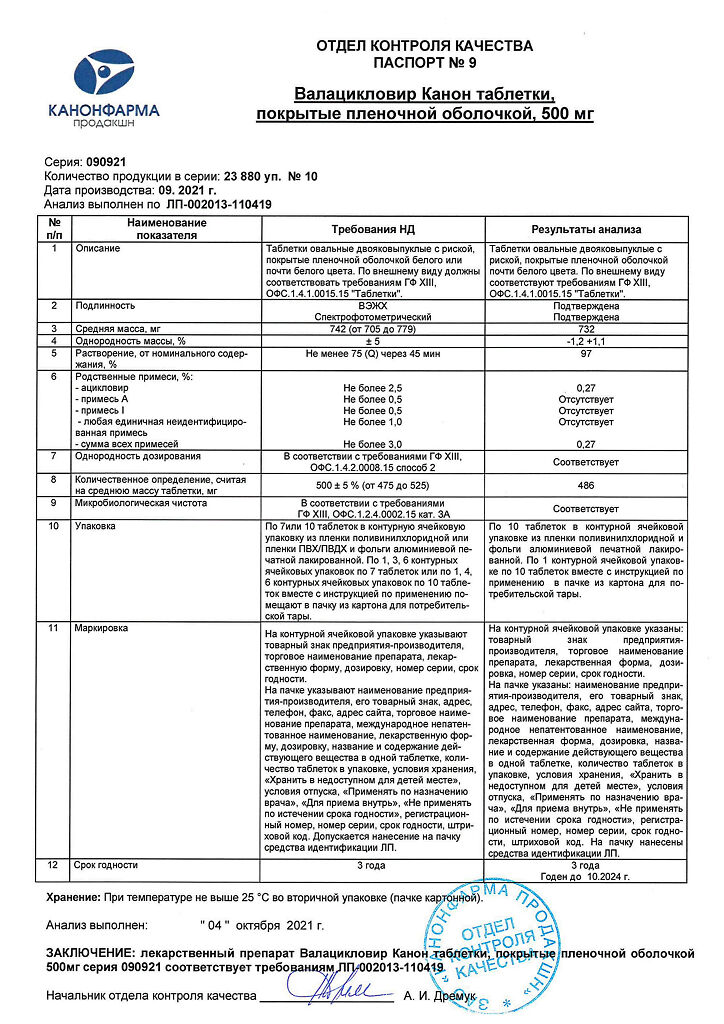
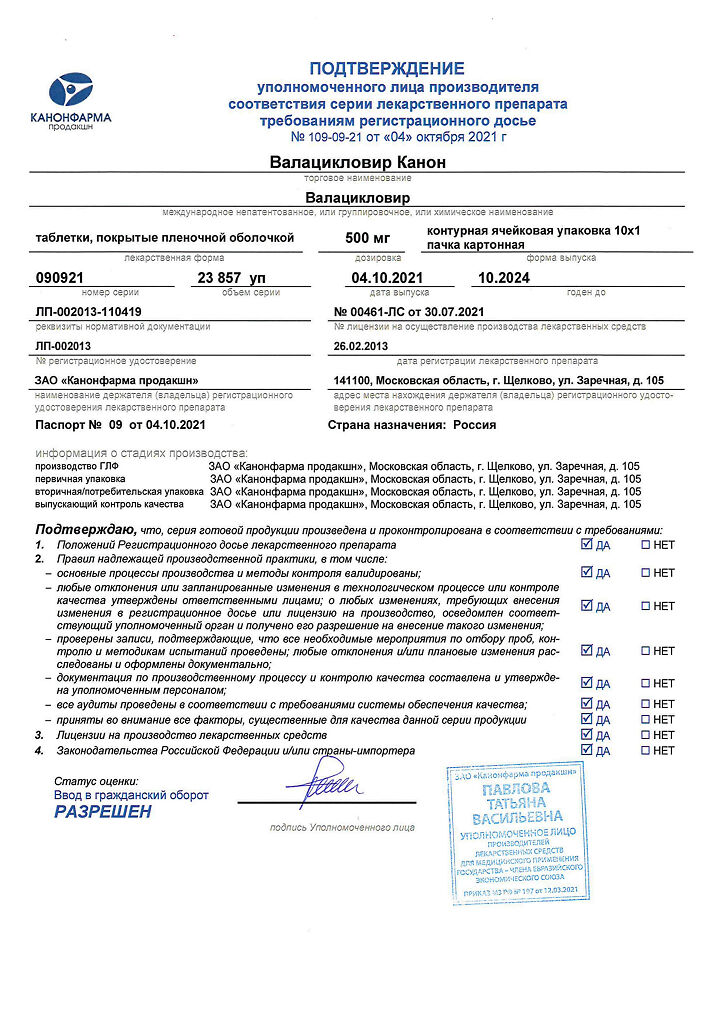
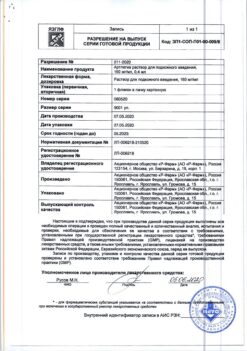
No products in the cart.
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
antiviral agent.
ATX code:
J05AB11
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Mechanism of action
Valacyclovir is an antiviral agent and is an L-valine complex ester of acyclovir. Acyclovir is an analog of the purine nucleotide (guanine).
In the human body, valacyclovir is rapidly and almost completely converted to acyclovir and valine, presumably by the enzyme valacyclovirhydrolase.
Aciclovir is a specific herpes virus inhibitor with in vitro activity against herpes simplex virus (HPV) types 1 and 2, Varicella zoster virus (VZV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and human herpes virus type 6.
Acyclovir inhibits the synthesis of viral deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) immediately after phosphorylation and transformation into the active form – acyclovir triphosphate. The first stage of phosphorylation requires the activity of virus-specific enzymes. For HPV, VZV and VEB this enzyme is viral thymidine kinase, which is present only in virus-affected cells.
Part of the phosphorylation selectivity is maintained in CMV indirectly through the product of the UL97 phosphotransferase gene. This need for activation of acyclovir by a specific viral enzyme largely explains its selectivity.
The process of acyclovir phosphorylation (conversion from mono- to triphosphate) is completed by cellular kinases. Acyclovir triphosphate competitively inhibits viral DNA polymerase and, being a nucleoside analog, is incorporated into viral DNA, which leads to obligate breaking of the chain, cessation of DNA synthesis and, consequently, to blocking of virus replication.
