia.
Other: dysmenorrhea, nasopharyngitis, respiratory tract infections, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, fatigue;
Cases of renal failure, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia (sometimes in combination) have been observed in patients with severe immunocompromise, especially in adult patients with advanced HIV infection, receiving valacyclovir in high doses (8 g/day daily) for a long time.
Similar adverse reactions have been observed in patients with the same diseases, but not receiving valacyclovir.
Interaction
Interaction
Cimetidine and tubular secretion blockers reduce the effect (they reduce the rate, but not the completeness of conversion to acyclovir). No dosage adjustment is required in individuals with normal creatinine clearance.
Nephrotoxic drugs increase the risk of developing renal dysfunction. Caution should be exercised (monitor changes in renal function) when combining Valcicon in higher doses (4 g per day or more) with drugs that affect other renal functions (for example: cyclosporine, tacrolimus).
Acyclovir is excreted by the kidneys, mainly unchanged, through active renal secretion. Concomitant use of drugs with this elimination mechanism may lead to increased plasma concentrations of acyclovir.
After prescribing Valcicon at a dose of 1000 mg, cimetidine and probenecid, which are eliminated in the same way as valacyclovir, increase the AUC value of acyclovir and thus reduce its renal clearance. Due to the wide therapeutic index of acyclovir, dose adjustment of Valcicon is not required in this case.
Caution must be exercised in the case of simultaneous use of valacyclovir in higher doses (4 g per day or higher) and drugs that compete with acyclovir for the elimination pathway, since there is a potential threat of increased plasma levels of one or both drugs or their metabolites. An increase in the AUC value of acyclovir and the inactive metabolite mycophenolate mofetil was noted when these drugs were used simultaneously.
The pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir does not change when taken concomitantly with digoxin, aluminum/magnesium-containing antacids, and thiazide diuretics.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:
In case of an overdose of valacyclovir, acute renal failure and the development of neurological symptoms may occur, including confusion, hallucinations, agitation, depression of consciousness and coma, nausea and vomiting are also noted. To prevent overdose, caution should be exercised when using the drug. Many cases of overdose have been associated with the use of the drug to treat patients with impaired renal function and elderly patients due to non-compliance with the dosage regimen (repeatedly receiving doses of valacyclovir that exceed the recommended ones).
Treatment.
Patients should be closely monitored for timely diagnosis of toxic manifestations. Hemodialysis significantly accelerates the elimination of acyclovir from blood plasma and can be considered the optimal treatment method in case of symptomatic overdose.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Vertex, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Vertex, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Vertex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Valcicon, 500 mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.