No products in the cart.
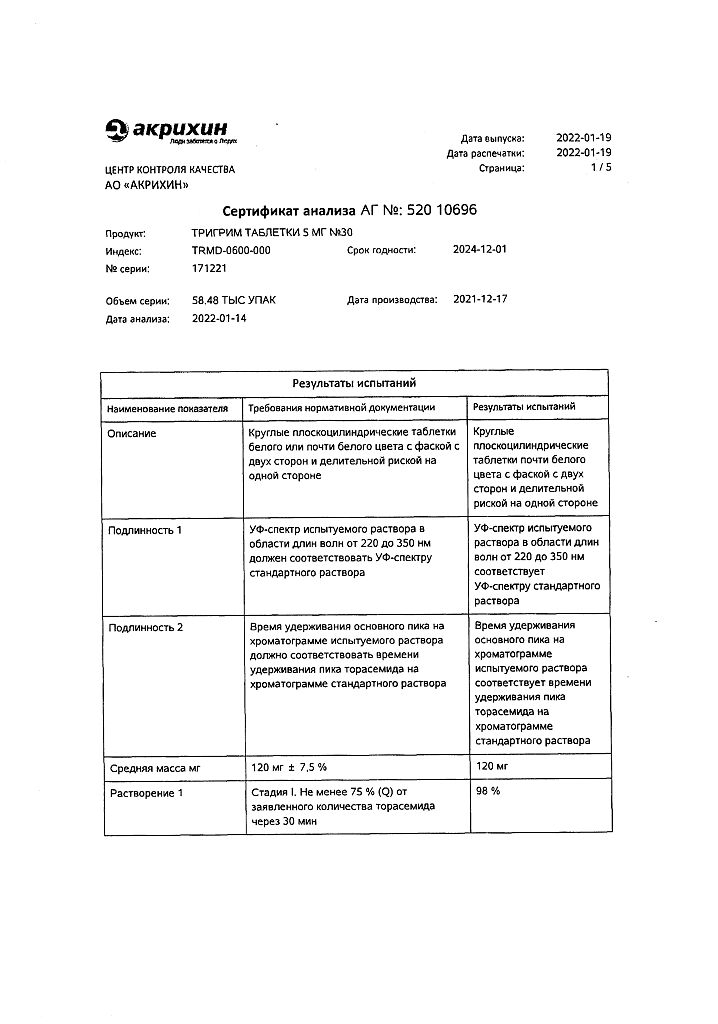
Trigrim, tablets 5 mg 30 pcs
€13.42 €11.18
Description
Diuretic drug. The main mechanism of action is due to the reversible binding of thoracemide to the Na+/2Cl–/K+ transporter.located in the apical membrane of the thick segment of the ascending loop of Genle, resulting in a reduction or complete inhibition of sodium ion reabsorption, which leads to a decrease in the osmotic pressure of intracellular fluid and water reabsorption.
With this, due to its anti-aldosterone action, thorasemide causes hypokalemia to a lesser extent than furosemide, with greater activity and duration of action.
Pharmacokinetics
Intake
After oral administration, torasemide is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the GI tract. Cmax of torasemide in plasma is noted 1-2 h after ingestion. Bioavailability is about 80-91% or more in edema.
Eating has no effect on absorption of the drug.
Distribution
Binding to plasma proteins is 99%. Vd – 16 l.
Metabolism
Metabolized in the liver with the participation of cytochrome P450 system isoenzymes to form 3 metabolites M1, M3 and M5.
T1/2 of torasemide and its metabolites in healthy volunteers is 3-4 hours. Total clearance of torasemide is 40 ml/min and renal clearance is about 10 ml/min. On average 80-83% of taken dose is excreted by kidneys through tubular secretion unchanged (24-25%) and as metabolites (M1 – 11-12%, M3 – 3%, M5 – 41-44%).
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases
In renal failure T1/2 torasemide does not change.
Indications
Indications
Edema caused by heart failure, liver, kidney and lung diseases.
Primary arterial hypertension (used as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Diuretic drug. The main mechanism of action is due to the reversible binding of torasemide to the Na+/2Cl-/K+ contransporter located in the apical membrane of the thick segment of the ascending loop of Henle, as a result of which the reabsorption of sodium ions is reduced or completely inhibited, which leads to a decrease in the osmotic pressure of intracellular fluid and water reabsorption.
Moreover, due to the antialdosterone effect, torasemide causes hypokalemia to a lesser extent than furosemide, with greater activity and duration of action.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After oral administration, torasemide is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax of torasemide in plasma is observed 1-2 hours after administration. Bioavailability is about 80-91% and more for edema.