Resistance to acyclovir is usually due to thymidine kinase deficiency, which leads to excessive spread of the virus in the host. In rare cases, decreased sensitivity to acyclovir is due to the emergence of virus strains with disrupted viral thymidine kinase or DNA polymerase structure. The virulence of these strains of the virus is similar to that of its wild strain.
. In an extensive study of HBV and EHV strains sampled from patients treated with acyclovir or used as prophylaxis, it was found that viruses with hypersensitivity to Valacyclovir are extremely rare and may be found in rare cases in patients with severe immune impairments, such as bone marrow or organ transplant recipients, patients receiving chemotherapy for malignancies, and HIV-infected patients.
Valacyclovir helps manage pain: decreasing its duration and decreasing the percentage of patients with pain caused by herpes zoster, including acute post-herpetic neuralgia.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, valacyclovir is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and is rapidly and almost completely converted to acyclovir and valine. This conversion is probably carried out by the liver enzyme valacyclovir hydrolase.
The bioavailability of acyclovir is 54% when taking valacyclovir at a dose of 1000 mg or more and is not reduced by food intake.
The pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir are not dose-dependent. The rate and extent of absorption decrease with increasing dose, resulting in a less proportional increase in maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) compared to the therapeutic dose range and decreased bioavailability at doses above 500 mg.
Table 1. Results of acyclovir pharmacokinetics assessment of single doses of valacyclovir from 250 mg to 2,000 mg in healthy volunteers with normal hepatic function
/p>
| Pharmacokinetic parameters of acyclovir | 250 mg (N=15) | 500 mg (N=15) | 500 mg (N=15)/td> | 1000 mg (N=15) | 2000 mg (N=8) | ||
| Cmax | μmol/L | 9.78±1.71 | 15.0±4.23 | 23.1±8.53 | 36.9±6.36 | ||
| µg/mL | 2.20±0.38 | 3.37±0.95 | 5.20±1.92 | 8.30±1.43 | |||
| Tmax | hours (h) | 0.75 (0.75-1.5) | 1.0 (0.75-2.5) | 2.0 (0.75-3.0) | 2.0 (1.5-3.0) | ||
| AUC | h-mcmol/l | 24.4±3.65 | 49.3±7.77 | 83.9±20.1 | 131±28.3 | ||
| h-mcg/mL/td> | 5.50±0.82 | 11.1±1.75 | 18.9±4.51 | 29.5±6.36 | |||
Cmax – maximum concentration in plasma;
Tmax – time to reach maximum concentration in blood plasma;
AUC – area under the pharmacokinetic curve “concentration-time”.
The values of Cmax and AUC reflect the mean standard deviation. The values for Tmax reflect the median value and range of values.
The maximum plasma concentration of valacyclovir is only 4% of that of acyclovir; the median time to reach it is from 30 to 100 min after drug administration.
In 3 hours after taking the drug, the concentration of valacyclovir reaches the level of quantification or lower. Valacyclovir and acyclovir have similar pharmacokinetic parameters after single and multiple dosing. VZV and HPV do not significantly change the pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir and acyclovir after oral valacyclovir administration.
Distribution
The degree of binding of valacyclovir to plasma proteins is very low (15%). The degree of penetration into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is determined as the ratio of AUC in CSF to AUC in plasma and is about 25% for acyclovir and metabolite 8-hydroxyaciclovir (8-OH-ACV); about 2.5% for metabolite 9-(carboxymethoxy)methylguanine (CMMG).
Metabolism
After oral administration, valacyclovir is converted to acyclovir and L-valine via presystemic metabolism in the intestine and/or hepatic metabolism.
Aciclovir is converted to minor metabolites: CMMG by ethyl alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase; 8-OH-ACV by aldehydoxidase. Approximately 88% of the total cumulative plasma exposure is to acyclovir, 11% to CMMG, and 1% to 8-OH-ACV. Valacyclovir and acyclovir are not metabolized by cytochrome P450 isoenzymes.
In patients with normal renal function the elimination half-life of acyclovir from the blood plasma after single or multiple doses of valacyclovir is about 3 hours. Less than 1% of the dose of valacyclovir taken is excreted unchanged by the kidneys.
Valacyclovir is excreted from the body by the kidneys primarily as acyclovir (more than 80% of the dose taken) and acyclovir metabolite – CMMG.
Special patient groups
Patients with impaired renal function
Aciclovir excretion correlates with renal function, exposure to acyclovir increases with the severity of renal failure. In patients with end-stage renal failure, the average half-life of acyclovir after valacyclovir administration is about 14 hours, compared to about 3 hours with normal renal function.
. Exposure of acyclovir and its metabolites CMMG and 8-OH-ACV in plasma and CSF was evaluated at steady state after multiple doses of valacyclovir in 6 patients with normal renal function (mean creatinine clearance 111 mL/min, range 91-144 mL/min) who received 2,000 mg every 6 hours and in 3 patients with severe renal impairment (mean creatinine clearance 26 mL/min, range 17-31 mL/min) who received 1,500 mg every 12 hours.