Eating does not affect the absorption of the drug.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding – 99%. Vd – 16 l.
Metabolism
Metabolized in the liver with the participation of isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system with the formation of 3 metabolites M1, M3 and M5.
Removal
T1/2 of torasemide and its metabolites in healthy volunteers is 3-4 hours. The total clearance of torasemide is 40 ml/min and renal clearance is about 10 ml/min. On average, 80-83% of the dose taken is excreted by the kidneys by tubular secretion unchanged (24-25%) and in the form of metabolites (M1 – 11-12%, M3 – 3%, M5 – 41-44%).
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In renal failure, T1/2 of torasemide does not change.
Special instructions
Special instructions
During long-term treatment, it is recommended to monitor electrolyte balance, glucose, uric acid, creatinine and blood lipids.
In case of hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypovolemia or urinary disorders, all of these conditions should be eliminated before prescribing Trigrim.
If you have diabetes, it is necessary to control carbohydrate metabolism.
In case of thrombocytopenia or suppression of bone marrow function, as well as skin rashes, the drug should be discontinued.
Use in pediatrics
There are no data regarding the use of Trigrim in children.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
At the initial stage of admission, it is not recommended to drive vehicles or operate machinery due to the possibility of dizziness.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Torasemide
Composition
Composition
1 tab.
torasemide
5 mg
Excipients:
lactose,
corn starch,
colloidal silicon dioxide,
magnesium stearate.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The drug Trigrim is contraindicated during pregnancy, lactation, and under the age of 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
Contraindications
Contraindications
Anuria.
Hepatic coma and precomatose state.
Chronic renal failure with increasing azotemia.
Arrhythmia.
Arterial hypotension.
Pregnancy.
Lactation period (no data on use during lactation).
Age up to 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
Hypersensitivity to torasemide and sulfonamides.
The drug should be used with caution in patients with:
Diabetes mellitus.
Gout.
Violations of water and electrolyte balance.
Impaired liver function.
Cirrhosis of the liver.
Predisposition to hyperuricemia.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the hematopoietic system: in some cases – a decrease in the number of red and white blood cells, as well as platelets.
From the metabolic side: in some cases – hypovolemia, electrolyte imbalance, hypokalemia, increased levels of uric acid, glucose and lipids in the blood serum.
From the cardiovascular system: in some cases – circulatory disorders and thromboembolism (due to dehydration), decreased blood pressure.
From the digestive system: symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction, loss of appetite, dry mouth; in some cases – increased activity of liver enzymes (including GGT), pancreatitis.
From the urinary system: acute urinary retention, increased levels of urea and creatinine in plasma.
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: headache, dizziness, weakness, drowsiness, confusion, convulsions, paresthesia in the extremities.
From the senses: visual disturbances, tinnitus, deafness.
Allergic reactions: skin itching, rashes and photosensitivity.
Interaction
Interaction
Trigrim® increases the sensitivity of the myocardium to cardiac glycosides in case of potassium or magnesium deficiency.
When taken simultaneously with mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and laxatives, an increase in potassium excretion is possible.
Trigrim® enhances the effect of antihypertensive drugs.
In high doses, Trigrim® can enhance the toxic effect of aminoglycosides, antibiotics, and cisplatin; nephrotoxic effect of cephalosporins, as well as cardio- and neurotoxic effects of lithium.
Torsemide may enhance the effect of curare-like muscle relaxants and theophylline.
When salicylates are used in high doses, their toxic effect may be enhanced, and the effect of antidiabetic agents, on the contrary, may be weakened.
Sequential or simultaneous use of torasemide with ACE inhibitors may lead to a transient drop in blood pressure. This can be avoided by reducing the initial dose of ACE, or reducing the dose of torasemide (or temporarily discontinuing it).
Torsemide reduces the effect of vasoconstrictors (epinephrine and norepinephrine).
NSAIDs and probenecid may reduce the diuretic and hypotensive effects of torsemide.
Cholestyramine can reduce the absorption of torasemide from the gastrointestinal tract (in experimental animal studies).
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: there is no typical picture of poisoning; in case of overdose, increased diuresis is observed, accompanied by hypovolemia, electrolyte imbalance, followed by a drop in blood pressure, drowsiness, confusion, collapse, and gastrointestinal disorders are possible.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy – dose reduction or discontinuation of the drug while simultaneously replenishing the loss of fluid and electrolytes. A specific antidote is unknown.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Akrikhin JSC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Akrihin HFC JSC, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Akrihin HFC JSC |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Trigrim, tablets 5 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.