In severe renal failure compared with normal renal function, plasma concentrations of acyclovir, CMMG, and 8-OH-ACV were 2, 4, and 5-6 times higher in plasma as well as in CSF, respectively. There was no difference in the penetration of acyclovir in CSF (defined as the ratio of AUC in CSF to AUC in plasma), CMMG, or 8-OH-ACV between the two populations with severe renal failure and normal renal function.
Patients with impaired hepatic function
Pharmacokinetic data show that in patients with hepatic impairment the rate of conversion of valacyclovir to acyclovir is reduced, but not the extent of this conversion. The half-life of acyclovir is independent of hepatic function.
Pregnancy
A study of the pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir and acyclovir in late pregnancy found an increase in the steady state daily AUC of valacyclovir at a daily dose of 1000 mg daily, which was approximately 2 times the AUC when acyclovir was taken orally at a dose of 1200 mg daily.
HIV infection
In patients with HIV infection, the distribution and pharmacokinetic characteristics of acyclovir remain unchanged after oral administration of one or more doses of 1000 mg or 2000 mg of valacyclovir compared with healthy volunteers.
Organ transplantation
The maximum concentration of acyclovir in patients after organ transplantation receiving 2000 mg valacyclovir 4 times daily was comparable to or higher than the maximum concentration observed in healthy volunteers receiving the same dose. The established daily AUC values can be characterized as markedly higher.
Indications
Indications
Adults and teenagers aged 12 to 18 years
treatment of skin and mucous membrane infections caused by HSV, including newly diagnosed and recurrent genital herpes (Herpes genitalis), as well as labial herpes (Herpes labialis);
prevention (suppression) of recurrent infections of the skin and mucous membranes caused by HSV, including genital herpes, including in adults with immunodeficiency;
prevention of infections caused by cytomegalovirus (CMV) and diseases after solid organ transplantation.
Adults
treatment of herpes zoster (Herpes zoster) and ophthalmic herpes zoster.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
antiviral agent.
ATX code:
J05AB11
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Mechanism of action
Valaciclovir is an antiviral agent, an L-valine ester of acyclovir. Acyclovir is an analogue of purine nucleotide (guanine).
In the human body, valacyclovir is quickly and almost completely converted to acyclovir and valine, presumably under the influence of the enzyme valacyclovir hydrolase.
Acyclovir is a specific inhibitor of herpes viruses with in vitro activity against herpes simplex viruses (HSV) types 1 and 2, varicella zoster virus (VZV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and human herpes virus type 6.
Acyclovir inhibits the synthesis of viral deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) immediately after phosphorylation and conversion to the active form – acyclovir triphosphate. The first stage of phosphorylation requires the activity of virus-specific enzymes. For HSV, VZV and EBV, this enzyme is viral thymidine kinase, which is present only in cells affected by the virus.
Phosphorylation selectivity is partially maintained in CMV indirectly through the product of the UL97 phosphotransferase gene. This requirement for activation of acyclovir by a specific viral enzyme largely explains its selectivity.
The process of phosphorylation of acyclovir (conversion from mono-to triphosphate) is completed by cellular kinases. Acyclovir triphosphate competitively inhibits viral DNA polymerase and, being a nucleoside analogue, is incorporated into viral DNA, which leads to obligate chain breakage, cessation of DNA synthesis and, consequently, blocking viral replication.
Resistance to acyclovir is usually caused by a deficiency of thymidine kinase, which leads to excessive spread of the virus in the host. In rare cases, a decrease in sensitivity to acyclovir is due to the emergence of virus strains with a disruption in the structure of the viral thymidine kinase or DNA polymerase. The virulence of these variants of the virus resembles that of the wild strain.
Based on the results of an extensive study of HSV and VZV strains collected from patients receiving aciclovir therapy or using it for prophylactic purposes, it was found that viruses with reduced sensitivity to valacyclovir are extremely rare, but can be found in rare cases in patients with severe immune impairment, for example, bone marrow or organ transplant recipients, patients receiving chemotherapy for malignant neoplasms, and HIV-infected patients.
Valacyclovir helps relieve pain: reduces its duration and reduces the percentage of patients with pain caused by herpes zoster, including acute postherpetic neuralgia.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After oral administration, valacyclovir is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), quickly and almost completely converted to acyclovir and valine. This conversion is probably carried out by the liver enzyme valacyclovir hydrolase.
When taking valacyclovir in a dose of 1000 mg, the bioavailability of acyclovir is 54% and is not reduced by food intake.
The pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir is not dose-dependent. The rate and extent of absorption decrease with increasing dose, resulting in a less proportionate increase in maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) compared to the therapeutic dose range and decreased bioavailability at doses above 500 mg.
Table 1. Results of assessing the pharmacokinetics of acyclovir when taking single doses of valacyclovir from 250 mg to 2000 mg in healthy volunteers with normal liver function
Pharmacokinetic
acyclovir parameters
250 mg
(N=15)
500 mg
(N=15)
1000 mg
(N=15)
2000 mg
(N=8)
Cmax
µmol/l
9.78±1.71
15.0±4.23
23.1±8.53
36.9±6.36
µg/ml
2.20±0.38
3.37±0.95
5.20±1.92
8.30±1.43
Тmax
hours (h)
0.75
(0.75-1.5)
1.0
(0.75-2.5)
2.0
(0.75-3.0)
2.0
(1.5-3.0)
AUC
hµmol/l
24.4±3.65
49.3±7.77
83.9±20.1
131±28.3
hµg/ml
5.50±0.82
11.1±1.75
18.9±4.51
29.5±6.36
Cmax – maximum concentration in blood plasma;
Tmax – time until the maximum concentration in the blood plasma is reached;
AUC – area under the pharmacokinetic concentration-time curve.
Cmax and AUC values reflect the average standard deviation. Values for Tmax reflect the median value and range of values.
The maximum concentration of valacyclovir in blood plasma is only 4% of the concentration of acyclovir, the median time to reach it ranges from 30 to 100 minutes after taking the drug.
3 hours after dosing, the concentration of valacyclovir reaches the level of quantitative determination or below. Valacyclovir and acyclovir have similar pharmacokinetic parameters after single and multiple doses. VZV and HSV do not significantly alter the pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir and acyclovir after oral administration of valacyclovir.
Distribution
The degree of binding of valacyclovir to plasma proteins is very low (15%). The extent of penetration into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is defined as the ratio of AUC in CSF to AUC in plasma and is about 25% for acyclovir and the metabolite 8-hydroxyacyclovir (8-OH-ACV); about 2.5% for the metabolite 9-(carboxymethoxy)methyl-guanine (CMMG).
Metabolism
After oral administration, valacyclovir is converted to acyclovir and L-valine through first-pass metabolism in the intestine and/or hepatic metabolism.
Acyclovir is converted into small metabolites: CMMG under the influence of ethyl alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase; 8-OH-ACV under the influence of aldehyde oxidase. Approximately 88% of the total cumulative plasma exposure is due to acyclovir, 11% to CMMG, and 1% to 8-OH-ACV. Valacyclovir and acyclovir are not metabolized by isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system.
Removal
In patients with normal renal function, the half-life of acyclovir from the blood plasma after a single or multiple doses of valacyclovir is approximately 3 hours. Less than 1% of the administered dose of valacyclovir is excreted unchanged by the kidneys.
Valaciclovir is excreted from the body by the kidneys mainly in the form of acyclovir (more than 80% of the dose taken) and the metabolite of acyclovir – CMMG.
Special patient groups
Patients with impaired renal function
The elimination of acyclovir correlates with renal function, and acyclovir exposure increases with the severity of renal failure. In patients with end-stage renal disease, the mean half-life of acyclovir following valacyclovir administration is approximately 14 hours, compared with approximately 3 hours in those with normal renal function.
Plasma and CSF exposures to acyclovir and its metabolites CMMG and 8-OH-ACV were assessed at steady state after multiple doses of valacyclovir in 6 patients with normal renal function (mean creatinine clearance 111 mL/min, range 91-144 mL/min) receiving 2000 mg every 6 hours and 3 patients with severe renal impairment (mean creatinine clearance 26 ml/min, range 17-31 ml/min) receiving 1500 mg every 12 hours.
In severe renal failure, compared with normal renal function, plasma and CSF concentrations of acyclovir, CMMG, and 8-OH-ACV were 2-, 4-, and 5-6-fold higher, respectively. There was no difference in the extent of acyclovir CSF penetration (defined as the ratio of CSF AUC to plasma AUC), CMMG, or 8-OH-ACV between the two populations with severe renal impairment and normal renal function.
Patients with liver dysfunction
Pharmacokinetic data show that in patients with hepatic impairment, the rate of conversion of valacyclovir to acyclovir is reduced, but not the extent of this conversion. The half-life of acyclovir is independent of liver function.
Pregnancy
A study of the pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir and acyclovir in late pregnancy found an increase in the daily AUC value at steady state when taking valacyclovir daily at a dose of 1000 mg per day, which was approximately 2 times higher than the AUC when taking oral acyclovir at a dose of 1200 mg per day.
HIV infection
In patients with HIV infection, the distribution and pharmacokinetic characteristics of acyclovir after oral administration of one or more doses of 1000 mg or 2000 mg of valacyclovir remain unchanged compared with healthy volunteers.
Organ transplantation
The maximum concentration of acyclovir in organ transplant patients receiving 2000 mg valacyclovir 4 times daily was comparable to or higher than the maximum concentration observed in healthy volunteers receiving the same dose. The established daily AUC values can be characterized as noticeably higher.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Elderly patients and persons with dehydration during the treatment period need to increase the volume of fluid consumed (risk of developing acute renal failure).
When treating genital herpes, sexual contact should be avoided, because the drug does not protect against transmission of infection.
Taking the drug in high doses for a long time in conditions accompanied by severe immunodeficiency (bone marrow transplantation, clinical forms of HIV infection, kidney transplantation) led to the development of thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic-uremic syndrome, including death.
If side effects from the central nervous system occur (including agitation, hallucinations, confusion, delirium, convulsions and encephalopathy), the drug is discontinued.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Valaciclovir
Composition
Composition
1 film-coated tablet contains:
active ingredient:
valacyclovir hydrochloride in terms of valacyclovir 500 mg;
excipients:
corn starch,
colloidal silicon dioxide,
croscarmellose sodium,
magnesium stearate,
microcrystalline cellulose;
film shell composition:
Opadry II white, including: macrogol (polyethylene glycol), polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Fertility
In animal studies, valacyclovir had no effect on fertility. However, high doses of parenteral acyclovir have been associated with testicular effects in rats and dogs. No studies have been conducted on the effects of valacyclovir on fertility in humans.
However, no changes in sperm count, motility or morphology were observed in 20 patients after 6 months of daily use of valacyclovir in doses ranging from 400 mg to 1000 mg.
Pregnancy
There are limited data on the use of valacyclovir during pregnancy.
The drug should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
Pregnancy registries documented pregnancy outcomes in women taking valacyclovir or other drugs containing acyclovir (acyclovir is the active metabolite of valacyclovir), with 111 and 1246 cases, respectively (of which 29 and 756 taking the drugs in the first trimester of pregnancy) representing pregnancy outcomes recorded prospectively.
Analysis of data from the registry of pregnant women exposed to acyclovir did not reveal an increase in the number of birth defects in their children compared with the general population, and no specificity or pattern was found for any of the malformations that would indicate a common cause.
Since the registry of pregnant women included a small number of women who took valacyclovir during pregnancy, reliable and definite conclusions about the safety of valacyclovir during pregnancy cannot be made.
Breastfeeding period
Acyclovir, the main metabolite of valacyclovir, passes into breast milk. After taking valacyclovir at a dose of 500 mg orally, Cmax in breast milk was 0.5-2.3 times (on average 1.4 times) higher than the corresponding concentrations of acyclovir in maternal blood plasma. The ratio of acyclovir AUC values in breast milk to maternal serum AUC ranged from 1.4 to 2.6 (mean 2.2).
The mean concentration of acyclovir in breast milk was 2.24 μg/ml (9.95 μmol/L). When the mother takes valacyclovir at a dose of 500 mg 2 times a day, breastfed children are exposed to the same effects of acyclovir as when it is taken orally at a dose of about 0.61 mg/kg/day. The half-life of acyclovir from breast milk is the same as from blood plasma.
Valacyclovir unchanged was not detected in maternal plasma, breast milk or infant urine. The drug Valacyclovir Canon should be prescribed with caution to women during breastfeeding.
However, intravenous acyclovir is used to treat HSV in infants at a dose of 30 mg/kg/day.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, HIV infection with a CD4+ lymphocyte count of less than 100/μl, childhood (up to 12 years for CMV, up to 18 years for other indications).
With caution. Liver/renal failure, old age, hypohydration, simultaneous use of nephrotoxic drugs, pregnancy, lactation, childhood.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, increased activity of ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, hepatitis.
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, depression, aggressive behavior, agitation, ataxia, coma, confusion or depression of consciousness, dysarthria, encephalopathy, mania, psychosis, incl. auditory and visual hallucinations, convulsions, tremors.
From the senses: visual impairment.
From the urinary system: pain in the projection of the kidneys, acute renal failure.
From the hematopoietic organs: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, aplastic anemia, leukoclastic vasculitis, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
From the skin: erythema multiforme, rash, photosensitivity, alopecia.
Allergic reactions: angioedema, shortness of breath, itching, rash, urticaria, anaphylactic reactions.
Laboratory indicators: decreased Hb, hypercreatininemia.
Other: dysmenorrhea, arthralgia, nasopharyngitis, respiratory tract infections, facial swelling, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, fatigue; additionally in children – fever, dehydration, rhinorrhea.
Interaction
Interaction
Clinically significant interactions have not been established.
Acyclovir is excreted by the kidneys, mainly unchanged through active renal secretion. The combined use of drugs with this elimination mechanism can lead to increased concentrations of acyclovir in the blood plasma.
After prescribing the drug Valacyclovir Canon at a dose of 1000 mg and the drugs cimetidine, probenecid, which are eliminated in the same way, a decrease in renal clearance and an increase in the AUC of acyclovir are observed. However, due to the broad therapeutic index of acyclovir, no dose adjustment of valacyclovir is required.
When treating herpes labialis, in the prevention and treatment of diseases caused by CMV, caution must be exercised in the case of simultaneous use of valacyclovir in higher doses (4000 mg per day or higher) and drugs that compete with acyclovir for the elimination route, since there is a potential threat of increasing the plasma concentration of one or both drugs or their metabolites.
An increase in the AUC of acyclovir and the inactive metabolite mycophenolate mofetil (an immunosuppressant used in organ transplant patients) has been observed when these drugs are administered concomitantly.
Concomitant use of Valacyclovir Canon with nephrotoxic drugs, including aminoglycosides, organic platinum compounds, iodinated contrast agents, methotrexate, pentamidine, foscarnet, cyclosporine and tacrolimus, should be carried out with caution, especially in patients with impaired renal function, and requires regular monitoring of renal function.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: possible deposition of acyclovir in the renal tubules, with the development of acute renal failure and anuria.
Treatment: hemodialysis.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Kanonpharma production CJSC, Russia
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Kanonfarma Production ZAO, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Kanonfarma Production ZAO |
Related products
Buy Valacyclovir Canon, 500 mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.